* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
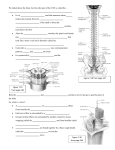
Ch 11-Nervous System II • The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the _____________ and __________ _____________. • The ___________________ connects the brain to the spinal cord. • Communication to the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is by way of the __________ _____________. • The meninges • _____________________ of CNS • Protect the CNS • Three (3) layers: • _____________ ____________ • “Tough mother” • Venous sinuses • Falx • ______________ ___________ • “Spiderweb-like” • Space contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) • _____________ ____________ • “Faithful mother” • Encapsulates blood vessels Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid • There are four (4) ventricles • The ventricles are interconnected cavities within cerebral hemispheres and brain stem • The ventricles are continuous with the ___________ __________ of the spinal cord • They are filled with ____________________ ____________ (CSF) • The four (4) ventricles are: • ______________________ ventricles (2) • Known as the first and second ventricles • ______________ ventricle • ______________ ventricle • Interventricular foramen • Cerebral aqueduct Cerebrospinal Fluid • Secreted by the _________________ ______________ • Circulates in ventricles, central canal of spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space • Completely surrounds the brain and spinal cord • Excess or wasted CSF is absorbed by the ___________________ ___________ • _____________ _____________ similar to blood plasma • Volume is only about ______ ml. • _______________ and ____________________ • Helps maintain stable ion concentrations in the CNS Spinal Cord • Slender column of nervous tissue continuous with brain and brainstem • Extends downward through vertebral canal • Begins at the _________________ ______________ and terminates at the _______ and _____________ lumbar vertebrae (L1/L2) interspace Functions of Spinal Cord • _________________ (pathway) for nerve impulses to and from the brain and brainstem • Center for __________________ _________________ Reflex Arcs • Reflexes are __________________, ____________________ responses to stimuli within or outside the body • • Simple reflex arc (sensory – motor) Most common reflex arc (sensory – association – motor) Reflex Behavior • Example is the knee-jerk reflex • Simple monosynaptic reflex • Helps maintain an upright posture • Example is a withdrawal reflex (flexor reflex) • Prevents or limits tissue damage Tracts of the Spinal Cord • Ascending tracts conduct ____________________ impulses to the brain • Descending tracts conduct_________________ impulses from the brain to motor neurons reaching muscles and glands • Major ascending (sensory) spinal cord tracts: • Fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus • Spinothalamic tracts • Lateral and anterior • Spinocerebellar tracts • Posterior and anterior • Major descending (motor) spinal cord tracts: • Corticospinal tracts • Lateral and anterior • Reticulospinal tracts • Lateral, anterior and medial • Rubrospinal tract Brain • Functions of the brain: • • • • • • • • • Major parts of the brain: • _____________________ • Frontal lobes • Parietal lobes • Occipital lobes • Temporal lobes • Insula • _____________________ • _____________________ • _____________________ • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla oblongata Brain Development • Neural tube • Three primary vesicles: • Forebrain(Prosencephalon) • Midbrain(Mesencephalon) • Hindbrain(Rhombencephalon) • Five secondary vesicles: • Telencephalon • Diencephalon • Mesencephalon • Metencephalon • Myelencephalon Structure of the Cerebrum • _________________ ___________________ • Connects cerebral hemispheres (a commissure) • ______________ • Bumps or convolutions • ______________ • Grooves in gray matter • Central sulcus • ______________ • _____________________: separates the cerebral hemispheres • _____________________: separates cerebrum from cerebellum • _____________________ fissure of Sylvius Lobes of the Cerebrum • Five (5) lobes bilaterally: • _______________ lobe • _______________ lobe • _______________ lobe • _______________ lobe • ________________ aka ‘Island of Reil’ Functions of the Cerebrum • Interpreting _________________________ • Initiating _________________________ movements • Storing information as __________________ • Retrieving stored _______________________ • __________________________ • Seat of ______________________ and _________________________ • Cerebral cortex • Thin layer of gray matter that constitutes the ___________________ portion of cerebrum • Contains __________ of all neurons in the nervous system Sensory Areas (___________________________) • Cutaneous sensory area • Parietal lobe • Interprets _______________ on skin • Sensory area for _______________ • Near base of the central sulcus • Sensory area for _______________ • Arises from centers deep within the cerebrum • Visual area • Occipital