* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Living Things and Cells - Sterlingmontessoriscience
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
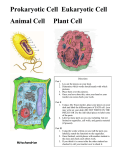
Living Things and Cells Structures that make things be “alive” Life Processes: What makes something “alive”? ALL living things do these six processes: 1. Take in nutrients. 2. Use energy 3. Produce wastes. 4. Grow 5. Reproduce 6. Respond to their environment Cell Size Characteristics of All Cells • • • • A surrounding membrane Protoplasm – cell contents in thick fluid Organelles – structures for cell function Control center with DNA Two cell types –Prokaryotes (Prokaryotic Cells) –Eukaryotes (Eukaryotic Cells) Prokaryotic Cells • First cell type on earth • Cell type of Bacteria and Archaea Prokaryotic Cells • No membrane bound nucleus • Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration • Organelles not bound by membranes Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus bound by membrane • Include fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells • Possess many organelles Protozoan Two Types of Eukaryotic Cells 1. Animal Cell 2. Plant Cell Both cells function similarly Cell Organelles • Organelle = “little organs” – Specialized structures that perform specific jobs in the cell • Found only in eukaryotic cells • Many are “membrane-bound” (a membrane surrounds the organelle) • All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol • Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm Plasma (Cell) Membrane • Contains cell contents • Double layer of phospholipids & proteins Phospholipids • Polar – Hydrophylic head – Hydrophobic tail • Interacts with water Movement Across the Plasma Membrane • A few molecules move freely – Water, Carbon dioxide, Ammonia, Oxygen • Carrier proteins transport some molecules – Proteins embedded in lipid bilayer – Fluid mosaic model – describes fluid nature of a lipid bilayer with proteins Membrane Proteins 1. Channels or transporters – Move molecules in one direction 2. Receptors – Recognize certain chemicals Membrane Proteins 3. Glycoproteins – Identify cell type 4. Enzymes – Catalyze production of substances Cell Wall • Rigid, protective barrier (maintains cell shape) • Found in plant and bacterial cells • Located outside of the cell membrane • Made of cellulose (Carbohydrate fiber) Cytoplasm • Viscous fluid containing organelles • components of cytoplasm – Interconnected filaments & fibers – Fluid = cytosol – Organelles (not nucleus) – storage substances Cytoskeleton • Filaments & fibers • Made of 3 fiber types – Microfilaments – Microtubules – Intermediate filaments • 3 functions: – mechanical support – anchor organelles – help move substances Nucleus • Control center of the cell • Stores DNA (chromosomes) • Surrounded by the nuclear membrane – Pores let material in and out • Also contains the Nucleolus, which makes ribosomes Nuclear Envelope • Separates nucleus from rest of cell • Double membrane • Has pores DNA • Hereditary material • Chromosomes – DNA – Protiens – Form for cell division • Chromatin Nucleolus • Most cells have 2 or more • Directs synthesis of RNA • Forms ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • Transport system for materials in cell • Two Types: • Rough ER: covered with ribosomes; site of protein synthesis • Smooth ER: NO ribosomes; it makes hormones & lipids Ribosome • Smallest organelle • NOT surrounded by a membrane • Makes proteins according to DNA instructions. • Two Types: – Free ribosomes: float free in cytosol – Bound ribosomes: attached to rough ER That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? Golgi Apparatus • Delivery system of the cell • Collects, modifies, and packages molecules in the cell • Distributes and transports molecules in vesicles Lysosomes • Clean-up crew of the cell • Contain digestive enzymes that break down macromolecules for the cell to use • Removes waste particles Vacuoles • Storage tank • Holds water, food, enzymes, wastes, etc • Large central vacuole usually in plant cells – Supports cell shape in plants • Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Mitochondria • “Powerhouse” of the cell • Site of cellular respiration • Converts energy stored in food into energy the cell needs – ATP Sugar + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water + ATP ATP = Adenosine triphosphate Chloroplast • Site of photosynthesis • Changes sunlight energy into chemical energy (glucose) • Contains green pigment, chlorophyll • Found only in plant cells and algae Sunlight + Carbon Dioxide + Water Sugar + Oxygen Review of Eukaryotic Cells Exterior Structures Review of Eukaryotic Cells Interior Structures