* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 07_lecture
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Split-brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
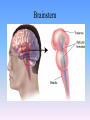
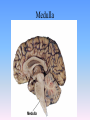
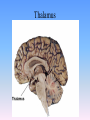
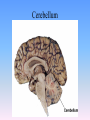
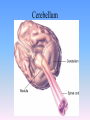
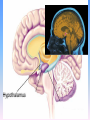
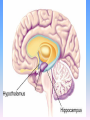
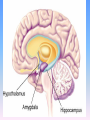
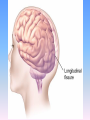
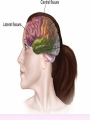
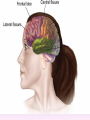
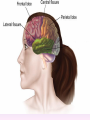
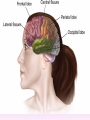
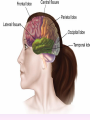
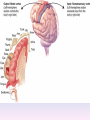
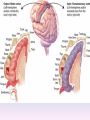
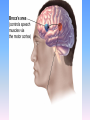
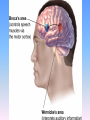
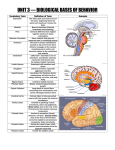
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Biopsychological Domain The Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter Module 07 The Brain Phineas Gage • Play “Phineas Gage” (12:00) Module 7: The Brain Lower-Level Brain Structures: The Brainstem Brainstem • The oldest part and central core of the brain; • It begins where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull • Is responsible for automatic survival functions Brainstem Medulla • Located at the base of the brainstem • Controls life-supporting functions like heartbeat and breathing • Damage to this area can lead to death. Medulla Brain Structures - Brainstem/Medulla • Play (side one) - Chapter 20: Internal Structures: Medulla and Pons (1909419328) (0:07) and (0:10) Reticular Formation • A nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling wakefulness and arousal • Extending up and down the spinal cord into the brain • Controls an organism’s level of alertness • Damage to this area can cause a coma. Module 7: The Brain Lower-Level Brain Structures: The Thalamus Thalamus • Sits atop the brainstem • The brain’s sensory switchboard • Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex • Thalamus is Greek for “inner chamber.” • See story: “I had a stroke at 33.” Thalamus Brain Structures - Thalamus • Play (side one): Chapter 16: Internal structures: Hypothalamus & Thalamus (17890-18167) (0:09) Module 7: The Brain Lower-Level Brain Structures: The Cerebellum Cerebellum • Latin for the “little brain” • Attached to the rear of the brain • Helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance • If damaged, the person could perform basic movements but would lose fine coordination skills. Cerebellum Cerebellum Brain Structures - Cerebellum • Play (side one): Chapter 19: Internal Structures: Cerebellum (18706-19093) (0:12) Module 7: The Brain Lower-Level Brain Structures: The Limbic System Limbic System • A ring of structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral cortex • Helps regulate memory, aggression, fear, hunger, and thirst • Includes the hypothalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala Brain Structures – Limbic System • Play: “How the Body Works – The Limbic System” (0:44) • Play: “BBT – Prefrontal Cortex vs. Limbic System” (1:06) Hypothalamus • A neural structure lying below the thalamus • Regulates the body’s maintenance activities such as; eating, drinking, body temperature, and it linked to emotion • Plays a role in emotions, pleasure, and sexual function Hypothalamus and Aggression • Play “Aggression, Violence, and the Brain” (7:17) Module #24 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2nd edition). Hippocampus • A neural center located in the limbic system that wraps around the back of the thalamus • Helps processing new memories for permanent storage • Looks something like a seahorse – Hippo is Greek for “horse.” Amygdala • Two almond shaped neural cluster in the limbic system • Controls emotional responses such as fear and anger Brain Structures – Lower Brain • Play (side one): • -Chapter 12 “Brain Revealed” (15276) (0:32) and “Lobes of the Brain” (16258) • -Chapter 13: “Brain Rotations” (16259) and Olfactory Lobes/Cerebellum/Optic Chiasm” (0:03) and (0:09) Brain Structures – Lower Brain • Play (side one) Chapter 14: “Visual Pathways” (16671) (0:09), “Optic Chiasm/Optic