* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuroanatomy
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
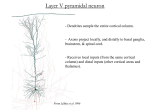
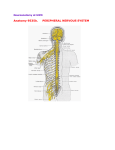
Gross Neuroanatomy Directional Terms Rostral toward the nose Caudal toward the tail Dorsal toward the back Ventral toward the belly Medial toward the midline Lateral away from the midline Anterior toward the front Posterior toward the rear Superior above Inferior below (superior) (Anterior) (Posterior) (inferior) Anterior (Posterior) Posterior (Anterior) Relational Terms Afferent projecting toward Efferent projecting away from Ipsilateral on the same side Contralateral on the opposite side Proximal near a point of reference Distal distant from a point of reference Planes of Section Coronal or frontal perpendicular to the neuraxis perpendicular to ground apply only to brain Sagittal parallel to neuraxis perpendicular to ground midsagittal = plane of symmetry Horizontal parallel to ground parallel to neuraxis applies only to brain Transverse perpendicular to neuraxis applies to brain and spinal cord Oblique any section not in a standard plane Neuraxis Swanson, L.W. (2000) What is the brain? Trends Neurosci, 23, 519-527. (Swanson, 2000) (Swanson, 2000) SYSTEM NERVORUM CENTRALE (Central nervous system) I. ENCEPHALON (brain) A. PROSENCEPHALON (forebrain) 1. TELENCEPHALON (endbrain; limbic system, basal ganglia & cerebral cortex) 2. DIENCEPHALON (between-brain, or interbrain; hypothalamus & thalamus) B. MESENCEPHALON (midbrain; tectum & tegmentum) C. RHOMBENCEPHALON (hindbrain) 1. METENCEPHALON (pons & cerebellum) 2. MYELENCEPHALON (medulla oblongata) II. MEDULLA SPINALIS (spinal cord) Notes: "BRAINSTEM" is an imprecisely defined term which usually refers to the rhombencephalon and mesencephalon together. It may or may not include the cerebellum, and sometimes the diencephalon is included. "CEREBRUM" or "CEREBRAL HEMISHPHERES" refer to the telencephalon. Prosencephalon = diencephalon + telencephalon Mesencephalon = tegmentum + tectum Rhombencephalon = metencephalon (pons, + cerebellum) + myelencephalon (medulla) (Swanson, 2000) Humans Vertebrae Spinal Nerves Cervical 1-7 Thoracic 1-12 Lumbar 1-5 Sacral 1-5 Coccygeal 1-2 Cervical 1-8 Thoracic 1-12 Lumbar 1-5 Sacral 1-5 Coccygeal 1 Totals 31 31 Shepherd, G.M. (1974) The Synaptic Organization of the Brain. Figure 17-14 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus of Cat Rabbit Neonatal Cat Five Organizational Principles of the CNS 1. Parallel processing within functional systems 2. Axons with common origins and terminations form bundles 3. Topographical mapping 4. Hierarchical organization 5. Decussation of long tracts Two More Organizational Principles 1. Laminar (layered) organization of sensory structures; nuclear/columnar organization of motor structures 2. Columnar (modular) organization of cerebral cortex Cytology of Cerebral cortex Layer I: acellular dendrites and axons; local processing Layer II: granule cells; local processing Layer III: External pyramidal cells; intracortical projections Layer IV: Granule cells, stellate cells, pyramidal cells; principle sensory input layer Layer V: Pyramidal cells; projections from cortex to other CNS structures Layer VI: Heterogeneous; pyramidal cells, granule cells; local and projection neurons Layer II—local interneurons Layer III—cortico-cortical projections Layer IV—principle input layer Layer V—long extrinsic projections Layer VI—intracranial projections Nerves 9-12: Medullary Nerves 5-8: Pontine Nerves 3, 4: Mesencephalic Nerves 1, 2: Telencephalic