two types of titin interactions lead to an asymmetrical sorting of actinin
... (actin) filaments, links titin (also called connectin) and actin filaments from opposing sarcomere halves in a lattice connected by α-actinin. We demonstrate by protein interaction analysis that two types of titin interactions are involved in the assembly of α-actinin into the Z-disk. Titin interact ...
... (actin) filaments, links titin (also called connectin) and actin filaments from opposing sarcomere halves in a lattice connected by α-actinin. We demonstrate by protein interaction analysis that two types of titin interactions are involved in the assembly of α-actinin into the Z-disk. Titin interact ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... The investigation of plant myosin had begun from attempting to elucidate the molecular mechanism of characean cytoplasmic streaming [82]. In 1970–1990, several proteins with ATPase activities had been isolated biochemically and reported as plant myosins (cited in [84]). However, none of these result ...
... The investigation of plant myosin had begun from attempting to elucidate the molecular mechanism of characean cytoplasmic streaming [82]. In 1970–1990, several proteins with ATPase activities had been isolated biochemically and reported as plant myosins (cited in [84]). However, none of these result ...
Plasma Gelsolin
... cellular actin filaments associated with cell shape changes and movement [1]. Subsequent research revealed that gelsolin is nearly unique among mammalian cytosolic proteins in having a secreted isoform. Originally defined by its interactions with actin, this secretory form, now called plasma gelsoli ...
... cellular actin filaments associated with cell shape changes and movement [1]. Subsequent research revealed that gelsolin is nearly unique among mammalian cytosolic proteins in having a secreted isoform. Originally defined by its interactions with actin, this secretory form, now called plasma gelsoli ...
Self-Incompatibility-induced Programmed Cell
... Dangl, 1996; van Doorn, 2011; van Doorn et al., 2011). There is considerable biochemical evidence for the involvement of caspase-like activities in plant PCD (van Doorn and Woltering, 2005). For example, Vacuolar Processing Enzyme (VPE) has YVADase (caspase-1-like) activity (Hatsugai et al., 2004; R ...
... Dangl, 1996; van Doorn, 2011; van Doorn et al., 2011). There is considerable biochemical evidence for the involvement of caspase-like activities in plant PCD (van Doorn and Woltering, 2005). For example, Vacuolar Processing Enzyme (VPE) has YVADase (caspase-1-like) activity (Hatsugai et al., 2004; R ...
Inhibitory Regulation of Higher-Plant Myosin by
... axillitormis causes a reversible inhibition of cytoplasmic streaming (Kikuyama and Tazawa, 1982). The membranepermeabilized cell model prepared from characean cells provides direct evidence that cytoplasmic streaming is reversibly inhibited by an elevation of Ca21 to 1026 m (Tominaga et al., 1983). ...
... axillitormis causes a reversible inhibition of cytoplasmic streaming (Kikuyama and Tazawa, 1982). The membranepermeabilized cell model prepared from characean cells provides direct evidence that cytoplasmic streaming is reversibly inhibited by an elevation of Ca21 to 1026 m (Tominaga et al., 1983). ...
Interactions of Elongation Factor 1 Cell Protrusions with F-Actin and
... actin to maintain actin filament polymerization over a period of time longer than the duration of the initial protrusion. As a result, the cells would have a slower rate of migration. Alternatively, the site of actin synthesis (and of other functionally related proteins) may affect the location of n ...
... actin to maintain actin filament polymerization over a period of time longer than the duration of the initial protrusion. As a result, the cells would have a slower rate of migration. Alternatively, the site of actin synthesis (and of other functionally related proteins) may affect the location of n ...
Assessing the Flexibility of Intermediate Filaments by Atomic Force
... than 600 nm, some deviation from the theoretical value of 3 (see equation (5)) is observed due to the finite pixel size and the smoothing procedure. Above 600 nm, it was possible to estimate the apparent persistence length lkQ2 l for each support by fitting the behaviour of the mean-square angle kQ2 ...
