* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
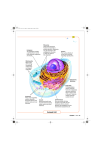
Generalized plant cell with cell wall, large vacuole and chloroplasts •Cell wall – made of cellulose •For support and protection •Generalized animal cell •Showing the “organelles” ( mini – organ ,with a specific job), suspended in the jelly-like cytoplasm •Outer cell or plasma membrane for protection •Also, regulates what is going in and out of the cell •NUCLEUS– circular, located in the center of the cell, contains the DNA which is attached to proteins forming chromatin •Information stored in the DNA directs the activities of the cell •Nuclear membrane, with pores, surrounds nucleus •Nucleolus – ball like mass of fibers and granules that make RIBOSOMES •RIBOSOMES – scattered throughout the cytoplasm or attached to the Endoplasmic reticulum •Proteins assembled here – “Protein Assembly Lines” •ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM(ER) – extensive network of membranes throughout cytoplasm, arranged in tubes and sacs •Manufacture of molecules and transport throughout the cell •RER – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – bound ribosomes on the outside,produce proteins that go straight into the ER •SER – Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum – lacks ribosomes,builds lipid molecules •GOLGI APPARATUS - Scattered throughout cytoplasm ,arranged in series of flattened sacs •Processing and shipping center – one side receives the vesicles coming from the ER, refines and modifies the structure and the other side moves it to other locations •VACUOLES – scattered throughout the cytoplasm membrane bound •Store undigested materials •Contractile vacuoles – pumps out excess water •Plants – large, central vacuole - stores chemicals that contribute to plant growth •LYSOSOMES – scattered throughout the cytoplasm, membrane bound •Contain digestive enzymes that can break down macromolecules •Nourishes the cell •Destroy harmful bacteria •Recycling centers for damaged organelles •CHLOROPLASTS - scattered throughout the plant cell,enclosed in envelope made up of two membranes ; internal membranes divide the chloroplasts into compartments which contain “membrane bound disks which trap light energy” •Conversion of light energy into chemical energy •MITOCHONDRIA – scattered throughout the cytoplasm •Site of cellular respiration which is a process which releases energy from sugars and then uses it in the formation of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) – which is a kind of energy currency •Structure – envelope of 2 membranes, inner membrane has numerous foldings called “cristae” •CYTOSKELETON – network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm •Microtubules straight hollow tubes that give rigidity and shape •Provide tracks along which other organelles can move •Microfilaments – thinner solid rods of protein,enable cell to move or change shape •FLAGELLA – long, thin , whip –like structures with a core of microtubules •Move with an “S-shaped” movement •CILIA – shorter and more numerous, bundles of microtubules •With a “back and forth” movement