* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
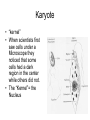
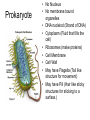
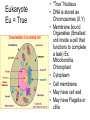
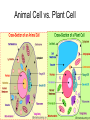
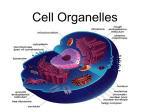
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Karyote • “kernel” • When scientists first saw cells under a Microscope they noticed that some cells had a dark region in the center while others did not. • The “Kernel”= the Nucleus Prokaryote • No Nucleus • No membrane bound organelles • DNA nucleiod (Strand of DNA) • Cytoplasm (Fluid that fills the cell) • Ribosomes (make proteins) • Cell Membrane • Cell Wall • May have Flagella (Tail like structure for movement) • May have Pili (Hair like sticky structures for sticking to a surface.) Eukaryote Eu = True • “True” Nucleus • DNA is stored as Chromosomes (X,Y) • Membrane bound Organelles (Smallest unit inside a cell that functions to complete a task) Ex. Mitochondria, Chloroplast • Cytoplasm • Cell membrane • May have cell wall • May have Flagella or cillia Animal Cell vs. Plant Cell