lobe • Interprets ______________ • Auditory area • Temporal lobe • Interprets ___________________ Association Areas • Regions that are not primary motor or primary sensory areas • Widespread throughout the cerebral cortex • Analyze and interpret ___________________ ______________________ • Provide memory, _______________, verbalization, _______________, emotions Frontal lobe association areas • _______________________ • Planning • Complex ______________________ _________________ Temporal lobe association areas • Interpret complex _________________ ___________________ • Store memories of _______________ ____________, _____________, and complex patterns Parietal lobe association areas • Understanding ___________________ • Choosing _________________ to express __________________ Occipital lobe association areas • Analyze and combine _______________ _______________ with other sensory experiences Motor Areas (pre-central sulcus) • Primary motor areas • Frontal lobes • Control ____________________ muscles • Broca’s area • Anterior to primary motor cortex • Usually in _____________ hemisphere • Controls muscles needed for _________________ • Frontal eye field • Above Broca’s area • Controls voluntary movements of _____________ and _______________ Hemisphere Dominance • The ____________ hemisphere is dominant in most individuals • Dominant hemisphere controls: • • • • • • • Nondominant hemisphere controls: • • • Understanding and interpreting ______________ and _________ patterns • Provides ________________ and _______________ thought processes Memory • Short term memory • ____________________ memory • Closed neuronal circuit • • Circuit is stimulated over and over When impulse flow ceases, memory does also unless it enters long-term memory via memory consolidation • Long term memory • Changes _________________ ___ _________________ of neurons • Enhances synaptic transmission Basal Nuclei • Masses of gray matter • Deep within cerebral hemispheres • Caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus • Produce _______________________ • Control certain ____________________ activities • Primarily by inhibiting motor functions Diencephalon • Between cerebral hemispheres and above the brainstem • Surrounds the third ventricle • Thalamus • Epithalamus • Hypothalamus • Optic tracts • Optic chiasm • Infundibulum • Posterior pituitary • Mammillary bodies • Pineal gland • Thalamus • Gateway for ______________ _____________ heading to cerebral cortex • Receives all ________________ impulses (except _______________) • Channels impulses to appropriate part of cerebral cortex for interpretation • Hypothalamus • Maintains __________________ by regulating visceral activities • Links nervous and ___________________ systems (hence some say the neuroendocrine system The Limbic System • Consists of: • Portions of _________________ lobe • Portions of ________________ lobe • ____________________ • ____________________ • Basal nuclei • Other deep nuclei • Functions: • Controls ___________________ • Produces __________________ • Interprets sensory impulses Brainstem Three parts: 1. 2. 3. Midbrain • Between ___________________ and ____________ • Contains bundles of fibers that join lower parts of brainstem and spinal cord with higher part of brain • Cerebral aqueduct • Cerebral peduncles (bundles of nerve fibers) • Corpora quadrigemina (centers for visual and auditory reflexes) Pons • Rounded bulge on underside of brainstem • Between ____________ _______________ and _________________ • Helps regulate rate and depth of __________________ • Relays nerve impulses to and from medulla oblongata and cerebellum Medulla Oblongata • Enlarged continuation of spinal cord • Conducts ascending and descending impulses between brain and spinal cord • Contains ______________, vasomotor, and ________________ control centers • Contains various nonvital ________________ control centers (coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting) Reticular Formation • Complex network of nerve fibers scattered throughout the brain stem • Extends into the diencephalon • Connects to centers of hypothalamus, basal nuclei, cerebellum, and cerebrum • Filters incoming _______________________ information • Arouses cerebral cortex into ______________ _____ _____________________ Types of Sleep • ____________ ______________ • Non-REM sleep • Person is tired • Decreasing activity of reticular system • __________________ • ___________________ • Reduced blood pressure and respiratory rate • Ranges from light to heavy • Alternates with REM sleep • _________________ __________ ______________ (REM) • Paradoxical sleep • Some areas of brain active • Heart and respiratory rates irregular • _______________ occurs Cerebellum • Inferior to __________________ lobes • Posterior to ____________ and _____________ ________________ • ________ hemispheres • Vermis connects hemispheres • _______________ ____________ (gray matter) • _____________ ___________ (white matter) • Cerebellar peduncles (nerve fiber tracts) • Dentate nucleus (largest nucleus in cerebellum) • Integrates