* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
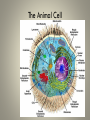
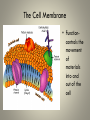
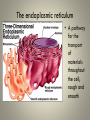
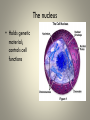
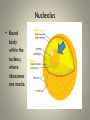
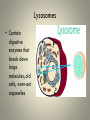
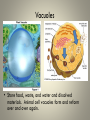
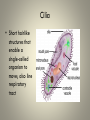
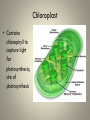
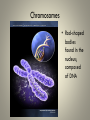
Cell Organelles and Their Functions The Animal Cell The Plant Cell The Cell Membrane • Functioncontrols the movement of materials into and out of the cell The cytoplasm • Cytoplasm fills cell from the nucleus to the cell membrane; includes fluid, cytoskeleton, and all organelles (except nucleus) The endoplasmic reticulum • A pathway for the transport of materials throughout the cell; rough and smooth The nucleus • Holds genetic material; controls cell functions Nucleolus • Round body within the nucleus; where ribosomes are made. Ribosomes • They build protein; made of RNA and protein. Some are free, some attached to ER. Lysosomes • Contain digestive enzymes that break down large molecules, old cells, worn-out organelles Mitochondria • The powerhouse of the cell; transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP Golgi Apparatus • Packages and secretes products of the cell. Centrioles (animal cells) • Involved in cell division in animal cells Vacuoles • Store food, waste, and water and dissolved materials. Animal cell vacuoles form and reform over and over again. Cell Wall • Gives a plant cell its shape; provides structure; not found in animal cells Cilia • Short hairlike structures that enable a single-celled organism to move; also line respiratory tract Flagella • Long, hairlike structures used for movement Chloroplast • Contains chlorophyll to capture light for photosynthesis; site of photosynthesis Chromosomes • Rod-shaped bodies found in the nucleus; composed of DNA Microtubule • Cylinders that support and give the cell shape Pink fuzzy slippers • What organelle do these represent?