* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Architecture 2 Dr Mahjabeen
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
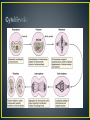
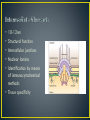
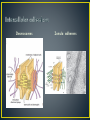
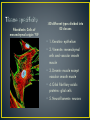
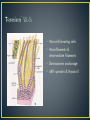
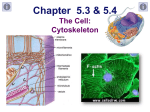
Dr Mah Jabeen Muneera Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KEMU • Shape: double sranded helix • Diameter: 7nm • Basic protein subunit: monomer of G-actin (globular or free actin) polymerizes to F- actin (filamentous), in presence of K & Mg. • Formin • Polarity: _ pointed end and + barbed end • Treadmilling • Stable- muscle cells and microvilli • Dissociate and reassemble • Profilin & Cofilin • Prevent polymerization • Prevent depolymerization (phalloidin found in poisosnous mushrooms) • Disrupt the dynamic equilibrium between F-actin and G-actin causing cell death Core of actin filaments ABPs- Actin Binding Proteins • Villin and fimbrin • Tropomyosin • Spectrin • Myosin 1 and 2 • • • • • 10-12nm Structural function Intercellular junctions Nuclear lamina Identification by means of immunocytochemical methods • Tissue specificity Desmosomes Zonula adherens Fibroblasts: Cells of mesenchymal origin- ? IF ›50 different types divided into 05 classes • 1. Keratins- epithelium • 2. Vimentin- mesenchymal cells and vascular smooth muscle • 3. Desmin- muscle except vascular smooth muscle • 4. Glial fibrillary acidic proteins- glial cells • 5. Neurofilaments- neurons • Presence of a specific type of intermediate filament in tumors can reveal which cell originated the tumor • Identification of intermediate filament proteins by means of immunocytochemical methods is a routine procedure • Microvilli bearing cells • Microfilaments & intermediate filaments • Desmosomes anchorage • ABP: spectrin & Myosin II • Neurofibrillary tangles: presence of structurally abnormal but phosphorylated neurofilaments and microtubule associated proteins ?? • • • • Disorder of CNS Mutations in the coding region of GFAP gene Altered GFAP prevents the assembly of intermediate filaments Accumulation of intermediate filament protein GFAP leads to cytoplasmic inclusions in astrocytes (Rosenthal fibres)