sensory information concerning __________________ of body parts • Coordinates _______________ ______________ activity • Maintains ________________ Peripheral Nervous System • _____________________ nerves arising from the_____________ • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • _______________ nerves arising from the __________________ • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera Nerve and Nerve Fiber Classification • _____________________ nerves • Conduct impulses into brain or spinal cord • _____________________ nerves • Conduct impulses to muscles or glands • ___________________ (both sensory and motor) nerves • Contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers • Most nerves are mixed nerves • ALL spinal nerves are mixed nerves (except the first pair) Nerve Fiber Classification • ___________________________________________ (GSE) fibers • Carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles • ___________________________________________ (GSA) fibers • Carry sensory impulses to CNS from skin and skeletal muscles • ___________________________________________ (GVE) fibers • Carry motor impulses away from CNS to smooth muscles and glands • ___________________________________________ (GVA) fibers • Carry sensory impulses to CNS from blood vessels and internal organs • ____________________________________________ (SSE) fibers • Carry motor impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing, swallowing, speaking and forming facial expressions • _____________________________________________ (SVA) fibers • Carry sensory impulses to brain from olfactory and taste receptors • _____________________________________________ (SSA) fibers • Carry sensory impulses to brain from receptors of sight, hearing and equilibrium Cranial Nerves • Remember: • Cranial nerves are designated ‘CN’ • Cranial nerves are designated with Roman numerals (I – XII) • __________________________ nerve (CN I) • Sensory nerve • Fibers transmit impulses associated with smell • _______________________ nerve (CN II) • Sensory nerve • Fibers transmit impulses associated with vision • _______________________ nerve (CN III) • Primarily motor nerve • Motor impulses to muscles that: • Raise eyelids • Move the eyes • Focus lens • Adjust light entering eye • Some sensory • Proprioceptors • _________________________ nerve (CN IV) • Primarily motor nerve • Motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes • Some sensory • Proprioceptors • ____________________________ nerve (CN V) • Mixed nerve • “Three (3) sisters” • (1) Ophthalmic division • Sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, and upper eyelids • (2) Maxillary division • Sensory from upper teeth, upper gum, upper lip, palate, and skin of face • (3) Mandibular division • Sensory from scalp, skin of jaw, lower teeth, lower gum, and lower lip • Motor to muscles of mastication and muscles in floor of mouth • ____________________________ nerve (CN VI) • • • • • • • • • Primarily motor nerve Motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes Some sensory • Proprioceptors ______________________ nerve (CN VII) • Mixed nerve • Sensory from taste receptors • Motor to muscles of facial expression, tear glands, and salivary glands ______________________________ nerve (CN VIII) • A.k.a acoustic or auditory nerve • Sensory nerve • Two (2) branches: • Vestibular branch • Sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear • Cochlear branch • Sensory from hearing receptors _______________________________ nerve (CN IX) • Mixed nerve • Sensory from pharynx, tonsils, tongue and carotid arteries • Motor to salivary glands and muscles of pharynx ________________________ nerve (CN X) • Mixed nerve • Somatic motor to muscles of speech and swallowing • Autonomic motor to viscera of thorax and abdomen • Sensory from pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and viscera of thorax and abdomen _____________________________ nerve (CN XI) • Primarily motor nerve • We called this “Spinal” Accessory because: • Cranial branch • Motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx and larynx • Spinal branch • Motor to muscles of neck and back • Some sensory • Proprioceptor ________________________________ nerve (CN XII) • Primarily motor • Motor to muscles of the tongue • Some sensory • Proprioceptor Spinal Nerves • ALL are ___________________ nerves (except the first pair) • 31 pairs of spinal nerves: • ___ cervical nerves • (C1 to C8) • ___ thoracic nerves • (T1 to T12) • ___ lumbar nerves • (L1 to L5) • ___ sacral nerves • (S1 to S5) • ___ coccygeal nerve • (Co or Cc) • Dorsal root (aka posterior root) • _______________________ root • Axons of sensory neurons are in the dorsal root ganglion • Dorsal root ganglion • Aka DRG • Cell bodies of sensory neurons whose axons conduct impulses inward from peripheral body parts Dermatome • An area of skin that the sensory nerve fibers of a particular spinal nerve innervate Spinal Nerves • Ventral root (aka anterior root) • __________________ root • Axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in the spinal cord Spinal nerve • Union of _______________ root and __________________ roots • Hence we now have a “mixed” nerve Nerve Plexuses • Nerve plexus • Complex networks formed by anterior branches of spinal nerves • The fibers of various spinal nerves are sorted and recombined • There are three (3) nerve plexuses: • (1) _________________ plexus • Formed by anterior branches of C1-C4 spinal nerves • Lies deep in the neck • Supply to muscles and skin of the neck • C3-C4-C5 nerve roots contribute to phrenic nerves bilaterally • (2) __________________ plexus • Formed by anterior branches C5-T1 • Lies deep within shoulders • There are five (5) branches: • 1. _____________________________ nerve • Supply muscles of anterior arms and skin of forearms • 2. ________________ and 3. ______________________ nerves • Supply muscles of forearms and hands • Supply skin of hands • 4. ___________________________ nerve • Supply posterior muscles of arms and skin of forearms and hands • 5. ___________________________ nerve • Supply muscles and skin of anterior, lateral, and posterior arms • • (3) ___________________________ plexus • Formed by the anterior branches of L1-S5 roots • Can be a lumbar (L1-L5) plexus and a sacral (S1-S5) plexus • Extends from lumbar region into pelvic cavity • ______________________ nerve • Supply motor impulses to adductors of thighs • ______________________ nerve • Supply motor impulses to muscles of anterior thigh and sensory impulses from skin of thighs and legs • ______________________ nerve • Supply muscles and skin of thighs, legs and feet Autonomic Nervous System • Functions without _______________________ effort • Controls ______________________ activities • Regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • Efferent fibers typically lead to ganglia outside of the CNS • Two autonomic divisions regulate: • _________________________ division (speeds up) • Prepares body for ‘_____________________________ situations • __________________________________ division (slows down) • Prepares body for ‘______________________________ activities Autonomic Nerve Fibers • All of the neurons are motor (efferent) • Preganglionic fibers • Axons of preganglionic neurons • Neuron cell bodies in CNS • Postganglionic fibers • Axons of postganglionic neurons • Neuron cell bodies in ganglia Sympathetic Division • Thoracolumbar division – location of preganglionic neurons • Preganglionic fibers leave spinal nerves through white rami and enter paravertebral ganglia • Paraverterbral ganglia and fibers that connect them make up the sympathetic trunk • Postganglionic fibers extend from sympathetic ganglia to visceral organs • Postganglionic fibers usually pass through gray rami and return to a spinal nerve before proceeding to an effector • Exception: preganglionic fibers to adrenal medulla do not synapse with postganglionic neurons Parasympathetic Division • Craniosacral division – location of preganglionic neurons • Ganglia are near or within various organs • Terminal ganglia • Short postganglionic fibers • Continue to specific muscles or glands • Preganglionic fibers of the head are included in nerves III, VII, and IX • Preganglionic fibers of thorax and abdomen are parts of nerve X Autonomic Neurotransmitters • Cholinergic fibers • Release acetylcholine • Preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers • Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers • Adrenergic fibers • Release norepinephrine • Most postganglionic sympathetic fibers Actions of Autonomic Neurotransmitters • Result from binding to protein receptors in the membrane of effector cells: • Cholinergic receptors • Bind to acetylcholine (Ach) • Muscarinic • Excitatory • Slow • Nicotinic • Excitatory • Rapid • Adrenergic receptors • Bind to epinephrine and norepinephrine • Alpha and beta • Both elicit different responses on various effectors Terminating Autonomic Neurotransmitter Actions • The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine that cholinergic fibers release. • Norepinephrine from adrenergic fibers is removed by active transport. Control of Autonomic Activity • Controlled largely by __________ • _________________ ________________ regulates cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory activities • _________________________ regulates visceral functions, such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, and water and electrolyte balance • _________________ _____________ and cerebral cortex control emotional responses Lifespan Changes • Brain cells begin to die ________________ ________________ • Over average lifetime, brain shrinks _____% • Most cell death occurs in ______________________ lobes • By age 90, frontal cortex has lost ________________ its neurons • Number of dendritic branches decreases • Decreased levels of _____________________________ • Fading _____________________ • Slowed _________________ and ________________________ • Increased risk of falling • Changes in sleep patterns that result in _________________ sleeping hours