* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses - apbio107
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
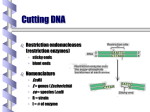
Viruses & Biotechnology Pre-discussion Questions Name: _______________ Read chapter 19 & 20 in your text and watch the virus and biotechnology Prezi’s available on our class website or at http://prezi.com/bdrtbhglgy4c/ap-bio-molecular-genetics-4-viruses/ , http://prezi.com/-rsuasafhata/ap-biomolecular-genetics-5-biotechnology/ . Viruses 1. Why are viruses classified as "obligate intracellular parasites"? 2. What are the minimum parts required for a functional virus? 3. Diagram the lytic and lysogenic cycles of bacteriophages and give examples of viruses that follow each. 4. What is the evolutionary advantage of an RNA genome in eukaryotic cell virus? 5. Why is permanent immunity to the flu impossible to acquire? 6. What cell type does HIV infect? How does this lead to AIDS? Biotechnology Restriction Enzymes: 7. How do restriction enzymes work? 8. Explain the significance of “sticky ends” and why they were given that name. Vectors: 9. Diagram a typical designed plasmid vector. Label and define each of the following parts: A. The ori B. The multiple cloning sequence (you might need the internet) C. Selectable markers--give two examples of genes used as selectable markers. Genetic Engineering: 10. How does bacterial transformation work? What do bacteria use it for? What do genetic engineers use it for? 11. What is cDNA? How is it made? Why is it necessary? 12. Diagram the process of genetic engineering a bacterium on a separate sheet. A. B. C. D. E. Begin with a plasmid and the gene of interest. Show how the gene is inserted in the plasmid. Show how the plasmid is incorporated into a bacterial cell. Show how the cell copies the plasmid. Show how the cell expresses the gene of interest. 13. Explain how reporter genes (selectable markers) can be used to separate bacteria who have taken up the transformed plasmid from those who have taken up the non-transformed plasmid. Gel Electrophoresis & Labeling: 14. How does gel electrophoresis work? What properties of the DNA does it utilize? 15. Where will the smallest fragments of DNA be found on a gel after it runs? Where will the largest fragments be found? How is the size of a particular fragment determined? 16. Why is it necessary to utilize probes for labeling particular DNA sequences? How is this process accomplished? The Polymerase Chain Reaction: 17. Explain the purpose of the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Why is it useful? 18. Explain the function of the following in PCR A. Taq polymerase B. primers. C. thermal cycler. 19. Explain what happens during each phase of a PCR cycle, and the temperature at which each phase occurs: A. Denaturation. B. Annealing. C. Elongation. Genetic Testing: 20. Explain the relationship between single nucleotide polymorphisms (“SNPs”) and restriction fragment length polymorphisms (“RFLPs”)? How are they caused and why do they matter? 21. Pick one real-world application that uses PCR and gel electrophoresis and specifically explain how each process is used in that application Cloning: 22. Compare and contrast therapeutic cloning with reproductive cloning. DNA Libraries: 23. What is the purpose of a DNA “library”? How can specific genes be retrieved from a DNA library? DNA Sequencing: 24. What are dideoxynucleotides? Why are they used in DNA sequencing? 25. Explain how the Sanger sequencing method works. 26. How has sequencing technology advanced since the development of the process by Fred Sanger? Microarrays: 27. What is the purpose of a microarray? Give an example of a real-world application of microarray analysis (use the internet or your text).