* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
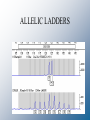
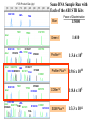
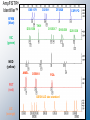
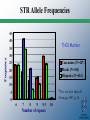
Three generations of DNA testing RFLP AUTORAD Allele = BAND DQ-alpha TEST STRIP Allele = BLUE DOT Automated STR ELECTROPHEROGRAM Allele = PEAK How do they fare? DQ-alpha RFLP Discriminating power □ □ Sensitivity □ Technical artifacts □ Speed □ Mixtures ٱDatabasing Discriminating power Sensitivity Technical artifacts Speed □ Mixtures □ Databasing STR Discriminating power Sensitivity □ Technical artifacts Speed □ Mixtures Databasing RFLP technology What we would like for them to look like. What they often look like. Incomplete digest Available Kits for STR Analysis • Kits make it easy for labs to just add DNA samples to a pre-made mix • 13 CODIS core loci – Profiler Plus and COfiler (PE Applied Biosystems) – PowerPlex 1.1 and 2.1 (Promega Corporation) • Increased power of discrimination – CTT (1994): 1 in 410 – SGM Plus™ (1999): 1 in 3 trillion – PowerPlex ™ 16 (2000): 1 in 2 x 1017 Overview of Steps Involved in DNA Typing TPOX TH01 D3 AMEL D5 VWA D7 D13 D21 D8 CSF D16 D18 FGA Penta D Penta E Blood Stain PCR Amplification with Fluorescent STR Kits and Separation with Capillary Electrophoresis DNA Quantitation using Slot Blot Genotyping by Comparison to Allelic Ladder REPEATED DNA • Satellite DNA – Around chromosomal centromere – Long repeats can be 100s to 1000s bp long • Minisatellite DNA – VNTR – Medium repeats 10 to 100 bp long • Microsatellites – STR – Short repeats 2 to 6 bp long SHORT TANDEM REPEATS • Easy to amplify • Both heterozygote alleles amplify well • Number of repeats highly variable • Good for identification • Many different sites STR NOMENCLATURE • Simple Repeats – Identical length and sequence • agat agat agat agat agat • Compound Repeats – Two or more adjacent simple repeats • agat agat agat ttaa ttaa ttaa • Complex Repeats – Variable unit length & possible intervening seq • agat agat aggat agat agat ttaacggccat agat agat STR NOMENCLATURE • Microvariants – Alleles that contain incomplete units • TH01 9.3 • aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg - 10 • aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg aatg atg aatg aatg aatg - 9.3 STRs Used In Forensic Science • Need lots of variation - polymorphic • Overall short segments - 100-400 bp – Can use degraded DNA samples – Segment size usually limits preferential amplification of smaller alleles • Single base resolution – TH01 9.3 STRs Used In Forensic Science • TETRANUCLEOTIDE REPEATS – Narrow allele size range - multiplexing – Reduces allelic dropout (stochastic effects) – Use with degraded DNA possible – Reduced stutter rates - easier to interpret mixtures STR NOMENCLATURE • Use the 5’ to 3’ (Top) strand • Start with the first 5’ nucleotide in the repeat • Microvariants designated by decimal places – Number of complete repeats – Number of bases in incomplete repeat (9.3) • Allelic ladders used as reference – Contain all common alleles ALLELIC LADDERS • Artificial mixture of common alleles • Reference standards • Enable forensic scientists to compare results – Different instruments – Different detection methods • Allele quantities balanced • Produced with same primers as test samples • Commercially available in kits Allelic Ladder Formation Separate PCR products from various samples amplified with primers targeted to a particular STR locus Polyacrylamide Gel Combine Re-amplify Find representative alleles spanning population variation Profiler Plus Allelic Ladders VWA D3S1358 AMEL D8S1179 D5S818 FGA D21S11 D13S317 D18S51 D7S820 ALLELIC LADDERS THE 13 CODIS