... than 600 nm, some deviation from the theoretical value of 3 (see equation (5)) is observed due to the finite pixel size and the smoothing procedure. Above 600 nm, it was possible to estimate the apparent persistence length lkQ2 l for each support by fitting the behaviour of the mean-square angle kQ2 ...
The intercalated disc-associated Xin family of proteins in cardiac
... Intercalated discs (ICDs) are cardiac-specific structures located at the longitudinal termini of cardiomyocytes. Classically, the functions assigned to ICDs include mechanical and electrical communication among adjacent cardiomyocytes. More recently, it has been increasingly realized that ICDs also ...
... Intercalated discs (ICDs) are cardiac-specific structures located at the longitudinal termini of cardiomyocytes. Classically, the functions assigned to ICDs include mechanical and electrical communication among adjacent cardiomyocytes. More recently, it has been increasingly realized that ICDs also ...
Profilin association with monomeric actin in
... 5 minutes at 4°C to yield a low speed supernatant (LSS) and centrifuged at 200,000 g in a Beckman TL100 ultracentrifuge for 30 minutes at 4°C to yield a high speed supernatant (HSS). To determine the concentration of profilin in the extracts, samples of 10-50 µl were diluted into boiling sample buff ...
... 5 minutes at 4°C to yield a low speed supernatant (LSS) and centrifuged at 200,000 g in a Beckman TL100 ultracentrifuge for 30 minutes at 4°C to yield a high speed supernatant (HSS). To determine the concentration of profilin in the extracts, samples of 10-50 µl were diluted into boiling sample buff ...
Myosin V Plays an Essential Role in the Thyroid Hormone
... in the absence and presence of T4. No differences in total actin content were observed, and ⬎90% of the immunoreactive actin was found in the Triton-insoluble pellet in both thyroid hormone-deficient and T4-treated cells as determined by densitometry (data not shown). In control experiments, no spec ...
... in the absence and presence of T4. No differences in total actin content were observed, and ⬎90% of the immunoreactive actin was found in the Triton-insoluble pellet in both thyroid hormone-deficient and T4-treated cells as determined by densitometry (data not shown). In control experiments, no spec ...
Polarization of the endomembrane system is an early event in fucoid
... Endocytosis contributes to polar endomembrane labeling. A 6 h-old zygote was labeled for 2 min and the spatial distribution of endocytosis was immediately imaged by confocal microscopy. Image is a single optical section near the median plane demonstrating preferential FM4-64 uptake at the rhizoid po ...
... Endocytosis contributes to polar endomembrane labeling. A 6 h-old zygote was labeled for 2 min and the spatial distribution of endocytosis was immediately imaged by confocal microscopy. Image is a single optical section near the median plane demonstrating preferential FM4-64 uptake at the rhizoid po ...
Coordination of microtubule and microfilament dynamics by
... of this hypothesis, the two loci interact genetically, and the FH2 domain of Capu binds to SpireD in vitro (Fig. 3i). We mapped this interaction to a smaller construct, SpireD3, which contains the four tandem WH2-domains and the Rho1 binding site (Fig. 3i). We then conducted actin polymerization ass ...
... of this hypothesis, the two loci interact genetically, and the FH2 domain of Capu binds to SpireD in vitro (Fig. 3i). We mapped this interaction to a smaller construct, SpireD3, which contains the four tandem WH2-domains and the Rho1 binding site (Fig. 3i). We then conducted actin polymerization ass ...
Rho signaling pathway and apical constriction in the - ICB-USP
... invaginating event. After the ingression of the whole placode toward the underlying optic cup, the edges fuse and detach from the surface ectoderm, forming the lens vesicle (Schook, 1980b). A variety of mechanisms have been suggested to contribute to the initial inward buckling of the placode, such ...
... invaginating event. After the ingression of the whole placode toward the underlying optic cup, the edges fuse and detach from the surface ectoderm, forming the lens vesicle (Schook, 1980b). A variety of mechanisms have been suggested to contribute to the initial inward buckling of the placode, such ...
