* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Purdue Physics
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
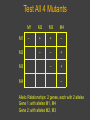
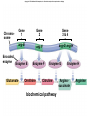
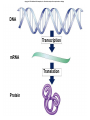
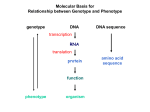
Geneticist Definition of Gene If you ask 10 different geneticist to define gene, you would get 10 different answers Genes must involve information Information must be contained in a molecule Need to define nature of information Then look at molecules Mutations as a Tool To geneticist mutations are data Mutations shows us the effect of removing or disrupting a process If you are interested in a process Then make mutants to disrupt the process Number of different mutants will tell you steps in the process Can be used to determine order of events Combinations of mutants: double mutants Functional Test for Allelism Two mutants with the same phenotype Are they alleles of one gene? Do they represent alleles of two different genes? We could isolate the genes, sequence them and compare... Can we do this with simple genetic crosses? Complementation Test Complementation Test Only works with recessive alleles Logic is simple: Cross homozygous mutants—>heterozygote Assess phenotype If wild type (doubly heterozygous) Then different genes, we say they complement (provide wild type function) If mutant (heteroallelic) Then alleles of same gene, we say they fail to complement (no wild type function) Treat with mutagen Isolate (recessive) mutants Make homozygous Mutant 1 Mutant 2 Mutant 3 How many genes do these represent? Mutant 4 Consider Single Test complements (+) X w1 w2+ w1 w2+ w1+ w2 w1+ w2 w1 w2+ w1+ w2 fails to complement (-) X w1a w1a w1b w1b w1a w1b Test All 4 Mutants M1 M2 M3 M4 M1 M2 M3 M4 – + + – – – + – + – Allelic Relationships: 2 genes, each with 2 alleles Gene 1: with alleles M1, M4 Gene 2: with alleles M2, M3 Genes and Proteins Relationship of genotype and phenotype First clue came from Beadle and Tatum: Studied synthesis of arginine in Neurospora Isolate mutant alleles of genes Correlate with biochemical pathway Mutants identified by failure to make Arg Call this kind of mutant auxotroph Supplement media with Arg = growth No Arg in media = no growth Supplement with intermediates = pathway Media Supplement Ornithine Citrulline Arginine Mutant Wild type Mutant A Mutant B Mutant C precursor A + + - ornithine + + + B citrulline + + + + C arginine Conclusions? Supplement with intermediate after block in pathway = growth Can dissect pathways using genetics Beadle and Tatum concluded each gene encoded a single enzyme in the pathway: One gene-one enzyme One gene one polypeptide is better Even this is an oversimplification Begins to get at the relationship Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Gene 1 Chromosome Gene 2 arg-E arg-G arg-H arg-F Encoded enzyme Enzyme E Glutamate Gene 3&4 Enzyme F Ornithine Enzyme G Citruline biochemical pathway Enzyme H Arginosuccinate Arginine The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Is that a cool phrase or what?! But what does it mean? A brief description of the most important overall concept of molecular biology What is this all about? Information Central Dogma describes the flow of information in cells CDMB DNA makes RNA makes Protein replication DNA transcription RNA translation Protein DNA Stores information, and is replicated RNA contains information in DNA RNA is used to direct synthesis of proteins CDMB A more modern version is below: DNA RNA Protein This encompasses the original idea DNA can be made from RNA (reverse transcription) Gene Expression Central dogma describes flow of information Actual process is called Gene Expression Transcription Translation How genotype is converted into phenotype Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. DNA Transcription mRNA Translation Protein