* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch - Paint Valley Local Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
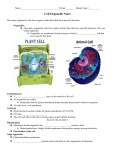
Name _________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # ________ Ch. 4-5 Review Cells & Cellular Transport 1. Compare and contrast the structural differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Prokaryotic cells have NO true nucleus NOR memebrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells have both. 2. 1. 2. 3. What are the three major parts of the cell theory? All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of a living thing. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 3. Which three scientists are credited with independently coming up with the cell theory that ultimately disproved spontaneous generation? Schleiden, Shwann, and Virchow 4. This well known person is credited with being the first to discover cells when he looked at cork underneath the microscope. He said that it looked like rooms in a monestary. Robert Hooke 5. Compare and contrast the structural differences between plant and animal eukaryotic cells. Remember the Venn diagram you constructed in the cell city assessment #3 b. The differences between these cells are that plant cell have a large, central vacuole, chloroplasts, and a cell wall while animal cells have centrioles. They have all other organelles in common. 6. What type of microscope would you have to use to see viruses? Electron microscope (transmission or scanning) We don’t have one of these in our lab due to the enormous cost. You have used a compound light microscope which can only magnify up to 400 times the actual size of the specimen. 7. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution? It will swell up and eventually pops. 8. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution? It will shrivel (shrink) up. 9. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in an isotonic solution? Nothing 10. What happens to a plant cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution (plants prefer it)? It will swell up but will NOT pop. 11. What happens to a plant cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution? Name _________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # ________ It will shrink up and cause the plant to wilt and die. 12. What structure in the cell is responsible for allowing water to move through it to maintain homeostasis and proper cell functioning within the cell? (It is selectively permeable and made of a phospholipid bilayer.) cell membrane 13. Compare and contrast osmosis and diffusion. (Hint: For the comparison, discuss the type of transport- active or passive.) Both are types of passive transport and don’t require energy to happen. Osmosis moves water from high to low concentration while diffusion moves substances like sugar or salt from high to low concentration. 14. Name two cell structures that allow a cell to locomote (move). Flagellum(a) or cilia 15. Using your cell drawing, identify the following cell structures/organelles: nucleus, nucleolus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, smooth ER, rough ER, golgi complex, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, lysosome, centrioles, cholorplasts, and ribosomes. See your cell quiz and the cell drawing you made. Both of these are in your notebook. 15. Complete the following cell structure/organelle chart. You will need to know the functions of the following cell structures/organelles for your test. Look at the widget analogy from your cell city paperwork also. Cell Structure/Organelle Function of Cell Structure/Organelle Cell membrane (Plasma outer part of the cell which protects internal parts of the cell and membrane) regulates what enters and leaves the cell (THE GATEKEEPER) a jelly-like substance which holds the organelles in place, allows Cytoplasm substances to move from one place to another, and located outside the nucleus Nucleus the control center of the cell which contains the DNA (THE BRAIN) Nuclear Envelope covers the nucleus and is composed of a double layer of lipids (Nuclear Membrane) and proteins Nucleolus area within the nucleus where the ribosomes are made tiny organelles which generate energy from organic compounds Mitochondria to ATP (THE POWERHOUSE) the primary site for protein synthesis (making) in the cell; found in Ribosomes the RER near the nucleus and free-floating in the cytoplasm extends from the nucleus and is covered with ribosomes; Rough Endoplasmic responsible for helping with the synthesis, packaging, and Reticulum transporting of proteins in and out of the cell has no ribosomes; acts as a storage area for protein that will later Smooth Endoplasmic be exported out of the cell and where lipids and ions can be Reticulum stored for later use looks like flattened sacs located in the cytoplasm; responsible for Golgi Apparatus further sorting of, packaging of, and delivery of proteins and lipids throughout the cell; put products into vesicles membrane-enclosed vesicles that form in the Golgi apparatus; contain enzymes which digest and destroy large molecules, help Lysosomes white blood cells destroy viruses and bacteria, or help to recycle old or damaged organelles Name _________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # ________ internal framework of the cytoplasm that allows the cell to keep its shape, support organelles, and provide a means for intracellular transport of substances Centrioles (animal cells paired (two) organelles located close to the nucleus that allow the only) cell to divide by creating the mitotic spindle Short hair-like structures which extend from cell’s surface; they Cilia allow for movement (locomotion) (Ex. Paramecium) Long, whip-like structures which extend from a cell’s surface; it Flagellum(a) allows for movement (locomotion) (Ex. Human Sperm) Cell Wall (plant cells an extra layer surrounding the cell membrane in a plant cell which only) allows the cell to retain its shape and provides support Chloroplasts (plant organelle which allows plant to capture sunlight in order to cells only) perform photosynthesis Large Central Vacuole a large, fluid-filled organelle that stores water, enzymes, (plant cells only) metabolic wastes, and other materials Cytoskeleton 17. Explain how a cell’s structure is related to its function. Use a nerve cell as your example. A nerve cell is long and thin with branching arms so that it can send messages to and from the brain quickly. 18. Are viruses considered living? Why or why not? No, viruses are not considered living because they are NOT made of cells. 19. What is the overall shape of an animal cell? plant cell? An animal cell is round in shape while a plant cell is more square-shaped because it has a cell wall.