Separate Functions of Gelsolin Mediate Sequential Steps of
... functions of gelsolin in integrin-dependent processes have not been defined. Detailed studies of gelsolin structure using proteolytic fragments (Kwiatkowski et al., 1989; Kwiatkowski, 1999), recombinant truncations (Way et al., 1989), and crystallography (Burtnick et al., 1997) have shown that two d ...
... functions of gelsolin in integrin-dependent processes have not been defined. Detailed studies of gelsolin structure using proteolytic fragments (Kwiatkowski et al., 1989; Kwiatkowski, 1999), recombinant truncations (Way et al., 1989), and crystallography (Burtnick et al., 1997) have shown that two d ...
Actin Filaments Play a Critical Role in Vacuolar
... INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, a large number of proteins are targeted after translation to specific organelles by a process called intracellular trafficking. This targeting process is quite complex and involves many different pathways depending on the organelle involved (Rothman, 1994; Hawes et ...
... INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, a large number of proteins are targeted after translation to specific organelles by a process called intracellular trafficking. This targeting process is quite complex and involves many different pathways depending on the organelle involved (Rothman, 1994; Hawes et ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... aggregate to form punctate F-actin foci and they increase in size over time (Fig. 1C, D). Two ABPs, actin depolymerizing factor (ADF/cofilin) and cyclase-associated protein (CAP), rapidly colocalize to the actin foci (Poulter et al., 2010). It is thought that both the depolymerization and the format ...
... aggregate to form punctate F-actin foci and they increase in size over time (Fig. 1C, D). Two ABPs, actin depolymerizing factor (ADF/cofilin) and cyclase-associated protein (CAP), rapidly colocalize to the actin foci (Poulter et al., 2010). It is thought that both the depolymerization and the format ...
Organelle motility in the pollen tube: a tale of 20 years
... evidence that different organelle classes of pollen tubes move differentially. Since the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains 17 myosins belonging to families VIII and XI (Lee and Liu, 2004), pollen tubes presumably contain different members of the myosin XI family, each involved in the movement ...
... evidence that different organelle classes of pollen tubes move differentially. Since the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains 17 myosins belonging to families VIII and XI (Lee and Liu, 2004), pollen tubes presumably contain different members of the myosin XI family, each involved in the movement ...
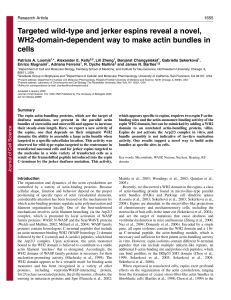
Targeted wild-type and jerker espins reveal a novel, WH2
... previously for espin 3A and espin 3B (Sekerková et al., 2004). Moreover, deletion of the 17-aa core also reduced the rapid recovery of photobleached GFP--actin observed throughout the length of the long microvilli of espin-expressing epithelial cells, suggesting that the WH2 domain of PAB-associate ...
... previously for espin 3A and espin 3B (Sekerková et al., 2004). Moreover, deletion of the 17-aa core also reduced the rapid recovery of photobleached GFP--actin observed throughout the length of the long microvilli of espin-expressing epithelial cells, suggesting that the WH2 domain of PAB-associate ...
Nuclear-fallout, a Drosophila protein that cycles from the cytoplasm
... cytoplasmic organelles, centrosomes are unique because they are precisely duplicated with each division cycle. In addition to organizing microtubules, centrosomes influence actin dynamics. In many instances, the effect of centrosomes on microfilament distribution occurs indirectly through their effe ...
... cytoplasmic organelles, centrosomes are unique because they are precisely duplicated with each division cycle. In addition to organizing microtubules, centrosomes influence actin dynamics. In many instances, the effect of centrosomes on microfilament distribution occurs indirectly through their effe ...
Chloroplast anchoring: its implications for the
... This led Seitz (1980) to propose that the cytoplasmic ATP level, supplied by photosynthesis and respiration, may change in relation to light intensity, and that a difference in ATP levels between the periclinal and anticlinal regions is the first cause for the different distribution patterns of chlo ...
... This led Seitz (1980) to propose that the cytoplasmic ATP level, supplied by photosynthesis and respiration, may change in relation to light intensity, and that a difference in ATP levels between the periclinal and anticlinal regions is the first cause for the different distribution patterns of chlo ...