Tracts/Olfactory Lobes” (16968), “Visual Pathways” (16969) (0:17), “Occipital Lobe/Ventricle” (17507) • Play (side one) Chapter 15: “Ventricles” (17508) (0:17) Module 7: The Brain The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex • The intricate fabric of interconnected neurons that form the body’s ultimate control and information processing center • Covers the brain’s lower level structures • Contains an estimated 30 billion nerve cells • Divided into four lobes Corpus Callosum • The large band of neural fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres and allows them to communicate with each other • Is sometimes cut to prevent seizures Corpus Callosum Corpus Callosum • Play “Severed Corpus Callosum” (10:00) Segment #7 from Scientific American Frontiers: Video Collection for Introductory Psychology (2nd edition). Longitudinal Fissure • The long crevice that divides the cerebral cortex into left and right hemispheres • This and other fissures in the brain create major divisions in the brain called lobes Frontal Lobes • The portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead • Is involved in planning and judgments • Includes the motor cortex The Frontal Lobe • Play “The Frontal Lobes: Cognition and Awareness” (9:05) Segment #7 from The Mind: Psychology Teaching Modules (2nd edition). Parietal Lobes • The portion of the cerebral cortex lying on the top of the head and toward the rear • Includes the somatosensory cortex and general association areas used in processing information • Regions available for general processing, including mathematical reasoning • Designated as the association lobes • Behind the frontal lobes Occipital Lobe • The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head • It includes the primary visual processing areas of the brain Temporal Lobes • Includes the auditory (hearing) areas of the brain • Where sound information is processed • Located roughly above the ears Motor Cortex • The strip of brain tissue at the rear of the frontal lobes • Controls voluntary movement • Different parts of the cortex control different parts of the body. • The motor cortex in the left hemisphere controls the right side of the body and visa versa. Somatosensory Cortex • Located in the front of the parietal lobes • Registers and processes body sensations • Soma is Greek for “body.” Motor and Sensory Cortex • Play “Image-Guided Surgery” (13:07) Segment #6 from Scientific American Frontiers: Video Collection for Introductory Psychology (2nd edition). Module 7: The Brain Differences Between the Two Hemispheres Hemispheric Differences • “Left-brained” and “right-brained” debunked • Brain is divided into two hemispheres but works as a single entity. • Both sides continually communicate via the corpus callosum, except in those with split brains. Split Brain Patient • Play (side one) Chapter 29: “Split Brain Research” (32251) (5:44) Module 7: The Brain Differences Between the Two Hemispheres: Language and Spatial Abilities The Brain’s Left Hemisphere • For most people, language functions are in the left hemisphere. • For a small percentage of people, language functions are in the right hemisphere. Broca’s Area • The brain area of the left frontal lobe • Directs the muscle movements involve in speech • If damaged the person can form the ideas but cannot express them as speech Wernicke’s Area • A brain area of the left temporal lobe • Involved in language comprehension and expression • Our ability to understand what is said to us • Usually in the left temporal lobe The Brain’s Right Hemisphere • Houses the brain’s spatial abilities • Our spatial ability allows us to perceive or organize things in a given space, judge distance, etc. • Helps in making connections between words Broca’s and Wernicke’s Areas • Play “Language and Speech: Broca’s and Wernicke’s Areas” (7:44) Module #6 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2nd edition). Brain Specialization • Play (side one) Chapters 23-28 (2342632250) • • • • • • -Brain Imaging (0:28) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (0:30) EEG (1:05) Regional Blood Flow Mapping (1:12) PET Scan (1:06) SPET (0:30) Split Brain Research Split Brain Research Split Brain Research Split Brain Research Split Brain Research Split Brain Research Split Brain Research The End