* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Actin dynamics - Journal of Cell Science
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
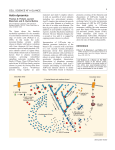
3 CELL SCIENCE AT A GLANCE Actin dynamics Thomas D. Pollard, Laurent Blanchoin and R. Dyche Mullins Structural Biology Laboratory, Salk Institute for Biological Studies, 10010 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA The figure shows the dendritic nucleation hypothesis for the assembly of actin filament networks at the leading edge of motile cells (Pollard et al., 2000). In this model, the actinmonomer-binding protein profilin (shown in black), with help in vertebrate cells from thymosin β4 (not shown), maintains a pool of unpolymerized ATPactin subunits (shown in lighter blue). Extracellular stimuli such as chemotactic factors bind to plasma membrane receptors, activating intracellular signalling molecules including Rho family GTPases. These GTPases bind to and activate WASP/Scar family proteins (shown in green) by freeing them from autoinhibition. Active WASP/Scar proteins bring together an actin monomer and Arp2/3 complex (shown in red), an assembly of seven subunits including two actin-related proteins. Arp2/3 complex then initiates the growth of a new actin filament as a branch on the side of an older actin filament. The branch grows rapidly at its barbed end by addition of actin-profilin complexes. As it grows, it pushes the plasma membrane forward. The new filament elongates for a second or two until it is capped by capping protein (shown in yellow). Incorporation of ATP-actin into a filament promotes hydrolysis of the bound ATP, a reaction with a half-time of a few seconds. Gamma phosphate dissociates slowly from polymerized ADP-P-actin subunits with a half time of 6 minutes, unless an ADF/cofilin protein (shown in gray) binds to a subunit and accelerates phosphate dissociation. Dissociation of phosphate promotes dissociation of branches from Arp2/3 complex and binding of ADF/cofilin to ADP-actin subunits (shown in darker blue). ADF/cofilin bound to filaments promotes severing of the filaments and dissociation of ADP-actin bound to ADF/cofilin. Profilin is the nucleotideexchange factor for actin and promotes the exchange of ADP for ATP. Profilin then binds tightly to ATP-actin monomers, refilling the actin monomer pool. Rho family GTPases also activate p21-activated protein kinase (PAK), which stimulates LIM kinase to phosphorylate ADF/cofilin. Phosphorylation inactivates ADF/cofilin and slows down the rate of filament disassembly. REFERENCE Pollard, T. D., Blanchoin, L. and Mullins, R. D. (2000). Biophysics of actin filament dynamics in nonmuscle cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomolec. Struct. 29, 545-576. Cell Science at a Glance on the Web Electronic copies of the full-size poster insert are available in the online version of this article (see www.biologists.com/jcs). Files in several formats are provided and may be downloaded for use as slides. Extracellular stimuli Extracellular stimuli 5. Growing filaments push membrane forward 4. Elo ng ati on 70 2. WASP/Scar activation & sis roly hyd TP 7. A 3. Arp2/3 complex activation and filament nucleation 6. Capping limits elongation PAK ion ciat isso Pi d LIM kinase 9. ADF-cofilin inhibition 8. ADF/cofilin severs & depolymerizes ADP-actin filamants 1. Profilin-bound ATP-actin 10. ADP-ATP exchange Journal of Cell Science 2001 (114, p. 3) Figure adapted, with permission, from the Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure 29 ©2000 by Annual Reviews, www.AnnualReviews.org. (See poster insert)