* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name __ DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS TEST (2 points each
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
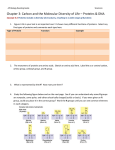
Name __________________________ DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS TEST (2 points each) MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the answer that best completes the statement on the blank and the left. ______ Which of the following shows the sequence for the way information is transferred in cells? A. PROTEINS DNA RNA B. DNA PROTEINS RNA C. PROTEINS RNA DNA D. DNA RNA PROTEINS _____ The “sides of the ladder” in a DNA molecule are made up of ______________. A. nitrogen bases B. phospholipids and proteins C. nitrogen bases and sugars D. sugars and phosphates ______ DNA wraps around proteins called ________________ when it condenses into chromosomes. A. histones B. promoters C. repressors D. ribosomes ______ Adenine, A. B. C. D. guanine, thymine, and cytosine are all _______________________. amino acids nitrogen bases proteins phospholipids _____ The “rungs A. B. C. D. of the ladder” in a DNA molecule are made of _______________. phosphate sugars nitrogen bases amino acids _____ According to Chargaff’s rules, which nucleotide is always paired with ADENINE in a DNA molecule? A. Uracil B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Cytosine _____ Ribosomes are made out of __________________________. A. RNA and proteins B. phospholipids and proteins C. glycoproteins and lipids D. DNA and proteins _____ Where in the cell does transcription take place? A. in the nucleus B. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm C. in Golgi bodies D. on the nucleosomes _____ Where in the cell does translation take place? A. in the nucleus B. on the nucleosomes C. in Golgi bodies D. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm _____ The molecule that caused transformation in Griffith’s pneumonia/mouse experiment was _______. A. a protein B. a bacteriophage C. DNA D. RNA _____ The Hershey-Chase blender experiments and Avery’s enzyme digestion experiments helped to prove that _____________________ A. DNA is a double helix. B. pneumonia causes dead mice. C. transformation is caused by proteins D. the genetic material is made of DNA _____ The series of genes that control differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo are called _____________ genes. A. TATA B. hox C. enhancer D. lac operon ______ A group of genes in prokaryotes that operate together is known as a(n) ________________ A. codon B. operator C. operon D. gene group ______ The place where RNA polymerase binds to start transcribing a gene is called the ____________ A. operator B. promoter C. repressor D. anticodon _____ The lac operon is found in _______________________ A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes _____ TATA boxes and enhancer sequences are found in _____________________ cells A. prokaryotes B. eukaryotes _____ The lac operon is normally turned OFF when _____________________________________, A. lactose is present B. the operator binds glucose C. the repressor binds the operator D. RNA polymerase binds the promoter _____ The presence of lactose turns the lac operon ON when ______________________________. A. the repressor binds lactose instead of the operator B. the repressor binds the operator C. anticodon binds the codon D. lactose binds the TATA box _____ The function of the TATA box is to ________________________________. A. bind the lac repressor B. turn on cell division genes C. help position the RNA polymerase D. edit introns * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * LABEL THE FOLLOWING: _____ Making a DNA copy of a DNA molecule (DNA DNA) A. B. C. D. _____ Making a complementary RNA message from a DNA code (DNA RNA) TRANSFORMATION REPLICATION TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION _____ Making a protein from an RNA message (RNA protein) ______ Process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by absorbing DNA from another strain of bacteria * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MATCH THE KIND OF RNA WITH ITS DESCRIPTION: (You can use them MORE THAN ONCE!) ______ Carries the DNA code from nucleus to cytoplasm ______ Made by the nucleolus A. messenger-RNA ______ Adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain B. transfer-RNA ______ Combines with proteins to form ribosomes C. ribosomal-RNA ______ Has a CODON region ______ Has an ANTICODON region * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MATCHING: Match the vocab word with its definition. ______ DNA that is spread out in the nucleus of a non-dividing cell so the code can be read ______ DNA that is scrunched up into bundles in a dividing cell ______ Sequence of DNA that is expressed in the final protein ______ Nitrogen base made with only one ring ______ Sequence of DNA which is cut out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes ______ Beadlike structure formed by coiling DNA around histone proteins that pack together to form chromosomes ______ A virus that infects bacteria ______ Nitrogen base made with 2 rings A. INTRON B. EXON C. NUCLEOSOME D. CHROMOSOME E. CHROMATIN F. BACTERIOPHAGE G. PURINE H. PYRIMIDINE * MATCH THE PARTS IN THE DIAGRAM WITH THE CORRECT LABEL _____ RIBOSOME _____ NUCLEUS _____ MESSENGER RNA _____ ANTICODON _____ AMINO ACID _____ CODON _____ TRANSFER RNA * * * * * * * * * * * * * * USE THE FOLLOWING DNA SEQUENCE TOMAKE A COMPLIMENTARY DNA STRAND A T T C G A T G C ___________________ USE THE FOLLOWING DNA SEQUENCE TO MAKE AN RNA MESSAGE A C T G G A T A C ___________________ USE the DECODING WHEEL to DETERMINE the AMINO ACID that corresponds to the m-RNA CODE GIVEN mRNA CODE UUC GCG CAC UGA AMINO ACID * MATCH THE MUTATION WITH ITS DESCRIPTION _____ One nucleotide in the code is replaced by another A. B. C. D. E. F. G. _____ Piece of DNA is added to the code _____ A piece of DNA is broken off and is lost _____ Extra copies of part of a chromosome are made POLYPLOIDY INVERSION INSERTION DUPLICATION TRANSLOCATION SUBSTITUTION DELETION _____ Complete set of chromosomes fails to separate resulting in 3N or 4N organisms _____ Piece of DNA breaks off and reattaches to another NON-homologous chromosome _____ Piece of DNA breaks off, flips, and reattaches so that it reads backwards * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * SHORT ANSWER: TELL one way DNA is DIFFERENT from RNA DNA RNA EXPLAIN WHY A FRAMESHIFT MUTATION AT THE BEGINNING OF A GENE IS MORE HARMFUL THAN AT THE END. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * BONUS: Name the woman scientist whose X-ray images helped Watson and Crick come up with the structure of DNA _____________________________ Look at the list of mutations in the matching section above. Which kind of mutation changes the hemoglobin code and causes sickle cell disease? _________________________ What is the “glue” that holds the 2 sides of the DNA “ladder” together? ________________________ Name __________________________ DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS TEST (2 points each) MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the answer that best completes the statement on the blank and the left. ______ Which of the following shows the sequence for the way information is transferred in cells? A. PROTEINS RNA DNA B. DNA PROTEINS RNA C. DNA RNA PROTEINS D. PROTEINS DNA RNA _____ The “sides of the ladder” in a DNA molecule are made up of ______________. A. nitrogen bases B. sugars and phosphates C. nitrogen bases and sugars D. phospholipids and proteins ______ DNA wraps around proteins called ________________ when it condenses into chromosomes. A. ribosomes B. promoters C. repressors D. histones ______ Adenine, A. B. C. D. guanine, thymine, and cytosine are all _______________________. nitrogen bases amino acids proteins phospholipids _____ The “rungs A. B. C. D. of the ladder” in a DNA molecule are made of _______________. phosphate nitrogen bases sugars amino acids _____ According to Chargaff’s rules, which nucleotide is always paired with ADENINE in a DNA molecule? A. Uracil B. Guanine C. Thymine D. Cytosine _____ Ribosomes are made out of __________________________. A. DNA and proteins B. phospholipids and proteins C. glycoproteins and lipids D. RNA and proteins _____ Where in the cell does transcription take place? A. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm B. in the nucleus C. in Golgi bodies D. on the nucleosomes _____ Where in the cell does translation take place? A. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm B. on the nucleosomes C. in Golgi bodies D. in the nucleus _____ The molecule that caused transformation in Griffith’s pneumonia/mouse experiment was _______. A. a protein B. a bacteriophage C. RNA D. DNA _____ The Hershey-Chase blender experiments and Avery’s enzyme digestion experiments helped to prove that _____________________ A. DNA is a double helix. B. pneumonia causes dead mice. C. the genetic material is made of DNA D. transformation is caused by proteins _____ The series of genes that control differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo are called _____________ genes. A. hox B. TATA C. enhancer D. lac operon ______ A group of genes in prokaryotes that operate together is known as a(n) ________________ A. codon B. operon C. operator D. gene group ______ The place where RNA polymerase binds to start transcribing a gene is called the ____________ A. anticodon B. repressor C. promoter D. operator _____ The lac operon is found in _______________________ A. eukaryotes B. prokaryotes _____ TATA boxes and enhancer sequences are found in _____________________ cells A. eukaryotes B. prokaryotes _____ The lac operon is normally turned OFF when _____________________________________, A. lactose is present B. the operator binds glucose C. RNA polymerase binds the promoter D. the repressor binds the operator _____ The presence of lactose turns the lac operon ON when ______________________________. A. the repressor binds the operator B. the repressor binds lactose instead of the operator C. anticodon binds the codon D. lactose binds the TATA box _____ The function of the TATA box is to ________________________________. A. bind the lac repressor B. help position the RNA polymerase C. turn on cell division genes D. edit introns * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * LABEL THE FOLLOWING: _____ Making a DNA copy of a DNA molecule (DNA DNA) A. B. C. D. _____ Making a complementary RNA message from a DNA code (DNA RNA) TRANSLATION TRANSCRIPTION REPLICATION TRANSFORMATION _____ Making a protein from an RNA message (RNA protein) ______ Process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by absorbing DNA from another strain of bacteria * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MATCH THE KIND OF RNA WITH ITS DESCRIPTION: (You can use them MORE THAN ONCE!) ______ Carries the DNA code from nucleus to cytoplasm ______ Made by the nucleolus A. messenger-RNA ______ Adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain B. transfer-RNA ______ Combines with proteins to form ribosomes C. ribosomal-RNA ______ Has a CODON region ______ Has an ANTICODON region * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MATCHING: Match the vocab word with its definition. ______ DNA that is spread out in the nucleus of a non-dividing cell so the code can be read ______ DNA that is scrunched up into bundles in a dividing cell ______ Sequence of DNA that is expressed in the final protein ______ Nitrogen base made with only one ring ______ Sequence of DNA which is cut out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes ______ Beadlike structure formed by coiling DNA around histone proteins that pack together to form chromosomes ______ A virus that infects bacteria ______ Nitrogen base made with 2 rings A. EXON B. INTRON C. BACTERIOPHAGE D. CHROMATIN E. CHROMOSOME F. NUCLEOSOME G. PYRIMIDINE H. PURINE * MATCH THE PARTS IN THE DIAGRAM WITH THE CORRECT LABEL _____ MESSENGER RNA _____ TRANSFER RNA _____ RIBOSOME _____ CODON _____ AMINO ACID _____ ANTICODON _____ NUCLEUS * * * * * * * * * * * * * * USE THE FOLLOWING DNA SEQUENCE TOMAKE A COMPLIMENTARY DNA STRAND C G A T G C A T T ___________________ USE THE FOLLOWING DNA SEQUENCE TO MAKE AN RNA MESSAGE G G A T A C A C T ___________________ USE the DECODING WHEEL to DETERMINE the AMINO ACID that corresponds to the m-RNA CODE GIVEN mRNA CODE UGA UUC CAC GCG AMINO ACID * MATCH THE MUTATION WITH ITS DESCRIPTION _____ One nucleotide in the code is replaced by another A. B. C. D. E. F. G. _____ Piece of DNA is added to the code _____ A piece of DNA is broken off and is lost _____ Extra copies of part of a chromosome are made INSERTION DUPLICATION POLYPLOIDY INVERSION DELETION TRANSLOCATION SUBSTITUTION _____ Complete set of chromosomes fails to separate resulting in 3N or 4N organisms _____ Piece of DNA breaks off and reattaches to another NON-homologous chromosome _____ Piece of DNA breaks off, flips, and reattaches so that it reads backwards * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * SHORT ANSWER: TELL one way DNA is DIFFERENT from RNA RNA DNA EXPLAIN WHY A FRAMESHIFT MUTATION AT THE BEGINNING OF A GENE IS MORE HARMFUL THAN AT THE END. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * BONUS: Name the woman scientist whose X-ray images helped Watson and Crick come up with the structure of DNA _____________________________ Look at the list of mutations in the matching section above. Which kind of mutation changes the hemoglobin code and causes sickle cell disease? _________________________ What is the “glue” that holds the 2 sides of the DNA “ladder” together? ________________________