* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.10 notes
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition and cognition wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Reconstructive memory wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
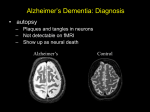
Unit III Lesson 10 Neuroscience of Memory Neuroscience of Memory • Procedural memories seem to be stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed Amnesia • Retrograde amnesia – Loss of memory for the past – Memory loss coincides with injury or illness • Anterograde amnesia – Inability to form new long-term memories • Senile dementia – Form of anterograde amnesia though retrograde amnesia may also be present Alzheimer’s Disease • 5.3 million Americans have Alzheimer’s (Alzheimer’s Association, 2010) • The most common type of dementia – 60 to 80 percent of all cases of dementia • Brain forms large number of betaamyloid protein deposits (plaques) – Strands of protein become twisted Alzheimer’s Disease (2) • Risk factors include diabetes, obesity, smoking, high cholesterol • Treatments slow but do not stop the disease • Involvement in new learning on daily basis stimulates brain derived neurotropic factors