* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bingo
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
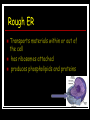
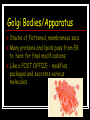
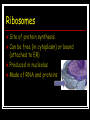
HOW WELL DO YOU KNOW THE CELL? Nucleus Contains DNA - chromosomes 2 membranes surrounding it, the envelope/membrane Controls all of the cell’s activities – including information needed to make proteins Microtubules Part of cytoskeleton Hollow tubes made of tubulin Hold organelles in place, maintain a cell’s shape, & act as tracks that guide organelles and molecules as they move through the cell Ex. cilia, flagella, centrioles Cell Membrane Covers cell surface Determines what enters or exits the cell – selectively permeable Prokaryotic Cell that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles Bacteria and Archea Hooke First person to identify and name cells – coined the term “cell” Microfilaments Part of cytoskeleton Long threads made of actin Changes cell shape, especially during muscle contraction Allows movement of cytoplasm within the cell (cytoplasmic streaming) Rough ER Transports materials within or out of the cell has ribosomes attached produces phospholipids and proteins Golgi Bodies/Apparatus Stacks of flattened, membranous sacs Many proteins and lipids pass from ER to here for final modifications; Like a POST OFFICE - modifies, packages and secretes various molecules Lysosomes Contain digestive enzymes to break down large molecules as well as nonfunctioning cell parts and cells Small, membrane-bound organelles formed by Golgi complex Leeuwenhoek Looked at living cells in pond water; invented first mini-microscope Centrioles Used in cell division Seen in animal cells Ribosomes Site of protein synthesis Can be free (in cytoplasm) or bound (attached to ER) Produced in nucleolus Made of RNA and proteins Smooth ER Transports materials within and out of the cell Functions in lipid synthesis ex. cholesterol No ribosomes attached Eukaryotic Type of cell with a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles Plant, protists, animal and fungi Mitochondria Transfer energy from organic molecules (like glucose) to ATP (cellular energy) Muscle cells have lots of these Nicknamed the POWERHOUSE Inner folds called cristae to increase surface area Plant Cell Type of cell with a cell wall, chloroplasts and a large central vacuole Virchow Stated cells come from the division of preexisting cells Cytoskeleton General term to describe the structures that give cells internal organization, shape, and ability to move Cell Wall Made of cellulose Protects, prevents excess H2O uptake, maintains shape of plant cell Animal Cell Type of cell with lysosomes and centrioles Lack a cell wall Chloroplasts Use light energy to make carbohydrates from CO2 and H2O Contains chlorophyll Responsible for photosynthesis Vacuole Stores water, enzymes, wastes, and other materials Largest organelle in a plant cell Schleiden Stated all plants are made of cells Schwann Stated all animals are made of cells Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things All cells come from preexisting cells Chromosomes Structures that form when DNA supercoils around proteins Organizes DNA for cell division Chromatin Uncondensed/uncoiled DNA DNA present in this form when the cell is not dividing Vesicle Stores and moves materials between cell organelles (ie. Rough ER to golgi) Moves materials to and from the cell membrane Cilia Short, hair-like projections found on the outside of cells Used for movement Flagella Long, tail-like projections found on the outside of cells Used for movement Cytoplasm Jelly-like material found between the cell membrane and the nucleus Contains the organelles of the cell Nucleolus Found inside of the nucleus Makes ribosomes