* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
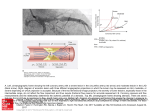
Apoptosis pathway. Two distinct, but not mutually exclusive, pathways of apoptotic cell death have been well desribed: extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, soluble or cell surface death ligands, such as TNF-α and Fas ligand, bind to the corresponding death receptors inducing activation of upstream caspases, such as caspase-8, followed by activation of downstream effector caspases. In the intrinsic pathway, cytochrome c is released from mitochondria into the cytoplasm, often initiated by stress stimuli such as ischemia, oxidative stress, genotoxic stress, and calcium excess. These stimuli activate BH3-only family members and inhibit the prosurvival BCL-2-like proteins. Cytoplasmic cytochrome c in presence of dATP/ATP binds Apaf-1 to activate caspase-9 and subsequently downstream effector caspases. Once activated, the effector caspases fragment intracellular proteins resulting in the Source: MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY OF THE HEART, Hurst's The Heart, 14e orderly destruction of the cell. The effector caspases also activate DNAses and lead to fragmentation of nuclear DNA.226 The death receptor and Fuster Harrington Narula J, Eapen ZJ. Hurst's cThe Heart,through 14e; 2017 Availablewith at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: AugustBax 10, mitochondrialCitation: pathways are V, linked by Bid,RA, which stimulates cytochrome release interactions the proapoptotic Bcl-family members, 2017 227 228 and/or Bak. The antiapoptotic Bcl-family members, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit cell death by competing with Bax and Bak. When apoptosis is induced, in Copyright ©c, 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved addition to cytochrome SMAC is also released from the mitochondria that binds to XIAP precluding its inhibition of caspases. APAF1, apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; SMAC, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases; tBID, truncated form of BID; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; XIAP, X-