* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hourly2_2012 - (canvas.brown.edu).
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
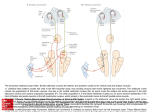
Name: _____________________________________________ SECOND HOURLY EXAMINATION Neur1650 - STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Total pages: 6 November 6, 2012 Total Points: 90 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the letter(s) corresponding to ALL correct answers to each question. There will always be one correct answer but there may be more than one. (45 points). 1. Dr. Consuela Q. Schnitzelmeister has made a monumental breakthrough!! She has generated a transgenic mouse in which green fluorescent protein (GFP) is selectively expressed in all primary (first-order) thermoreceptor neurons. The fluorescent protein is distributed throughout the soma and all processes of these cells. No other neurons are stained. If you were to look at tissue sections from this mouse, you could expect to see green GFP fluorescence in a. b. c. d. e. Pacinian corpuscles of the skin the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus the nucleus proprius the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve the anterolateral white matter of the spinal cord 2. Dr. Otis P. Kribblekoblitz discovers that a rare subterranean rodent, the shrew-faced schmoo, has a specialized sensory system for detecting microwave radiation. He identifies a thalamic nucleus that serves as the specific relay nucleus for the microwave sense, which he modestly names "the nucleus of Kribblekoblitz." He also identifies a primary microwave cortex (he calls it “MW1”); this is the main cortical target of the nucleus of Kribblekoblitz. Initial findings suggest that the schmoo’s thalamus and cortex are organized along the same principles as those of other mammals. Thus, it would be reasonable for Dr. K. to hypothesize that a. the nucleus of Kribblekoblitz projects most heavily to layer 5 of MW1 b. the nucleus of Kribblekoblitz receives a reciprocal projection from layer 6 of MW1 c. projections from cortical area MW1 to the pons and medulla arise mainly from layer 5 d. the excitability of cells in the nucleus of Kribblekoblitz is modulated by synaptic inputs from the brainstem e. cortical area MW1 receives direct inhibitory synaptic input from the thalamic reticular nucleus 2 3. Which of the following sets of motorneurons are located in the cranial nerve nuclei of the medulla? a. motor neurons driving pharyngeal movements as you guzzle warm, stale Budweiser® b. motor neurons that allow you to chew large mouthfuls of Slim Jims® that are years past their expiration date c. motor neurons that permit you use to lick the grease off your lips d. preganglionic autonomic motor neurons that drive contraction of gastrointestinal smooth muscle when your body revolts against what you have just consumed e. motor neurons necessary for looking skyward when your friend advises you to switch to spring water and locally grown organic produce 4. Ganglion cells of the retina a. b. c. d. receive glutamatergic synapses from bipolar cells have smaller dendritic fields in the peripheral retina than near the fovea lie closer to the sclera than the horizontal cells do that possess ON-center receptive fields have dendrites stratifying in the inner half of the inner plexiform layer (IPL) e. with OFF-center receptive fields have dendrites stratifying in the outer half of the outer plexiform layer 5. Layer 4 of the neocortex a. is the main recipient of “feedback” corticocortical projections b. is thicker in primary sensory areas than in other areas of the neocortex c. is essentially absent in primary motor cortex (area 4) d. is packed with pyramidal cells and contains few small stellate cells e. is the main source of callosal (interhemispheric) projections 6. Last night during a pickup basketball game, you got whacked in the face by an elbow. Today, the side of your face is swollen and throbbing unbearably. The pain you are experiencing is attributable in part to a. b. c. d. e. the archispinothalamic tract neurons of the facial nucleus neurons in the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve free nerve endings unmyelinated nociceptive afferents entering your brainstem at the level of the pons 3 7. Neurons with decussating axons can be found in a. b. c. d. e. the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus the main (principal) nucleus of the trigeminal the marginal nucleus of the cervical spinal cord the nucleus proprius of the thoracic spinal cord the gracile nucleus 8. Which of the following cells or structures are integral elements of the neural circuitry underlying fast pain? a. ventral root afferents b. medial lemniscus c. ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus d. free nerve endings e. Class Ia fibers of the spinal nerves 9. Which of the following can be found within the facial nerve (VII)? a. preganglionic sympathetic axons b. axons of motorneurons located in the salivatory nucleus c. axons of alpha motorneurons innervating muscles responsible for smiling d. cutaneous afferents carrying high resolution tactile information from the skin of the cheek e. axons from motorneurons located in the midbrain TRUE OR FALSE. Circle the correct letter. (32 points). T F 1. Activation of descending projections from serotonergic neurons in the brainstem raphe nuclei suppresses transmission of nociceptive signals through the spinal dorsal horn. T F 2. Parasympathetic control of heart rate is mediated by a cranial nerve nucleus of the pons. T F 3. A transverse section that includes the nucleus ambiguus would also include the pyramid. T F 4. The hippocampus is part of the cerebral cortex. T F 5. Glutamate hyperpolarizes retinal ON bipolar cells. T F 6. All free nerve endings are nociceptors. T F 7. The trochlear nerve emerges from brainstem through the interpeduncular fossa. T F 8. Preganglionic sympathetic motorneurons that increase heart rate during intense fear (‘fight or flight’ reaction) lie the medulla. 4 T F 9. The paleospinothalamic tract is the component of the anterolateral system that is the primary conduit of fast pain signals to the thalamus. T F 10. Some slow pain signals reach the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus after a synaptic relay in the brainstem reticular formation. T F 11. The face area of the postcentral gyrus gets its primary thalamic input from the ventral posteromedial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus. T F 12. The lens is the main optical element of the eye responsible for focusing parallel light rays from objects at infinity onto the retina. T F 13. When you dip your right big toe into steaming bath water, it is your left cerebral cortex that assesses the temperature. The decussation that accounts for this crossed (contralateral) representation of thermosensation is found at level of the medulla. T F 14. The areas of skin with the sparsest (most widely spaced) cutaneous receptors have the largest cortical magnification factors (mm2 of cortex per mm2 of skin) in the primary somatic sensory cortex T F 15. Retinotopic mapping is one method by which boundaries between areas of the visual cortex can be defined. T F 16. Koniocellular cortex is association cortex that lacks thalamic input. T F 17. A-delta fibers mediate the ‘wheal’ component of the triple response of Lewis. T F 18. Cortical pyramidal cells release glutamate from their axon terminals. T F 19. Intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus give rise to more widespread cortical projections than do thalamic nuclei receiving “lemniscal” sensory input. T F 20. The main projection of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus is to parietal association cortex. T F 21. The cingulate gyrus receives its main thalamic input from the anterior nuclei. T F 22. Some Class III fibers of the spinal nerves end in the skin as mechanoreceptors that lack any connective tissue encapsulation. T F 23. Damage to the parietal association cortex can produce astereognosis. T F 24. Neurons responding to sudden stretching of a muscle in the right forearm can be found in the left cuneate nucleus. T F 25. The ventral white commissure of the spinal cord is part of the main ascending pathway by which Pacinian corpuscles inform the cortex of mechanical deformations of the skin. 5 T F 26. Projections from the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus to the neocortex terminate most heavily in layer 4. T F 27. Feedback corticocortical connections originate mainly in the granular layer. T F 28. ON bipolar cells are depolarized by the glutamate released by rods and cones. T F 29. The center-surround antagonism of ganglion-cell receptive fields results in part from the lateral inhibitory influences of horizontal cells. T F 30. Axons in the spinal tract of the trigeminal (spinal V) originate from neurons in the trigeminal ganglion. T F 31. The thalamic reticular nucleus receives excitatory synaptic input from neurons in both the thalamus and the cortex. T F 32. In the dorsal columns at upper cervical levels, axons near the midline are more likely to carry signals from the feet than from the chest. 6 FILL IN THE BLANK. Identify each structure labeled on the last page of the exam. (13 points). a. _______________________________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________________________ c. _______________________________________________________________ d. ______________________________________________________________ e. _______________________________________________________________ f. _______________________________________________________________ g. _______________________________________________________________ h. _______________________________________________________________ i. _______________________________________________________________ j. _______________________________________________________________ k. _______________________________________________________________ l. _______________________________________________________________ m. _______________________________________________________________