* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane Structure
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
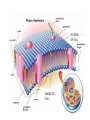
Cell Membrane Structure Phospholipids • • • • Hydrophilic Head made of Phosphate 2 Hydrophobic Tails made of Fatty Acids Makes up the majority of the membrane Mobile, not fixed in one place Phospholipid Bilayer • 2 layers of Phospholipids turned tail to tail • Semipermeable (selectively permeable) – Picky about what can move across the membrane – Only allows certain things through • Fluid Mosaic = made of many different parts that are not stuck in one spot Cholesterol • Adds strength, structure, and stability to the membrane • Decreases the phospholipids range of motion Proteins • Protein Channels – Passively allow large molecules through the membrane that cannot get past the phospholipids • Protein Pumps – Force molecules through the membrane against the concentration gradient • Structural – Provide strength, support, and sites for attachment Carbohydrate Chains • Identification of cells • Communication between cells • Always on the outside of the cell (outer membrane layer) OUTSIDE OF CELL INSIDE OF CELL Concentration • Solute = substance being dissolved • Solvent = substance doing the dissolving • Concentration = the amount of solute in a solution • Concentration is the referring to the DENSITY • Density = how crowded the molecules are Mass/Volume Hypertonic • Hypertonic Solution = MORE DENSE than the cell • “above strength” • More Solutes & Less Water in the solution OUTSIDE the Cell compared to the cytoplasm • Water Moves OUT of the cell • Cell SHRINKS Hypotonic • Hypotonic Solution = LESS DENSE than the cell • “below strength” • Less Solutes & More Water in the solution OUTSIDE the Cell compared to the cytoplasm • Water Moves INTO the cell • Cell SWELLS & may BURST Isotonic • • • • Isotonic Solution = SAME DENSITY as the cell “same strength” EQUILIBRIUM The solution OUTSIDE the cell has an equal concentration of solutes and water compared to the cytoplasm • Water Moves IN & OUT of the cell at the SAME RATE • Cell STAYS THE SAME