* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
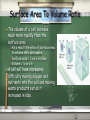
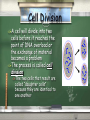
Cell Growth Section 10-1 Limits To Cell Growth There are two main reasons why cells divide DNA OVERLOAD: The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA EXCHANGE OF MATERIALS: The larger a cell becomes the more trouble it has moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane DNA Overload All of the information that controls a cell’s functions is stored in the DNA When a cell is small the information stored in the DNA is able to meet the cell’s needs As a cell increases in size the DNA can not keep up with all of the demands which are placed on it DNA Overload Cont. If a cell were to grow without limit an “information crisis” would occur Exchanging Materials Food, oxygen, and water enter the cell through the cell membrane Waste products leave in the same way The rate at which this exchange of materials takes place depends on the surface area of the cell This is the total area of the cell membrane Exchanging Materials Cont. However the rate at which food and oxygen are used up and waste products are produced depends on the volume of the cell Understanding the relationship between a cell’s volume and its surface area is the key to understanding why cells must divide Surface Area To Volume Ratio The volume of a cell increase much more rapidly than the surface area As a result the ratio of surface area to volume ratio decreases Surface area = l x w x 6 sides Volume = l x w x h A cell will have increasing difficulty moving oxygen and nutrients into the cell and moving waste products out as it increases in size. Cell Division A cell will divide into two cells before it reaches the point of DNA overload or the exchange of material becomes a problem The process is called cell division The two cells that result are called “daughter cells” because they are identical to one another Cell Division Cont. Before cell division occurs the cell replicates or copies all of its DNA The replication of DNA solves the problem of information storage Each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information Cell Division Cont. Cell division also solves the problem of increasing size by reducing the cells volume Each daughter cell has an increased ratio of surface area to volume This allows for efficient exchange of materials with the environment