* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acids and Bases Lab
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
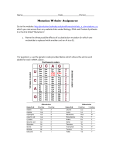
Name: 30 Points Period: Gene Mutations Background: Large-scale mutations affect the entire chromosome or number of chromosomes. Point mutations are small-scale, but can seriously affect the gene being copied. There is an error in around every 100,000 base pairs copied, but there are proofreading abilities within the enzymes that copy the DNA or RNA. However, nothing is foolproof. This handout describes the common mutations, and how they affect the entire sequence. 1) Prediction: What will happen if just one base pair is added or removed to a DNA sequence being replicated? _______________________________________________________________________ FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS: DNA sentence The man hit his eye and saw the red dot Insertion example t The man hit hi sey ean dsa wth ere ddo t The insertion shifts the readDin gfram et oth eright. The deletion shifts the rea(d)ingf ramet ot hel eft. Complete the following lines for frameshift mutations. WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE DNA sentence 2) Insertion 3) Deletion The man hit his eye and saw the red dot The man ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Insert a R after the h the three letter words should shift down The man hit Delete the I here ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ the three letter words should shift down Now use real DNA code and translate it into the correct amino acids. Decide where in the original DNA code to cause a mutation on the rest of the questions. Please use the codon table on the last page to find the corresponding amino acids. WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE AND CIRCLE THE MUTATED DNA BASE WHERE THE MUTATION TAKES PLACE. Original DNA TAC GGA 4) Insertion TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC ____ ____ ____ Insert a C after the G ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ CGA 5) Mutated mRNA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 6) Mutated Amino ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Original Amino acids MET PRO ALA ARG VAL LEU GLY TRY STOP 7) How did the mutation affect the amino acid sequence? WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE AND CIRCLE THE MUTATED DNA BASE WHERE THE MUTATION TAKES PLACE. Original DNA TAC GGA CGA TCT CAG GAG CCT ATA ATC 8) Deletion ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ _N/A_ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ _N/A_ GLY TRY STOP Delete the G 9) Mutated mRNA 10) Mutated Amino ____ Original Amino acids MET PRO ALA ARG VAL LEU 11) How did the mutation affect the amino acid sequence? Base Substitution Mutations (Point mutations): A different type of gene mutation is called base substitution or point mutation. It is the simplest type of mutation where a nucleotide pair is replaced with a different nucleotide pair. Base substitution GACGGC This may be a silent mutation, is which the amino acid is not affected. For example, the base substitution G A C G A G doesn’t change much since the mRNA would be C U G or C U C, both of which code for Leucine. WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE AND CIRCLE THE MUTATED DNA BASE WHERE THE MUTATION TAKES PLACE. Original DNA TAC CAT TCT TGT AAA AGG GCG ATT 12) Silent DNA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Change the last G to a C ____ ____ ____ ____ 13) Mutated mRNA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Original Amino acids MET VAL ARG ALA THR PHE SER ARG STOP 14) Mutated Amino CGG 15) How did the mutation affect the amino acid sequence? If there is a change that affects which amino acid is made, then the entire gene being made may be mutated. The two types of this are misssense and nonsense mutations. Missense mutation changes one or more amino acids. This may completely change the function of a gene. For example, G G A would code as C C U on mRNA, which is Proline. If a base was changed to G A A, then it would code as C U U, which is Leucine. WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE AND CIRCLE THE MUTATED DNA BASE WHERE THE MUTATION TAKES PLACE. Original DNA TAC GTC GCT CAA CGG GAC CTG ACC ACT 16) Missense DNA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Change the middle G to a C 17) Mutated mRNA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Original Amino acids MET GLN ARG VAL ALA LEU ASP TRP STOP 18) Mutated Amino 19) How did the mutation affect the amino acid sequence? Nonsense mutation changes the amino acid to a premature stop codon, stopping or altering the formation of the protein. WRITE EACH CODON PER LINE AND CIRCLE THE MUTATED DNA BASE WHERE THE MUTATION TAKES PLACE. Original DNA TAC GGT AAT CAA ATA GAA CCT GAG ACT ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Original Amino acids MET PRO LEU VAL TYR LEU GLY LEU 20) Nonsense DNA Change the second A to a C 21) Mutated mRNA ____ 22) Mutated Amino STOP 23) How did the mutation affect the amino acid sequence? Questions: 24) An error occurs in about how many base pairs being copied? 25) If there are 3 billion base pairs, why don’t all these mistakes in the DNA replication process cause a mutation every time there is a mistake? 26-27) Explain how mutations may be harmful and/or helpful to organisms (don’t list super-powers here) 27-30) List the 4 of the different types of mutations discussed in this activity. Deletion and insertion count as one type of mutation. _______________ _______________ ________________ ________________