* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
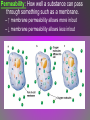
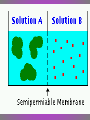
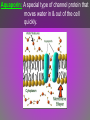
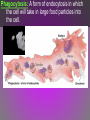
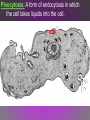
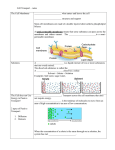
Diffusion: Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration. – Concentration & permeability are the factors that determine if diffusion occurs across a membrane or not. Concentration: The amount of dissolved solute (substance) in a volume of solvent (liquid). – Solution = solvent + solute – If a substance is present in unequal amounts on either side of a membrane, it will move to the area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. Permeability: How well a substance can pass through something such as a membrane. – ↑ membrane permeability allows more in/out – ↓ membrane permeability allows less in/out PASSIVE TRANSPORT • Passive transport: Movement of materials in or out of the cell which does NOT require use of cell energy (ATP). – Cells live in a liquid environment which makes it easier for materials (food, water, gases) to move in & out of the cell. – 2 types: Osmosis & facilitated diffusion Vorticella Osmosis: Diffusion of H2O molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of ↑ H2O concentration to ↓ H2O concentration. – 3 types of solutions (hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic) Osmotic pressure: The force exerted by osmosis, that moves water across a semi-permeable membrane from a diluted solution to a more concentrated solution. – Occurs in hypotonic, isotonic, & hypotonic solutions Hypertonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where solute concentration is higher than the concentration inside the cell. H2O leaves cell; Cell shrinks. – ↑ solute in solution, ↓ solute in cell – Plasmolysis: The shrinking of the cytoplasm due to the loss of H2O. Isotonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where the solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside the cell. H2O enters/ exits cell at an even rate. Cell doesn’t shrink or expand. Ideal conditions. – solute in solution ↔ solute out of cell Hypotonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where the solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside the cell. H2O enters cell; Cell expands. – ↓ solute in solution, ↑ solute in cell – Cytolysis: The bursting of a cell. HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC FACILITATED DIFFUSION Facilitated diffusion: The transport of materials across the plasma membrane by means of transport proteins. 1. Channel proteins 2. Carrier proteins Channel Protein: Tube-like proteins in the cell membrane through which small, dissolved particles can diffuse. Aquaporin: A special type of channel protein that moves water in & out of the cell quickly. Carrier proteins: A protein in the cell membrane whose shape fits a specific molecule or ion. – When the proper molecule binds with the protein, the protein changes shape and moves the molecule across the membrane. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Active transport: The movement of materials against the concentration gradient. – Molecules move from ↓ concentration to ↑ concentration • Chemical energy (ATP) from the cell is used to change the shape of a protein to move molecules across the cell membrane. ENDOCYTOSIS Endocytosis: A process in which a cell surrounds & takes in material from its environment. – A vacuole is then produced and taken into the cell. endocytosis Phagocytosis: A form of endocytosis in which the cell will take in large food particles into the cell. Pinocytosis: A form of endocytosis in which the cell takes liquids into the cell. EXOCYTOSIS Exocytosis: A process in which the cell removes large particles or wastes exocytosis