* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL CYCLE
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
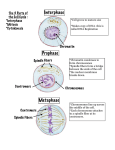
CELL CYCLE The events in the life of a cell What do cells do ??? • Interphase • Interphase is the time between cell divisions where the cell grows to full size, duplicates its DNA and rests Inter means between Interstate highway = BETWEEN States Interphase • Interphase is broken into three different sub-phases • G1, G0, (part of G1) • S • and G2 Cell Cycle Diagram . G1 Phase - Growth Occurs just after cell division • Cell must re-grow to normal size • Proteins are made G0 Phase – the Resting Phase • Cell is “normal” during this phase • Cell undergoes normal cell functions while resting • A cell that skips this phase can become cancerous, growing uncontrollably Check points • Places where cell checks itself for damage before proceeding • Cancer bypasses check points S Phase - Synthesis • DNA is synthesized or copied in preparation for cell division Point of no Return Once a cell enters the S phase it is committed to go through cell division (point of no return) G2 Phase - Growth • Cell grows larger in preparation for cell division (like a bear hibernating) Cell Division • The way a cell reproduces • 2 steps: 1) Mitosis (M) 2) Cytokinesis (C) M Phase - Mitosis • Division of cell Nucleus • DNA forms into chromosomes • Chromosomes separate with identical pairs moving to opposite sides of the cell • New nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes Mitosis Chromo/somes = colored / bodies Only appear during Mitosis Chromosomes – made of DNA 1) Prophase • • • • • Cell is beginning mitosis DNA coils up forming chromosomes Spindle fibers form Nuclear membrane dissolves Chromosomes Centrioles appear Centrioles Spindle fibers 2) Metaphase • Chromosomes line up along center • Centrioles migrate to poles • Spindle fibers attach to chromatids at centromere Chromosomes line up Spindle fibers centrioles 3) Anaphase • Spindle fibers pull duplicate chromatids apart • Chromatids migrate to opposite poles Spindle fibers Chromatids 4) Telophase • Chromotids gather together on separate sides • Membrane forms around chromatids making 2 separate nuclei • Chromatids unwind • Cell membrane begins to pinch together Chromatids Cleavage furrow Nuclear membrane C Phase – Cytokinesis • Division of the cytoplasm and organelles between cells • Membrane closes off each cell • 2 new daughter cells form, each an identical copy of the original parent cell. (but smaller) Daughter cells Nucleus DNA cytoplasm membrane In plants, a cell plate forms to make a new cell wall Interphase (again) • Each daughter cell enters Interphase, so it can regrow, rest and be a normal cell Cell cycle humorous animation • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qmTEid drGOM http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animati on__how_the_cell_cycle_works.html Cell cycle animation