* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain and Marijuana - Boston Children`s Hospital
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
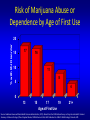
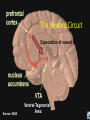
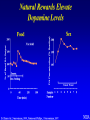
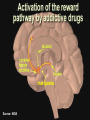
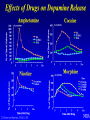
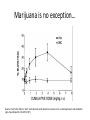
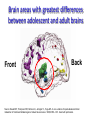
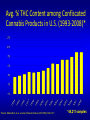
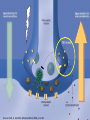
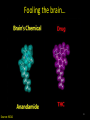
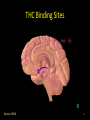
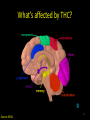
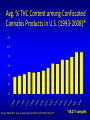
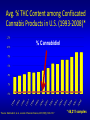
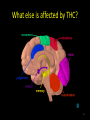
Marijuana: Emerging Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Sion Kim Harris, PhD Center for Adolescent Substance Abuse Research Children’s Hospital Boston Harvard Medical School Is marijuana addictive? Number of People Aged 12+ Receiving Drug Abuse Treatment in Past Year (2009) 1243 Marijuana 787 Cocaine Pain meds 739 Stimulants 517 Heroin 507 443 Hallucinogens Tranquilizers 421 0 250 500 750 1000 1250 1500 Numbers in Thousands Source: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2010). Results from the 2009 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Volume I. Summary of National Findings (Office of Applied Studies, NSDUH Series H-38A, HHS Publication No. SMA 10-4586Findings). Rockville, MD. Marijuana is especially addictive for teens … • More 15 to 17-year-olds are in treatment for a primary diagnosis of marijuana dependence than for all other illegal drugs combined. Source: Data from the Treatment Episodes Data Set (TEDS), SAMHSA, 2008 Risk of Marijuana Abuse or Dependence by Age of First Use % with MJ Disorder 20 15 17 16 10 11 8 5 4 0 13 15 17 19 Age at First Use 21+ Source: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2010). Results from the 2009 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Volume I. Summary of National Findings (Office of Applied Studies, NSDUH Series H-38A, HHS Publication No. SMA 10-4586Findings). Rockville, MD. Risk of Alcoholism by Age of First Drink % with Alcohol Disorder 60 50 40 47 45 38 30 32 28 20 15 10 17 11 9 20 >=21 0 <=13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Age at First Drink Source: Hingson RW, Heeren T, Winter MR. Age at drinking onset and alcohol dependence. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160:739-746. Why is the teen brain more susceptible to addiction? The Reward Circuit Expectation of reward Source: NIDA Ventral-Tegmental Area marijuana Source: NIDA Marijuana is no exception… Source: French ED, Dillon K, Wu X. Cannabinoids excite dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmentum and substantia nigra. NeuroReport 8, 649–652 (1997) Brain areas with greatest differences between adolescent and adult brains Front Back Source: Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Holmes CJ, Jernigan TL, Toga AW. In vivo evidence for post-adolescent brain maturation in frontal and striatal regions. Nature Neuroscience. 1999;2:859 – 861. Used with permission. The nucleus accumbens (NAcc) in teen brains behaves differently from adult brains… Functional brain imaging (fMRI) study of NAcc activation in children, teens, adults Children ages 7-11 Small Reward Teens ages 13-17 Adults ages 23-29 Large Reward Source: Galvan A, Hare AT, Parra, CE, Penn J, Voss H, Glover G, Casey BJ, Earlier Development of the Accumbens Relative to Orbitofrontal Cortex Might Underlie Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescents. Journal of Neuroscience, 2006,26(25):6885–6892 The prefrontal cortex (the “brakes”) develops more slowly… Adolescence Adult (about age 25) Source: Casey BJ, et al., Development Reviews. 2008; 28(1): 62-77 Source: Casey BJ, Getz S, Galvan A. The adolescent brain. Dev Rev. 2008;28(1):62-77. Used with permission. And… NAcc-PFC connectivity is not fully mature in the teen brain Key Point #1 Teen brains have higher risk for addiction than adults when exposed to HIGHLY REWARDING stimuli due to… greater reward sensitivity incomplete networking of the brain faster learning (neuroplasticity) 18 Risk for addiction is much higher when… Family history of any addiction Chronic stress Emotional trauma Chronic sleep deprivation Etc. 19 What other effects does marijuana have on the teen brain? What is in Marijuana? • Contains MANY chemicals including – Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol – Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol – Cannabidiol – Cannabinol – Cannabichromene – Cannabigerol – Etc. 21 In Source: Mechoulam R, Hanus L, The cannabinoid system from the point of view of a chemist. Marijuana and Madness. ed. Castle, Murray. Cambridge University Press, 2004 What is in Marijuana? • The main psychoactive chemical is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol or “THC” • Marijuana’s potency and effects depend on how much THC it contains 22 In Source: Mechoulam R, Hanus L, The cannabinoid system from the point of view of a chemist. Marijuana and Madness. ed. Castle, Murray. Cambridge University Press, 2004 Has there been a change in THC content in marijuana over time? Avg. % THC Content among Confiscated Cannabis Products in U.S. (1993-2008)* *Source: Mehmedic Z, et al., Journal of Forensic Science, 2010;55(5):1209-1217 * 46,211 samples What else has been found in marijuana? Marijuana Contaminants • Several studies show fungi, mold, and bacterial contamination in most samples tested • Evidence of Aspergillus fungi exposure in most marijuana smokers tested compared to 1/10 non-smokers Source: McLaren et al., Cannabis potency and contamination: a review. Addiction. 