* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are SNPs
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Haplogroup G-M201 wikipedia , lookup
“ From Genetics to Pharmacogenomics ”
What are SNPs ?
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
SNP Genetics
What are SNPs ?
ACGTTTGGATAC
TGCAAACCTATG
ACGTTTGTATAC
TGCAAACATATG
Single nucleotide polymorphisms consist of a single
change in the DNA code
SNPs occur with various allele frequencies. Those in
the 20-40% range are useful for genetic mapping.
Those at frequencies between 1% and 20% may be
used with candidate gene approaches. Usually bi-allelic.
Changes at 〈1% are called variants
What are the effects of SNPs ?
Where
Result
Effect
In coding
region
May be silent, o.g.,UUG→CUG, leu in both cases
sSNP
Usually no change in
phenotype
In coding
region
May change amino acid sequence, e.g., UUC→UUA,
phe to leu, Some characterize these as the least
common and most valuable SNPs, Many being
patented
cSNP
Phenotype change
(may be subtle
depending on amino
acid replacement and
position)
In coding
region
May create a "Stop"codon, e. g., UCA→UGA,
ser to stop
In coding
region
May affect the rate of transcription
(up-or down-regulate)
cSNP
Other
regions
No affect on gene products(7).
May act as genetic markers for multi-component
diseases. These are sometimes called anonymous SNPs
and are the most common.
rSNP
Phenotype change
Possible phenotype
Change
How many SNPs are there ?
It is estimated that the human genome contains between
3 million and 6 million SNPs spaced irregularly at
intervals of 500 to 1,000 bases.
The SNP Consortium estimates that as many as 300,000
SNPs may be needed to fuel studies.
100.000 or more SNPs may be required for complex
disease gene discovery
Applications
SNP Discovery
SNP Validation
- Fine Mapping
SNP Screening
- Testing
SNP Discovery
SNP Discovery refers to the initial identification of new
SNPs.
The established method is electrophoresis(DNA sequencing)
with subsequent data analysis. Some indirect Discovery
techniques (e.g., dHPLC, SSCP) only indicate that a SNP
(or other mutation) exists.
DNA sequencing of multiple individuals is used to determine
the point and type of polymorphism.
Low throughput, based on established DNA sequencing
analyses or collected data (also based on electrophoretic data)
SNP Validation
SNP Validation refers to genetic validation, the process
of ensuring that the SNP is not due to sequencing error
and that it is not extremely rear. This should not be
confused with assay, target or regulatory validation.
Confirmation of SNPs found in Discovery
Larger numbers of individual samples to get statistical
data on occurrence in the population
SNP Screening
SNP Screening refers to researchers running thousands of
genotypes (may SNPs or many individuals or both)
Thousands to hundreds of thousands of samples per day
Two different screening strategies
- Many SNPs in a few individuals
- A few SNPs in many individuals
Different strategies will require different tools
Important in determining markers for complex genetic states
SNP analysis costs are dependent on volume
Costs per assay are dependent upon the number of SNPs
being analyzed and the number of individuals.
Running cost
- one SNP in 100 individuals∼range $5∼$8/assay
- one SNP in 1,000 individuals∼range $3∼$5/assay.
- 1000 SNPs in 1000 individuals∼range $1.5~$3.00/assay.
- All these costs include the cost of the PCR step.
Future high through-put costs/assay will be driven toward
pennies per SNP.
What is a DNA Array ?
A collection of nucleic acid probes which are
attached to a surface in a predetermined grid
This grid is exposed to targets from a biological
sample and the complementary pairs are detected
("hybridization")
The complementary pairs are scored by software
What Good are DNA Arrays ?
Arrays
- nucleotide changes anywhere in a genome
- identity of and amount of unique mRNAs
- re-sequencing
Ideal for Screening large# SNPs:
Present formats not really a high throughput format
but by their massive parallelism they enable certain
types of analyses, e.g. global expression profiling or
genome wide SNP screening
DNA Arrays Are Valuable
Arrays allow massively parallel analysis for certain
applications this parallelism is enabling...i.e., global
expression profiling
For certain applications there may be labor savings..i.e.,
comparative sequencing
But...the present formats are not yet high throughput
technology Platform Extensions for SNP Screening in
Pharmaceuticals
Researcher determinants
Infrastructure:
- Lab. Instrument, labor & expertise
Investment:
- Start-up cost & running cost
Jobs:
- How big sample size ?
- How many SNPs ?
Best Choice
- Out-sourcing ?
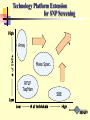
Technology Platform Extension
for SNP Screening
High
Array
Mass Spec.
RFLP
TaqMan
SBE
Low
Low
# of Individuals
High
Addendum
TSC I : The SNP Consortium
Pharmaceutical Partners:
AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.,
GlaxoWellcome PLC, Hoffmann-LaRoche, Hoechst
Marion Roussei, (now merged with RPR to form
Aventis), Merck, Pfizer lnc, Searle, SmithKline
Beecham PLC.
Academic Partners:
The Whitehead lnstitute at MIT, Wellcome Trust at
the Sanger Center,Stanford
TSC II : The SNP Consortium
At least $45 million ($3 million per pharmaceutical
company, $14 million form Wellcome Trust)
Reduction from %150 million in large part to the
efforts of Celera and NHGRI to sequence entire
genome.
What is happening now ?
Japanese SNP Project:
$ 5 Million over next two years to map 100K to 150K
SNPs. Probably concentrated at one site (U. Tokyo's
Human Genome Center)
Funded by Science & Technology Agency, Ministry of
Health & Welfare and private sector.






















![[edit] Use and importance of SNPs](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004266468_1-7f13e1f299772c229e6da154ec2770fe-150x150.png)