Pollen cytoskeleton during germination and tube growth
... conversely, myosins of 175 kDa were detected in association with vesicles and organelles (such as mitochondria)53. Different classes of myosins were also discovered using antibodies to specific myosin classes (I, II and V)54. The latter finding suggested that the movement of individual membrane-boun ...
... conversely, myosins of 175 kDa were detected in association with vesicles and organelles (such as mitochondria)53. Different classes of myosins were also discovered using antibodies to specific myosin classes (I, II and V)54. The latter finding suggested that the movement of individual membrane-boun ...
Multiple Roles of the Cytoskeleton in Bacterial Autophagy
... Several pathogenic bacteria can modulate the dynamics of microtubules during infection [20], and it is likely that pathogen interference with microtubules has a profound impact on autophagy. Listeria ActA can recruit LaXp180/CC1, a binding partner of the microtubule-sequestering protein stathmin [21 ...
... Several pathogenic bacteria can modulate the dynamics of microtubules during infection [20], and it is likely that pathogen interference with microtubules has a profound impact on autophagy. Listeria ActA can recruit LaXp180/CC1, a binding partner of the microtubule-sequestering protein stathmin [21 ...
Actin and Myosin Function in Directed Vacuole Movement during
... Simultaneous visualization of Myo2p and the vacuole membrane was performed in yeast zygotes. 2.5 OD600 U each of mid-log phase M A T a and M A T a strains were mixed together in YEPD medium and shaken at 24°C for 1 h. The cells were then harvested, plated onto YEPD plates, and allowed to incubate at ...
... Simultaneous visualization of Myo2p and the vacuole membrane was performed in yeast zygotes. 2.5 OD600 U each of mid-log phase M A T a and M A T a strains were mixed together in YEPD medium and shaken at 24°C for 1 h. The cells were then harvested, plated onto YEPD plates, and allowed to incubate at ...
Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
Actin

Actin is a globular multi-functional protein that forms microfilaments. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells (the only known exception being nematode sperm), where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. An actin protein's mass is roughly 42-kDa and it is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division.Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell signaling, and the establishment and maintenance of cell junctions and cell shape. Many of these processes are mediated by extensive and intimate interactions of actin with cellular membranes. In vertebrates, three main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta, and gamma have been identified. The alpha actins, found in muscle tissues, are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins coexist in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton, and as mediators of internal cell motility. It is believed that the diverse range of structures formed by actin enabling it to fulfill such a large range of functions is regulated through the binding of tropomyosin along the filaments.A cell’s ability to dynamically form microfilaments provides the scaffolding that allows it to rapidly remodel itself in response to its environment or to the organism’s internal signals, for example, to increase cell membrane absorption or increase cell adhesion in order to form cell tissue. Other enzymes or organelles such as cilia can be anchored to this scaffolding in order to control the deformation of the external cell membrane, which allows endocytosis and cytokinesis. It can also produce movement either by itself or with the help of molecular motors. Actin therefore contributes to processes such as the intracellular transport of vesicles and organelles as well as muscular contraction and cellular migration. It therefore plays an important role in embryogenesis, the healing of wounds and the invasivity of cancer cells. The evolutionary origin of actin can be traced to prokaryotic cells, which have equivalent proteins. Actin homologs from prokaryotes and archea polymerize into different helical or linear filaments consisting of one or multiple strands. However the in-strand contacts and nucleotide binding sites are preserved in prokaryotes and in archea. Lastly, actin plays an important role in the control of gene expression.A large number of illnesses and diseases are caused by mutations in alleles of the genes that regulate the production of actin or of its associated proteins. The production of actin is also key to the process of infection by some pathogenic microorganisms. Mutations in the different genes that regulate actin production in humans can cause muscular diseases, variations in the size and function of the heart as well as deafness. The make-up of the cytoskeleton is also related to the pathogenicity of intracellular bacteria and viruses, particularly in the processes related to evading the actions of the immune system.