STR LOCI • November 1997 • Average random match probability is greater than 1in 1 trillion • US slower than UK in selection of loci for database THE 13 CODIS STR LOCI • Four categories • Simple repeats – TPOX, CSF1PO, D5S818, D13S317, D16S539 • Simple repeats w/ non-consensus alleles – TH01, D18S51, D7S820 • Compound repeats w/ non-consensus alleles – vWA, FGA, D3S1358, D8S1179 • Complex repeats – D21S11 Commercial STR Kits • Applied Biosystems • AmpFlSTR Profiler Plus – 5-FAM (BLUE) – Joe (GREEN) – NED (YELLOW) Amelo • AmpFlSTR Cofiler vWA D3S1358 D8S1179 D5S818 FGA D21S11 D13S317 D18S51 D7S820 – 5-FAM (BLUE) – Joe (GREEN) D16S539 D3S1358 – NED (YELLOW) Amelo TH01 TPOX CSF1PO D7S820 Commercial STR Kits • Promega Corporation • PowerPlex 1.1 – Fluorescein (Blue) D5S818 D13S317 – TMR (Yellow) vWA TH01 D7S820 TPOX D16S539 CSF1PO • PowerPlex 2.1 – Fluorescein (Blue)D3S1358 – TMR (Yellow) Amelo TH01 vWA D21S11 D8S1179 D18S51 TPOX Penta E FGA Same DNA Sample Run with Each of the ABI STR Kits PCR Product Size (bp) D3S1358 vWA FGA Blue TH01 Amel Power of Discrimination CSF1PO TPOX Green I TH01 D13S317 D3S1358 Amel D5S818 vWA TPOX FGA D8S1179 vWA D13S317 Amel D3S1358 D5S818 D21S11 FGA D3S1358 Amel TH01 TPOX D3S1358 vWA Amel D8S1179 TH01 D21S11 D19S433 1:5000 1:410 CSF1PO D7S820 D7S820 D18S51 D7S820 CSF1PO D16S539 D16S539 D18S51 D2S1338 FGA Profiler 1:3.6 x 109 Profiler Plus 1:9.6 x 1010 COfiler 1:8.4 x 105 SGM Plus 1:3.3 x 1012 AmpFlSTR® Identifiler™ D8S1179 6FAM (blue) D3S1358 D7S820 D21S11 TH01 D13S317 D16S539 VIC (green) TPOX D19S433 D18S51 VWA NED (yellow) AMEL D5S818 FGA PET (red) GS500 LIZ size standard LIZ (orange) CSF1PO D2S1338 Genotyping by Comparison to Allelic Ladder PCR Amplification with Fluorescent STR Kits and Separation with Capillary Electrophoresis TPOX TH01 CSF D7 D16 D3 D5 AMEL VWA D13 D21 D8 D18 FGA Penta D Penta E Electropherogram STR LOCI ALLELES • CSF1PO – – – – c-fms proto-oncogene Chromosome 5 AGAT repeat 6 to 15 repeats • FGA – – – – alpha fibrinogen locus Chromosome 4 CTTT repeat 15 to 51.2 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • TH01 – – – – – TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE Chromosome 11 TCTA repeat (Bottom strand) 4 to 11 repeats Common microvariant 9.3 • TPOX – – – – THYROID PEROXIDASE Chromosome 2 AATG repeat 6 to 13 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • vWA – – – – von Willebrand Factor Chromosome 12 TCTA with TCTG repeat 10 to 22 repeats • D3S1358 – Chromosome 3 – AGAT with AGAC repeat – 12 to 20 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • D5S818 – Chromosome 5 – AGAT repeat – 7 to 16 repeats • D7S820 – – – – Chromosome 7 GATA repeat Some Microvariants 6 to 15 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • D8S1179 – Chromosome 8 – TCTA repeat with TCTG in alleles >13 – 7 to 19 repeats • D13S317 – Chromosome 13 – GATA repeat – 7 to 15 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • D16S539 – Chromosome 16 – AGAT repeat with TCTG in alleles >13 – 8 to 15 repeats • D18S15 – – – – Chromosome 18 AGAA repeat Some x.2 Microvariants 8 to 27 repeats STR LOCI ALLELES • D21S11 – – – – – – – Chromosome 21 TCTA repeat with TCTG Some x.2 Microvariants 24 to 38 repeats Over 70 reported alleles Fine differences must be sequenced 4 alleles are designated as 30 repeats 13 CODIS Core STR Loci with Chromosomal Positions TPOX D3S1358 D8S1179 D5S818 FGA CSF1PO TH01 VWA D7S820 AMEL D13S317 D16S539 D18S51 D21S11 AMEL Position of Forensic STR Markers on TPOX Human D3S1358 Chromosomes D5S818 D2S1338 FGA CSF1PO D8S1179 D13S317 D16S539 VWA D7S820 13 CODIS Core STR Loci Penta E TH01 AMEL Sex-typing D19S433 D18S51 D21S11 Penta D AMEL An Example Forensic STR Multiplex Kit