* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Stroop effect wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Indirect tests of memory wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Mind-wandering wikipedia , lookup
Prefrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Inferior temporal gyrus wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
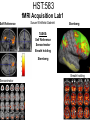
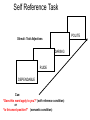
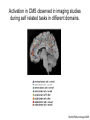
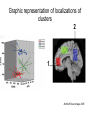
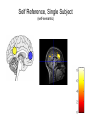
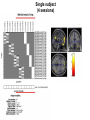
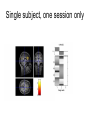
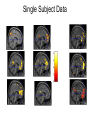
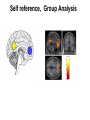
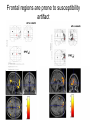
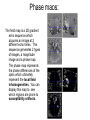
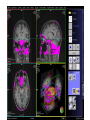
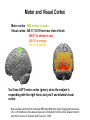
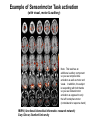
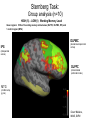
Self Reference Sensorimotor HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield-Gabrieli Sternberg TASKS: Self Reference Sensorimotor Breath holding Sternberg Breath holding Self Reference Task POLITE Stimuli: Trait Adjectives DARING RUDE DEPENDABLE Cue: “Does this word apply to you?” (self reference condition) or “Is this word positive?” (semantic condition) Self reference task design Stimuli: trait adjective words Words were drawn from Anderson’s (1968) list of normed trait adjectives. The lists were counterbalanced for word valence, length and number of syllables. Presentation: Words are presented in a blocked design. Each word is presented for 3 sec in blocks of ten and prior to each block onset subjects view a 2 sec cue describing their task for upcoming block. Each block is followed by 10 seconds of a rest condition. Each session has 2 blocks per self reference and 2 blocks per semantic conditions in the ABBA format. Total task time: 3min/session, 4 sessions or 12min Schematic illustration of cortical midline structures (CMS) MOPFC= medial orbital prefrontal cortex (BA11, BA12) VMPFC = ventromedial prefrontal cortex (BA10, 11) PACC = pre and subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (BA24, BA25, BA32) SACC = supragenual anterior cingulate cortex (BA24, BA32) PCC = posterior cingulate cortex (BA23) Northoff Neuroimage 2006 Activation in CMS observed in imaging studies during self related tasks in different domains. Northoff Neuroimage 2006 Graphic representation of localizations of clusters 2 1 Northoff Neuroimage 2006 Self Reference, Single Subject (self-semantic) Single subject (4 sessions) Single subject, one session only Single Subject Data Self reference, Group Analysis Frontal regions are prone to susceptibility artifact Phase maps: The field map is a 2D gradient echo sequence which acquires an image at 2 different echo times. This sequence generates 2 types of images, a magnitude image and a phase map. The phase map represents the phase differences of the spins which ultimately represent the local field inhomogeneities. You can display this map to see which regions are prone to susceptibility artifacts. Sensorimotor Task The task consists of a block design with block durations of 16s on/off. When checkerboard appears, subjects presses button using their right index finger and the off-block is fixation/no tapping. There are 15 total, 16s blocks. (4 min) On block parameters: ISI ranges from 500-1000ms, average ISI = 762ms, std. dev = 156ms. 21 checkerboard flashes per on block, each checkerboard flash duration = 200ms. The sequence begins with an off block.Scanner triggers the paradigm (after the dummy scans). fBIRN ( functional biomedical informatics research network) Motor and Visual Cortex Motor cortex - BA4 shown in green Visual cortex - BA 17,18,19 from rear view of brain BA 17 is shown in red. BA 18 is orange BA 19 is yellow You’ll see LEFT motor cortex (green), since the subject is responding with the right hand, and you’ll see bilateral visual cortex. Brain surface extracted from structural MRI data (Wellcome Dept. Imaging Neuroscience, UCL, UK). Brodmann Area data is based on information from the online Talairach demon (electronic version of Talairach and Tournoux, 1988). Example of Sensorimotor Task activation (with visual, motor & auditory) Note: This task has an additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) fBIRN ( functional biomedical informatics research network) Gary Glover, Stanford University Breath Holding Task This is a calibration task to measure subjects' global vascular reactivity. The task consists of a block design with alternating on/off blocks of 16-second periods of breath holding and normal breathing. During the off-block, the subject sees a green screen during which they are to breathe normally. During the last 2s of the off-block, the screen becomes yellow, signifying to the subject to take a deep breath in and hold. During the on-block (16s), the subject is shown a red screen, during which time they should hold their breath. The subject resumes breathing when they see a green colored screen. 15 total 16s blocks (4 min) Total task time: 4:06 Breath holding calibration • The entire gray matter volume is activated in each subject by the breath-holding task. This sample data is from Stanford’s 3T MRI shows the global response to holding one’s breath for 15 seconds. Sternberg Item Recognition Paradigm (SIRP) A Working Memory Task Each block is composed of three epochs: learn, encode, and probe: 1.5 sec for the “learn” prompt followed by .5 sec blank screen 6 sec to encode the target digits ( [1, 3, 5] digit sets providing a range of task difficulty) 38 sec for the probe digits (sequential presentation of digits) This means each working memory set lasts a total of 46 seconds. A block of each set size occurs twice in random order within a single run and each working memory set is sandwiched between fixation blocks. The duration of the fixation blocks within a run is random: Total time for all fixation blocks within a run = 78 seconds, (4,20) (min time = 4 sec, max time = 20 sec) Total scan time is thus 46 seconds*6 + 78 seconds+ 6 sec ddas = 360s Total task time: 6:00min Time frames: 180 Sternberg Task: Group analysis (n=10) HIGH (5) – LOW(1) Working Memory Load: Green regions: ROIs of 3 working memory related areas (DLPFC, DLPMC, IPS) and 1 control region (MTG) DLPMC IPS (dorsal lateral premotor cortex) (intraparietal sulcus) DLPFC (dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex) MTG (middle temp gyrus) Stuart Wallace, MIND, BIRN