Dissecting the Evolutionary Process of GENN
... This NN produces a classification error, just as a protein produces a phenotype within an organism. Function: In GE a lower classification error indicates higher fitness. Natural selection will work at the level of reproductive fitness, forcing changes in the heritable material of both biological or ...
... This NN produces a classification error, just as a protein produces a phenotype within an organism. Function: In GE a lower classification error indicates higher fitness. Natural selection will work at the level of reproductive fitness, forcing changes in the heritable material of both biological or ...
Minimum SNPs version 2043 user manual
... (Brisbane, Queensland, Australia) node of the Cooperative Research Centre for Diagnostics, with input from researchers at the University of Newcastle, Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. Minimum SNPs can only be obtained from www.ihbi.qut.edu.au/research/cells_tissue/phil_giffard/ ...
... (Brisbane, Queensland, Australia) node of the Cooperative Research Centre for Diagnostics, with input from researchers at the University of Newcastle, Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. Minimum SNPs can only be obtained from www.ihbi.qut.edu.au/research/cells_tissue/phil_giffard/ ...
Detection and analysis of disease-associated single nucleotide
... experimental phosphorylation binding sites and found 1,515 coding-region SNPs in the flanking phosphorylation binding sites with position -7 to +7. Ryu et al. [10] collected 33,651 protein-sequence variations from the SwissVariant database and predicted the effects of variants on phosphorylation bin ...
... experimental phosphorylation binding sites and found 1,515 coding-region SNPs in the flanking phosphorylation binding sites with position -7 to +7. Ryu et al. [10] collected 33,651 protein-sequence variations from the SwissVariant database and predicted the effects of variants on phosphorylation bin ...
Predicting Adaptive Phenotypes From Multilocus Genotypes in Sitka
... gradients. The removal of the population structure may thus result in overadjustment (false-negatives) for the effect of local adaptation to climate. Therefore, phenotype prediction was conducted both with and without an adjustment for population structure. For this analysis, 1500 regression trees w ...
... gradients. The removal of the population structure may thus result in overadjustment (false-negatives) for the effect of local adaptation to climate. Therefore, phenotype prediction was conducted both with and without an adjustment for population structure. For this analysis, 1500 regression trees w ...
IBDfinder and SNPsetter: tools for pedigree
... autozygous regions can still be a significant obstacle. For rapid gene identification, it may be desirable to integrate information from heterogeneous groups of affected individuals, both familial and isolated, under various assumptions of ancestry and locus heterogeneity, that are not amenable to f ...
... autozygous regions can still be a significant obstacle. For rapid gene identification, it may be desirable to integrate information from heterogeneous groups of affected individuals, both familial and isolated, under various assumptions of ancestry and locus heterogeneity, that are not amenable to f ...
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ectomycorrhizal mushroom
... mycorrhizal mushroom primarily associated with pine forests. However, little is known about its genetics and genomic variation, including SNP variation. To identify and analyse SNPs in T. matsutake, a genomic library was constructed and .72 000 nt were analysed from .200 random clones. Primers from ...
... mycorrhizal mushroom primarily associated with pine forests. However, little is known about its genetics and genomic variation, including SNP variation. To identify and analyse SNPs in T. matsutake, a genomic library was constructed and .72 000 nt were analysed from .200 random clones. Primers from ...
Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in human
... allowing organisms to accumulate SNPs in non-functional pseudogenes. The ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous amino acid changes are 2.80 and 2.76 for Chr 21 and 22 respectively, both higher than the corresponding numbers for exons (Table 2). Also, the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous changes wh ...
... allowing organisms to accumulate SNPs in non-functional pseudogenes. The ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous amino acid changes are 2.80 and 2.76 for Chr 21 and 22 respectively, both higher than the corresponding numbers for exons (Table 2). Also, the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous changes wh ...
A High Density Integrated Genetic Linkage Map of Soybean and the
... be the most abundant source of DNA polymorphisms in soybean (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). Despite being the most common molecular marker in soybean, the SNP frequency is relatively low compared to other cultivated crop species (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). The relatively low sequ ...
... be the most abundant source of DNA polymorphisms in soybean (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). Despite being the most common molecular marker in soybean, the SNP frequency is relatively low compared to other cultivated crop species (Hyten et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2003). The relatively low sequ ...
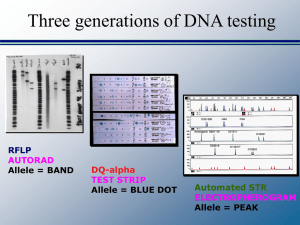
DNA Profile 911 - Bertino Forensics
... Without any instructions, ask the students to review the profile and look for anything that they might be able to interpret. a. Many students will notice the XX, XY in the electropherogram and note that gender of the sample was identified. Confirm the gender with the labels on the right for Mom, unk ...
... Without any instructions, ask the students to review the profile and look for anything that they might be able to interpret. a. Many students will notice the XX, XY in the electropherogram and note that gender of the sample was identified. Confirm the gender with the labels on the right for Mom, unk ...
[Full text/PDF]
... Step 2: Training and ranking all the SNP combinations included in the data following a cross-validation framework. After appropriate justification of covariates, ...
... Step 2: Training and ranking all the SNP combinations included in the data following a cross-validation framework. After appropriate justification of covariates, ...
