* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 - Duplin County Schools
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
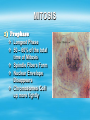
Chapter 10 Cell Growth & Division 10-1 Cell Growth Question: Are cells in a mouse and a whale the same size?? INTEREST GRABBER (10-1) The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wastes across the membrane Limits to Cell Growth 1) DNA “overload” DNA is unable to meet needs of a large cell 2) Surface area to volume ratio Volume increases more rapidly than surface area 3) Exchanging Materials The rate at which oxygen, food, & waste are used up depends on the cell’s volume The rate at which oxygen, food, & waste diffuse across the membrane depends on the cell’s surface area Division of the Cell Before cells become too big, they divide forming two “daughter” cells. The process of division is called cell division. 10-2 Cell Division In eukaryotic cells, genetic information is passed on from one generation to the next by chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of DNA Human cells have 46 chromosomes Purposes of Mitosis 1) Reproduction of unicellular organisms 2) Types of asexual reproduction 3) Growth / repair in multicellular organisms The Cell Cycle The cell cycle is a series of event that cells go through as they grow and divide. During the cell cycle, a cell … – Grows – Prepares for division – Divides to form 2 daughter cells Each of which begin the cell cycle again!! Events of the Cell Cycle Interphase – Has three phases: G1, S, and G2 – Cell Grows – Chromosomes replicate MITOSIS 1) Prophase Longest Phase 50 – 60% of the total time of Mitosis Spindle Fibers Form Nuclear Envelope Disappears Chromosomes Coil up more tightly 2) Metaphase Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell 3) Anaphase Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell 4) Telophase Chromosomes uncoil Nuclear Envelope reappears Spindle fibers disappear Cytokinesis Splitting of the cytoplasm into two cells! Mitosis video (15 minutes) 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle READ pages 250 – 253! Answer the following questions in your JOURNAL: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is Cancer and what causes it? Can cell division be turned on and off? What does Cyclin do? What are stem cells? Do you believe stem cell research should be allowed? Briefly support your answer Modeling the Phases of the Cell Cycle (pg. 254)