* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell in its Environment
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
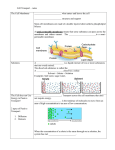
The Cell in its Environment The Cell Membrane stars in: What we ALREADY know: •Cell membrane is found around the outside of an animal cell and it is the second layer of a plant cell •The job of a cell membrane is to let “things” in and out of the cell What we will soon KNOW: •The Cell Membrane welcomes needed materials in 3 different ways… •The Cell Membrane disposes of unneeded materials inside the cell by sending them out in 3 different ways… Selectively Permeable: = some materials can pass through an object while others cannot Permeable= “to pass though” in Latin 1. Usually permeable to oxygen, water and carbon dioxide 2. Unlikely permeable to large objects and salts 3 Methods of Moving in and out of the Cell: 1. DIFFUSION Passive transport 3. ACTIVE TRANSPORT A. PASSIVE TRANSPORT: = the movement of materials across the membrane WITHOUT Energy Let’s learn about the methods of PASSIVE transport…….. What will happen?!? 1. Diffusion: Process where molecules in high conc. will move to areas of low conc. QUIZ!!! 2. Osmosis: Diff. of H2O Neato fact: osmosis is what makes fresh and salt water fish so different… B. ACTIVE TRANSPORT!!! = the movement of materials through a membrane USING energy 1. Gross… it did what?!?! Endocytosis!!! = 1) the cell membrane surrounds or engulfs a particle and then 2) it will pinch off to form a vacuole around it in the cell (this still uses E)