* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
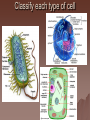
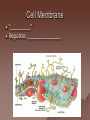
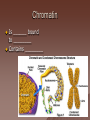
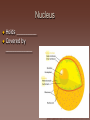
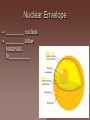
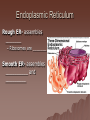
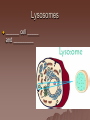
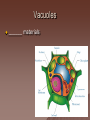
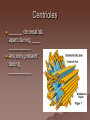
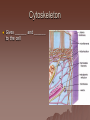
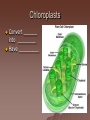
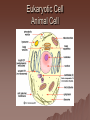
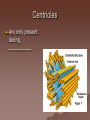
Cell Structure and Function Objective: To learn about the structure and function of organelles The Discovery of the cell 1665: Robert Hooke discovers cells – Looked at cork cells The Discovery of the Cell (Continued) 1665:Leeuwenhoek observes pond water – Found tiny living things The Discovery of the cell (Continued) 1838: Schleiden concludes that all plants are made up of cells The Discovery of the Cell (Continued) 1839: Schwan concludes that all animals are made up of cells The Discovery of the Cell (Continued) 1855: Virchow proposes “cells come from cells” The Cell Theory 1. 2. 3. All _________ are composed of _________ ______ are the basic unit of ______ New _______ are produced from ________ cells Cellular Organization Prokaryotic Cells vs Eukaryotic Cells What is the difference between each type of cell? Provide an example of each type of cell Classify each type of cell The Martian and the car These life forms rolling along roads in great numbers. They were giving off thick clouds of poisonous waste as they moved. Many of the cars moved in the same direction. They appeared to have a great deal of energy, some of them moved very quickly. When one of these life forms stopped or slowed down, the others behind it responded. They slowed down and gave off a reddish light from the back, and sometimes they would make honking noises. They would stop to feed on a liquid substance." Characteristics of Living Things What are the characteristics of living things? Organelles Act like specialized _______ within ______ Summary Questions 1. 2. 3. Are viruses classified as living things? Why or why not? Are plant cells classified as eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Are animal cells classified as eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Organelles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Centriole Ribosome Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi Apparatus Vesicle 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Lysosome Peroxisome Vacuoles Mitochondria Cell Wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cilia and Flagella Organelle Mind Map http://www.cellsalive.com/swf/cell_ model.swf – Click on either the plant cell or animal cell to complete your mind map www.interactivesites.weebly.com – Click on science then cells. Use the links on the page to complete your mind map Cytoplasm A _______ that holds the _______ Cilia and Flagella _________ in movement Present on ______ cells E.x. Vesicles Membrane bound sac that _________ Cell Membrane “_________” Regulates _______________ Chromatin Is ______ bound to ________ Contains ________ Nucleus Holds _________ Covered by ____________ Nuclear Envelope ________ nucleus ________ allow materials to_________ Ribosomes Build ________ Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER- assembles _______ – Ribosomes are _______ Smooth ER- assembles __________ and _________ Golgi Apparatus _______, sorts and _______ proteins The _____ of the cell Lysosomes ______ cell _____ and _________ Vacuoles ______ materials Cell Wall Provides _______ and ________ Centrioles ______ chromatids apart during ____ __________ Are only present during __________ Mitochondria Convert ______ into _______ “__________” of the cell Cytoskeleton Gives ______ and ______ to the cell Chloroplasts Convert ______ into ________ Have _________ Eukaryotic Cell Animal Cell Eukaryotic Cell Plant Cell Fluid Mosaic Model Basically describes ______ Centrioles Are only present during __________ What’s so special about the Mitochondria? Unique because: 1. Has it’s own ______ 2. Has an ______ and ________ membrane What are cristae? How cells make proteins Proteins assembled on _____ _______ move it to golgi protein is _______ vesicles ________ Summary Questions 1. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 2. What makes mitochondria unique? 3. Do all contain all organelles we discussed in class? Why or why not?