* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
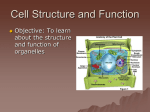
Life is Cellular SPI.1.1 Identify the cellular organelles associated with major cell processes. SPI.1.2 Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic • Prokaryotic – No Nucleus – No Membrane Covered Organelles – Circular DNA • Eukaryotic –Nucleus –Membrane covered organelles –Linear DNA Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Two Types of Eukaryotic Cells • Animal –Cell membrane –Mitochondria –Small to no vacuole • Plant –Cell wall & membrane –Chloroplast & Mitochondria –Large Vacuole Eukaryotic Components • • • • • • • • • Cell Membrane (& Cell Wall) Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria (& Chloroplast) Golgi Complex Vesicle Vacuole Lysosome Cell Membrane • Made of phospholipids –Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic Cell Membrane • Functions: –Keep in cytoplasm –Allow in nutrients –Excrete waste Cell Wall • Found in plants and algae • Made of cellulose –Carb Cell Wall • Functions –Strength –Support • Prevents the tearing of the cell membrane Nucleus • Functions: –Control center –Stores genetic info –Instructs protein synthesis • Contains DNA • Contains Nucleolus –Make ribosomes Ribosomes • Makes proteins –Proteins = amino acids • Smallest organelle • No membrane –Made of RNA Cytoskeleton • Network of filaments & tubes that cross in the cytosol • Functions –Give shape (tent) –Tracks to move items Endoplasmic Reticulum • AKA – ER • Functions as the intracellular highway • Two types –Rough ER –Smooth ER Rough ER • Flattened sacs covered with ribosomes • Produces: –Phospholipids –Proteins • Most abundant: –Digestive –Antibody producing Smooth ER • No ribosomes on surface • Less than rough ER • Functions –Produces estrogen & testosterone –Detoxifies in liver & kidney Chloroplast • Plants and algae • Contains chlorophyll –Traps sunlight • Performs photosynthesis Mitochondria • Where most of the ATP is produced –Produced in the inner membrane –ATP= energy –Needs oxygen Endosymbiotic Theory • Mitochondria & chloroplast originated from a symbiotic relationship b/t prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells • Prokaryotic cells –Mitochondria = aerobic bacteria –Chloroplast = cyanobacteria Endosymbiotic Theory • Evidence –Own DNA –Double membrane –Binary Fission (independent) –Size –Own ribosomes Golgi Apparatus • Process and ships out proteins & other materials out of the cell • Close to cell membrane • Modify the ER products –Add carb labels = direction to other cells Lysosomes • Special vesicles that contain enzymes • Originate from Golgi • Functions –Break down carbs, lipids, & proteins from food –Destroy worn out organelles –Rid cell of waste Vacuoles • Store water for the cell • Large in plant cells –Supports the cell • Wilting