* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
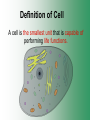
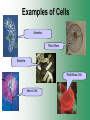
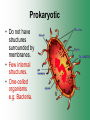
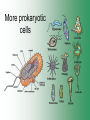
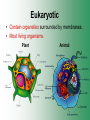
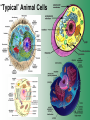
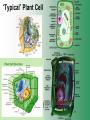
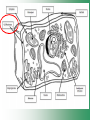
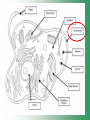
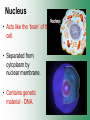
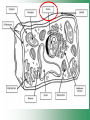
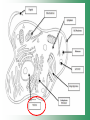
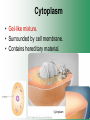
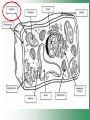
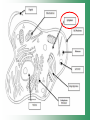
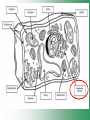
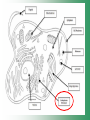
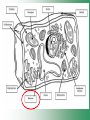
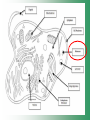
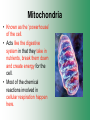
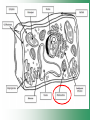
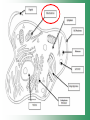
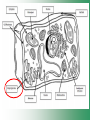
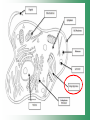
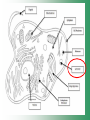
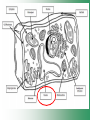
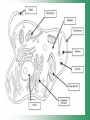
Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory • There are three main elements • 1. All living things are made up of cells. • 2. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • 3. All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Examples of Cells Amoeba Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Label your diagram first & then colour it in. Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes. • Few internal structures. • One-celled organisms e.g. Bacteria. More prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes. • Most living organisms. Plant Animal “Typical” Animal Cells 10 “Typical” Plant Cell 11 Cell Parts Common features of all cells (organelles) Cell Membrane • Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell. • It is like a big plastic bag with lots of tiny holes. Nucleus • Acts like the ‘brain’ of the cell. • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. • Contains genetic material - DNA. Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture. • Surrounded by cell membrane. • Contains hereditary material. Endoplasmic Reticulum • Acts as the ‘packaging system’ of the cell. • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes. • Rough type: ribosomes embedded in surface. Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands. • Protein builders of the cell. • Can be found floating throughout the cell or attached to the E.R. Mitochondria • Known as the ‘powerhouse’ of the cell. • Acts like the digestive system in that they take in nutrients, break them down and create energy for the cell. • Most of the chemical reactions involved in cellular respiration happen here. Golgi Apparatus • A series of membranes shaped like pancakes. • Protein 'packaging plant'. Lysosome • Digestive 'factory' for proteins, fats and carbohydrates. • The hold enzymes created by the cell. • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes. Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal. • Plants also use it to store water. • In plant cells, they are much larger.