* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of a Cell: Animal Cells
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
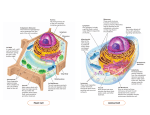
Animal Cells This is a diagram of an animal cell. Each cell has several organelles. Let's learn about them! Animal cells are different from plant cells, though they have many similar structures, called organelles. Here we will learn about the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi bodies, mitochondria, ribosomes, and vacuoles. For personal use only. Copyright 2014 Virginia George Parts of a Cell Cut out the pieces and paste them together to make your own animal cell! Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Golgi Bodies Vacuoles Ribosomes (draw onto cell) Cell Flash Cards Cut each page in half horizontally and fold the piece in half so the definition is on the back side. Quiz yourself, how many organelle functions do you know? They are small organelles, bound by single membrane. Vacuoles These organelles are often used as "storage units". Vesicles are smaller vacuoles which function for transport in/out of the cell. The fluid that fills the cell is the cytoplasm, water based. Cytoplasm The cellular organelles are suspended in this matrix of the cytoplasm. This matrix maintains the pressure of the cell, ensures the cell doesn't shrink or burst. Cell Membrane Semi-permeable barrier, allowing only select molecules to move across it. Consists of protein and fat. Basic purpose is to protect the cell from it's surroundings. The house for most of the cells genetic material- the DNA and RNA. Nucleus It is surrounded by a porous membrane known as the nuclear membrane. Controls the activity of the cell and is known as the control center. Nucleolus A structure contained within the nucleus. Responsible for assembling ribosomes. The site for protein synthesis where the translation of the RNA takes place. Ribosomes As protein synthesis is very important to the cell, these are found in large number in all cells. Found freely suspended in the cytoplasm and also attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic Reticulum The transport system of the cell. It transports molecules that need certain changes and also molecules to their destination. Thee are two types, rough and smooth. Rough has ribosomes bound to it, making it appear rough; while the smooth does not have the ribosomes. Mitochondria The main energy source of the cell. They are called the power house of the cell because energy is created here. This spherical or rod shaped organelle consists of an inner and outer membrane. The packaging center of the cell. Golgi Bodies Modifies the molecules from the rough ER by dividing them into smaller units with membrane known as vesicles. They are flattened stacks of membrane-bound sacs.