* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
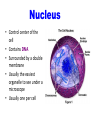
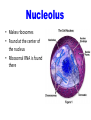
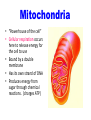
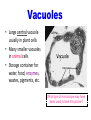
Cell Organelles © J Beauchemin 2006 Cell Organelles • Organelle= “little organ” • All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol • Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm Cell Membrane • Boundary of the cell • Made of a phospholipid bilayer Nucleus • Control center of the cell • Contains DNA • Surrounded by a double membrane • Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope • Usually one per cell Nucleolus • Makes ribosomes • Found at the center of the nucleus • Ribosomal RNA is found there Chromatin • Made of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Endoplasmic Reticulum • A.k.a. “ER” • Connected to nuclear membrane • Highway of the cell • Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins • Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids Ribosome • Site of protein synthesis • Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol • Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? Lysosomes • Garbage disposal of the cell • Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes • Engulf viruses or bacteria Which organelles do lysosomes work with? Golgi Apparatus • Looks like a stack of plates • Stores, modifies and packages proteins • Molecules transported to and from the Golgi by means of vesicles Mitochondria • “Powerhouse of the cell” • Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use • Bound by a double membrane • Has its own strand of DNA • Produces energy from sugar through chemical reactions. (charges ATP) Chloroplast • Found only in plant cells • Contains the green pigment chlorophyll • Site of food (glucose) production • Bound by a double membrane Cell Wall • Found in plant and bacterial cells • Rigid, protective barrier • Located outside of the cell membrane • Made of cellulose (fiber) Vacuoles • Large central vacuole usually in plant cells • Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells • Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? Centriole • Aids in cell division • Usually found only in animal cells • Made of microtubules Where else have we talked about microtubules? Plasmid • A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. Flagella • A flagellum is a whip-like structure that allows a cell to move. Pili • A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; plural : pili) is a hair-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria. • Cilia like structures that help bacteria attach to other cells • They help disease causing bacteria attach to their hosts. They are like teeth. Capsule • Protects some bacteria so they do not dry out. • Prevents some bacteria from being engulfed by white blood cells.