Linkage Disequilibrium and Inference of Ancestral
... high LD, but there remain regions of unusually low LD that will require large numbers of SNPs for coverage by LD mapping. In addition to the quantification and mapping of genomic regions of high and low LD, it is essential that the degree of heterogeneity in LD among human populations be understood ...
... high LD, but there remain regions of unusually low LD that will require large numbers of SNPs for coverage by LD mapping. In addition to the quantification and mapping of genomic regions of high and low LD, it is essential that the degree of heterogeneity in LD among human populations be understood ...
Trilateral Project WM4 Report on comparative study on Examination
... 1. An isolated nucleic acid molecule selected from the group consisting of haplotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 wherein each of haplotypes 1-5 comprises SEQ ID NO: 1 with the exception that the nucleotides specified in the table below for each haplotype are present at the corresponding position within SEQ I ...
... 1. An isolated nucleic acid molecule selected from the group consisting of haplotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 wherein each of haplotypes 1-5 comprises SEQ ID NO: 1 with the exception that the nucleotides specified in the table below for each haplotype are present at the corresponding position within SEQ I ...
Online resources for genetic variation study-Part One
... identify the location of the variant. Haplotype: A particular combination of alleles along a chromosome that tends to be inherited as a unit. http://www.hapmap.org/originhaplotype.html ...
... identify the location of the variant. Haplotype: A particular combination of alleles along a chromosome that tends to be inherited as a unit. http://www.hapmap.org/originhaplotype.html ...
Word - NIEHS SNPs Program
... the top of the image represent the SNPs (numbered along a reference sequence used in re-sequencing the gene). The SNPs here are sorted according to samples with the same haplotype. The numbers on the side of the image represent the sample ID. Each square represents an individual sample’s allele: com ...
... the top of the image represent the SNPs (numbered along a reference sequence used in re-sequencing the gene). The SNPs here are sorted according to samples with the same haplotype. The numbers on the side of the image represent the sample ID. Each square represents an individual sample’s allele: com ...
Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Mapping
... SNPs have two advantages over conventional marker mutations. First, unlike conventional visible markers, SNPs in general have no phenotype, allowing a mutation of interest to be scored in a neutral phenotypic background. As a result, many markers can be assayed simultaneously, without worrying about ...
... SNPs have two advantages over conventional marker mutations. First, unlike conventional visible markers, SNPs in general have no phenotype, allowing a mutation of interest to be scored in a neutral phenotypic background. As a result, many markers can be assayed simultaneously, without worrying about ...
SNP
... Polymorphisms (SNPs) the variant sequence type has a frequency of at least 1% in the population. high frequency of SNPs in human genome: estimated ~1 SNP/Kb. ...
... Polymorphisms (SNPs) the variant sequence type has a frequency of at least 1% in the population. high frequency of SNPs in human genome: estimated ~1 SNP/Kb. ...
Methods Five 1536-SNP GoldenGate assays (Fig. 1) Three pilot
... from 267,439 clones and was made using CAP3 [37] with parameter settings p = 75, d = 240, f = 250, h = 90. These relatively relaxed settings result in alleles being combined into a single contig more often than with relatively stringent settings of p = 95, d = 60, f = 100, h = 50 which were used for ...
... from 267,439 clones and was made using CAP3 [37] with parameter settings p = 75, d = 240, f = 250, h = 90. These relatively relaxed settings result in alleles being combined into a single contig more often than with relatively stringent settings of p = 95, d = 60, f = 100, h = 50 which were used for ...
Subset-Based Ant Colony Optimisation for the Discovery of Gene
... Many examples of GWAS data analysis exist in the literature that demonstrate the association between a single SNP and disease. There are known single associations for Type II diabetes and traits such as height for instance. However, there is a considerable amount of missing heritability, for example ...
... Many examples of GWAS data analysis exist in the literature that demonstrate the association between a single SNP and disease. There are known single associations for Type II diabetes and traits such as height for instance. However, there is a considerable amount of missing heritability, for example ...
SNP discovery
... reads were generated for the 27 apple accessions (Table 1). (2). The total sequences obtained among the accessions ranged from 6 to 60 millions (due to differences in cluster density) (3). A total of 10,915,756 SNPs was detected using SoapSNP of which 2,113,120 SNPs (19.5%) passed the filtering crit ...
... reads were generated for the 27 apple accessions (Table 1). (2). The total sequences obtained among the accessions ranged from 6 to 60 millions (due to differences in cluster density) (3). A total of 10,915,756 SNPs was detected using SoapSNP of which 2,113,120 SNPs (19.5%) passed the filtering crit ...
SNP Discovery and Genotyping Workshop (PowerPoint)
... Haplotypes in SeattleSNPs • >200 genes re-sequenced in inflammation response • 2 populations: European- and African-Americans ...
... Haplotypes in SeattleSNPs • >200 genes re-sequenced in inflammation response • 2 populations: European- and African-Americans ...
computational tools to detect single nucleotide polymorphism
... very small amounts of DNA are to be detected, the ...
... very small amounts of DNA are to be detected, the ...
Haplogroup G-M201
In human genetics, Haplogroup G (M201) is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of Haplogroup GHIJK, the other being Haplogroup HIJK. Haplogroup G has an overall low frequency in most populations but is widely distributed within ethnic groups of the Old World in the Middle East, Europe, Caucasus, South Asia, western and central Asia, and northern Africa.








![[Full text/PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008788999_1-38423c6451c3d81c8111681229069d71-300x300.png)