* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Two powerful transgenic techniques Addition of genes by nuclear
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
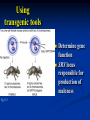
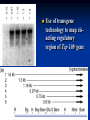
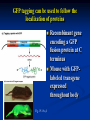
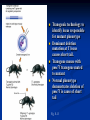
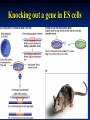
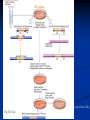
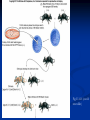
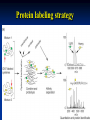
Two powerful transgenic techniques Addition of genes by nuclear injection Foreign DNA injected into pronucleus of fertilized egg Place injected one-cell embryo back into oviduct 25-50% of time DNA integrates randomly into chromosome Targeted mutagenesis Embryonic stem cells Integrate engineered gene into germ line Homologous recombination may Knockout constructs- nonfunctional gene exchanged for normal gene by homologous recombination How transgenic mice are created Fig. E.7 Using transgenic tools Fig. E.9 Determine gene function SRY locus responsible for production of maleness Application of transgenic technology Fig. E.10 Transgenic expression of myc gene provides information on role of myc in tumor formation (a) structure of gene (b) Northern blot analysis Using transgenic technology to characterize regulatory regions DNA construct containing mouse regulatory region of interest is attached to E. coli reporter gene. Function ascertained by b-gal expression in transgene fetus Fig. E..11 Use of transgene technology to map cisacting regulatory region of Tcp 10bt gene GFP tagging can be used to follow the localization of proteins Fig. 19.18 c,d Recombinant gene encoding a GFP fusion protein at C terminus Mouse with GFPlabeled transgene expressed throughout body Transgenic technology to identify locus responsible for mutant phenotype Dominant deletion mutation at T locus causes short tail. Transgene mouse with pme75 transgene mated to mutant Normal phenotype demonstrates deletion of pme75 is cause of short tail Fig. E.13 Knocking out a gene in ES cells Targeted mutagenesis to create a mouse model for human disease Fig. E.14 a-c (Cont’d next slide) ES culture (cont’d next slide) Fig. E.14 d,e Fig. E.14 f (cont’d next slide) Inheritance pattern Systems Biology – the global study of multiple components of biological systems and their interactions New approach to studying biological systems has made possible Sequencing genomes High-throughput platform development Development of powerful computational tools The use of model organisms Comparative genomics Two color DNA microarrays Two separate cDNA samples, one from normal yeast, and the other from mutant yeast labeled with red and green fluorescent dyes and hybridized to PCR microarray Fig. 10.25 Identification of protein-protein interactions yeast two-hybrid interaction Fig. 10.32 Quantification of changes in protein concentration in different cell or tissue states isotope-affinity tag approach Protein labeling strategy