* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth and Division
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ehud Shapiro wikipedia , lookup
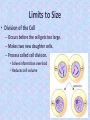
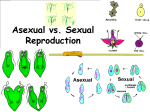
Cell Growth and Division Chapter 10 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Section 10.1 Limits to Cell Size • Two main reasons for cell division – The larger the size, the more demands there are on DNA. – Larger cells are less efficient at moving nutrients/wastes. Limits to Cell Size • Information Overload – Info stored in DNA – As a cell gets larger, DNA does not • DNA may not be able to serve needs of growing cell. Limits to Cell Size • Exchanging Materials – Materials enter/leave through cell membrane. – Rate at which materials used/expelled depends on… • Surface area • Volume Limits to Size • Division of the Cell – Occurs before the cell gets too large. – Makes two new daughter cells. – Process called cell division. • Solves information overload • Reduces cell volume Cell Division and Reproduction • Asexual – Making genetically identical offspring to a single parent. – Ex: bacteria, many multicellular organisms. • Sexual – More than one parent – Offspring inherit some genes from each parent. – Ex: Most animals/plants Comparing Asexual and Sexual Reproduction