* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download _____ Name Date ______ Mrs. G-M (Biology) Period ______ List of
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
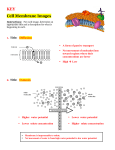
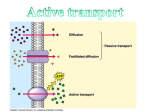
# _____ Name __________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (Biology) Period ___________ List of Topics to Know for Unit 4—The Cell & Its Environment Cells & Cell Theory Who first observed cells? o What was he looking at? o Did he see live cells? What are the 3 parts of cell theory? Cell (plasma) membrane structure What are the 2 main functions of the cell (plasma) membrane? o What does it mean that the membrane is “selectively permeable”/“semi-permeable”? In general, what does the cell (plasma) membrane look like? What does the cell (plasma) membrane look like in more detail? o Be able to sketch/identify a detailed view (“Fluid Mosaic Model”) of a cell membrane and label the parts. Movement of materials across the cell membrane What is passive transport? o Does it require energy? Why/why not? What can passive transport be compared to? o Examples of passive transport… During diffusion, which way do the molecules of the solute move? During diffusion, do the molecules ever completely stop moving? What does “dynamic equilibrium”/“no net movement” mean? What is osmosis? o Why is it important? Define “isotonic solution”. o Be able to: Sketch a cell in an isotonic solution. Label the amount of solute (ex. salt) and water inside the cell and outside the cell. Show which way will the water move and explain why it moves that way. What will happen to the size/shape of the cell? Define “hypotonic solution”. o Be able to: Sketch a cell in a hypotonic solution. Label the amount of solute (ex. salt) and water inside the cell and outside the cell. Show which way will the water move and explain why it moves that way. What will happen to the size/shape of the cell? o What saying can you use to remember what happens in a hypotonic solution. # _____ Name __________________________ Date ____________ Mrs. G-M (Biology) Period ___________ List of Topics to Know for Unit 4—The Cell & Its Environment Define “hypertonic solution”. o Be able to: Sketch a cell in a hypertonic solution. Label the amount of solute (ex. salt) and water inside the cell and outside the cell. Show which way will the water move and explain why it moves that way. What will happen to the size/shape of the cell? o What saying can you use to remember what happens in a hypertonic solution. What is the role of vacuoles in cells (in general)? o …in plant cells? o …in freshwater protists (ex. Paramecium)? Why do some protists need “contractile vacuoles”? What is facilitated diffusion?/When is it needed? o What helps out during facilitated diffusion? o Does facilitated diffusion require energy? Why/why not? What is active transport? o Does active transport require energy? Why or why not? What can passive transport be compared to? o …examples of active transport? o What allows for the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient during active transport? o What is the result of active transport? When materials can’t pass through the membrane, which processes can they use to get into/out of the cell? o Describe what happens during endocytosis./Which way do materials move during endocytosis? What are the two types of endocytosis? Does endocytosis require energy? Why or why not? o Describe what happens during exocytosis./Which way do materials move during exocytosis? Does exocytosis require energy? Why or why not? The Cell Wall What is the cell wall? o What types of organisms have cells with cell walls? o What are cell walls made of? o What does the cell wall do for the cell? o Do cell walls affect a cell’s permeability?