* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL DIVISION
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
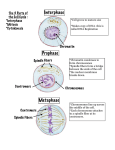
CELL DIVISION As cells grow they must divide Why?…(write your own answer) DNA and cell division Both daughter cells need a complete set of DNA, nothing missing, nothing extra DNA starts out as Chromatin (spread out DNA molecules) Chromatin turns into Chromosomes by the process of Condensation (tightly folding) Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the structures that contain genetic material we are passing from generation to generation in our cells. • Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes are much more organized than chromatin. nucleus DNA Very, very long! Wound up in a big mess=Chromatin! A very small piece of a chromosome=a GENE! Very Organized = Chromosomes How do we get chromosomes from our DNA? CELL DIVISION • • • A Chromosome 1 chromatid Centromere 2 Identical copies CELL CYCLE • Open book to pg 246 • Cell cycle is in 5 phases • G1 ; S ; G2 ; M ; C • G1 - Most of cell’s growth and activity • S - DNA replicates • G2 - Final preparations for division • M - Nuclear division (mitosis) - Divided into 4 stages • C - Cytokinesis - division of the cell Nuclear membrane INTERPHASE Centrioles . In between cell divisions (G1 , S, and G2 phases) Most of the cell’s life is in interphase Chromosomes are in the form of chromatin (diffuse and invisible) Each DNA replicates (makes a copy of itself) Centrioles begin to move to poles of cell Astral rays Aster PROPHASE Chromosomes First stage of actual mitosis Chromatin condenses into chromosomes Nuclear membrane disappears Asters form at poles of cell (Not visible in plants) Astral rays connect to centromeres on chromosomes Asters and Astral rays together called the spindle METAPHASE Chromosomes are pulled by astral rays Chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell ANAPHASE Centromeres break Each chromosome is pulled apart into separate chromatids Spindle pulls chromatids toward poles TELOPHASE Chromosomes disappear Nuclear membranes reappear Spindle disappears Cytokinesis -Cell membrane divides cell into 2 daughter cells (In plants cell wall forms between daughter cells) Daughter cells go back to interphase MITOSIS: ANIMAL CELL MITOSIS: PLANT CELL The Internet is full of great Mitosis study tools…. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pOsAb Ti9tHw