2006;103:1100-1109. Marijuana Contaminants • Aspergillus can produce mycotoxins (carcinogenic) and cause lung infections – could be fatal in people with immune system problems • Unlike tobacco, pesticide use is unregulated for marijuana, and little research done to date on amount in marijuana Tobacco vs. Marijuana Smoke Tobacco vs. Marijuana Smoke • Of the 74 chemicals and metals tested in tobacco and marijuana smoke under rigorously matched conditions… – Marijuana smoke contained most of the same carcinogenic chemicals as tobacco smoke – Amount of tar generated was the same The Brain and Marijuana 30 Cannabinoid receptors in our brains? Why? • Endogenous cannabinoid chemical called Anandamide • Important for modulating release of many different neurotransmitters • Inhibitory effect Source: Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science. 2002;296:678-682. 31 The Brain’s Endocannabinoid System A brief primer on how neurons work… After … 34 36 Source: Kraft, U. Scientific American Mind, 2006, p. 62-65 Endocannabinoid System Functions • Cannabinoid receptors located on neurons throughout brain • Regulates levels of the brain’s major inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters (GABA and glutamate) • Helps protect neurons from overactivity that could lead to cell damage or death Endocannabinoid System Part 2 • Shapes brain development by… – guiding correct growth and positioning of inhibitory and excitatory neurons – controlling synaptic activity, thereby shaping synaptic refinement, brain connectivity and efficiency – And more… Source: Galve-Roperh I, Palazuelos J, Aguado T, Guzman M. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;259:371-382. Fooling the brain… Source: NIDA 39 THC Binding Sites Source: NIDA 40 What’s affected by THC? Source: NIDA 41 Hippocampus 42 THC and Memory • Cannabinoids inhibit glutamate release in hippocampus, below the level needed to trigger memory formation • Anandamide exerts subtle, specific inhibition (may play role in extinction of fearful memories) • THC causes widespread, prolonged inhibition Source: Iversen L. How cannabis works in the brain. In Marijuana and Madness. Ed. Castle & Murray, 2004. Oxford University Press. Teen Working Memory Performance Source: Jacobsen et al. Impact of cannabis use on brain function in adolescents. Annals NY Acad Sci. 2004. 44 THC effects after chronic use • Suppresses cannabinoid receptor function; reduces number of receptors and decreases sensitivity to anandamide, so it can’t do it’s job • Causes too much excitation of neurons, leading to “Excitotoxicity” and cell damage/death Source: Bossong MG, Niesink RJM. Adolescent brain maturation, the endogenous cannabinoid system and the neurobiology of cannabis-induced schizophrenia. Progress in Neurobiology. 2010;92:370-385. The brain seeks balance… THC Inhibition Excitation Source: Valenzuela CF, Alcohol and neurotransmitter actions. Alcohol Health & Research World, 1997; 21(2), 144-148. More THC effects • Hippocampal synaptic connections are gradually lost due to continual inhibition/suppression • Dopamine receptors are damaged or lost leading to “Reward deficiency” Source: Bossong MG, Niesink RJM. Adolescent brain maturation, the endogenous cannabinoid system and the neurobiology of cannabis-induced schizophrenia. Progress in Neurobiology. 2010;92:370-385. NIDA Key Point #2 The endocannabinoid system is important in brain development… THC interferes with its proper functioning Teen brain development is shaped by experience Repeated THC exposure will change brain development 49 Marijuana and Mental Illness MANY longitudinal studies have found that regular marijuana users, especially those starting as teens, have higher rates of paranoia, anxiety, depression, psychotic symptoms, and schizophrenia as adults Source: Malone DT et al. Adolescent cannabis use and psychosis: epidemiology and neurodevelopmental models. Brit J Pharmacol. 2010;160:511-522 51 Similar altered white matter structure found in the brains of schizophrenics and teen marijuana users Bava S, Frank LR, McQueeny T, Schweinsburg BC, Schweinsburg AD, Tapert SF. Altered white matter microstructure in adolescent substance users. Psychiatry Research 52 Neuroimaging. 2009;173:228-237. Avg. % THC Content among Confiscated Cannabis Products in U.S. (1993-2008)* *Source: Mehmedic Z, et al., Journal of Forensic Science, 2010;55(5):1209-1217 * 46,211 samples Avg. % THC Content among Confiscated Cannabis Products in U.S. (1993-2008)* % Cannabidiol *Source: Mehmedic Z, et al., Journal of Forensic Science, 2010;55(5):1209-1217 * 46,211 samples What else is affected by THC? 55 Fertility and Hormones • Marijuana affects network of glands, organs and hormones involved in growth, development and energy levels • Lowers fertility of males and females through lowered sperm count and egg damage Source: Wenger T, Croix D, Tramu G. The effect of chronic prepubertal administration of marijuana (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) on the onset of puberty and the post-pubertal reproductive functions in female rats. Biology of Reproduction. 1988;39:540-545. And finally…. Does marijuana affect driving? Marijuana and Driving Studies of performance show that THC changes attention, working memory, coordination, reaction time, and visual perception 58 Source: Becker et al., 2010; Medina et al., 2007; Jacobsen et al., 2004. Marijuana and Traffic Fatalities Percent of Fatally-Injured Drivers Tested who were Drug-Positive In 2009, among drug-positive traffic deaths, marijuana was most common drug found, accounting for over 1 in 4 (28%) Adapted by CESAR from National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), “Drug Involvement of Fatally Injured Drivers,” Traffic Safety Facts, November 2010. Available online at http://www-nrd.nhtsa.dot.gov/Pubs/811415.pdf. Any other questions? Any Questions? 60