AmpFlSTR® Profiler Plus™ Kit available from PE Biosystems (Foster City, CA) 200 bp Color Separation 100 bp Size Separation D3 A vWA D8 D5 FGA 300 bp 400 bp 5-FAM (blue) D21 D18 JOE (green) D13 D7 NED (yellow) ROX (red) GS500-internal lane standard 9 STRs amplified along with sex-typing marker amelogenin in a single PCR STR Allele Frequencies 45 40 TH01 Marker Frequency 35 30 Caucasians (N=427) Blacks (N=414) Hispanics (N=414) 25 20 15 10 *Proc. Int. Sym. Hum. ID 5 (Promega) 1997, p. 34 0 6 7 8 9 9.3 Number of repeats 10 Human Identity Testing with Multiplex STRs AmpFlSTR® SGM Plus™ kit Two different individuals DNA Size (base pairs) amelogenin D19 D3 D8 TH01 VWA D21 D16 D18 D2 FGA probability of a random match: ~1 in 3 trillion amelogenin D3 D19 D8 VWA TH01 Results obtained in less than 5 hours with a spot of blood the size of a pinhead D16 D21 FGA D18 Simultaneous Analysis of 10 STRs and Gender D2 Exclusions don’t require numbers Matches do require statistics Hardy - Weinberg Equilibrium A1A1 A1A2 A2A2 p12 2p1p2 p22 freq(A1) = p1 freq(A2) = p2 A1 p12 A1 A 1 A 1 p1p2 A2 A 1 A 2 A2 p1p2 A1A 2 p22 A2 A 2 (p1 + p2 )2 = p12 + 2p1p2 + p22 A Hardy-Weinberg Population • • • • LARGE POPULATION NO NATURAL SELECTION NO MUTATION NO IMMIGRATION / EMIGRATION • RANDOM MATING Estimate genotype frequency: 1. Frequency at each locus 2. Frequency across all loci Product Rule Product Rule • The frequency of a multi-locus STR profile is the product of the genotype frequencies at the individual loci ƒ locus1 x ƒ locus2 x ƒ locusn = ƒcombined Criteria for Use of Product Rule Inheritance of alleles at one locus have no effect on alleles inherited at other loci Population database • Look up how often each allele occurs at the locus in a population (the “allele” frequency) ProfIler Plus Item D3S1358 vWA Q1 16,16 15,17 FGA D8S1179 D21S11 D18S51 D5S818 D13S317 D7S820 21,22 13,13 29,30 16,20 8,12 12,12 8,11 CoFIler Item Q1 D3S1358 16,16 D16S539 10,12 TH01 8,9.3 TPOX CSF1P0 9,10 12,12 D7S820 8,11 D3S1358 = 16, 16 (homozygote) Frequency of 16 allele = ?? D3S1358 = 16, 16 (homozygote) Frequency of 16 allele = 0.3071 When same allele: Frequency = genotype frequency (p2) (for now!) Genotype freq = 0.3071 x 0.3071 = 0.0943 ProfIler Plus Item D3S1358 vWA Q1 16,16 15,17 FGA D8S1179 D21S11 D18S51 D5S818 D13S317 D7S820 21,22 13,13 29,30 16,20 8,12 12,12 8,11 CoFIler Item Q1 D3S1358 16,16 D16S539 10,12 TH01 8,9.3 TPOX CSF1P0 9,10 12,12 D7S820 8,11 VWA = 15, 17 (heterozygote) Frequency of 15 allele = ?? Frequency of 17 allele = ?? VWA = 15, 17 (heterozygote) Frequency of 15 allele = ?? Frequency of 17 allele = ?? VWA = 15, 17 (heterozygote) Frequency of 15 allele = 0.2361 Frequency of 17 allele = 0.1833 When heterozygous: Frequency = 2 X allele 1 freq X allele 2 freq (2pq) Genotype freq = 2 x 0.2361 x 0.18331 = 0.0866 Overall profile frequency = Frequency D3S1358 X Frequency vWA 0.0943 x 0.0866 = 0.00817 What if… We encounter alleles not represented in the population database… …or alleles that are extremely rare in the database??? Where the random match probability is the sum of the squares of the observed phenotype/genotype frequencies in a database, The Power of Exclusion of a genetic locus is based on the 1 – the sum of squares of all the expected phenotypes/genotypes! These measures tell us two things about our markers and databases: Power of Discrimination – how powerful our loci are at individualizing Power of Exclusion – how powerful our marker panel is at excluding particular genotypes FBI’s CODIS DNA Database Combined DNA Index System • Launched October 1998 • Used for linking serial crimes and unsolved cases with repeat offenders • Links all 50 states • Requires >4 RFLP markers and/or 13 core STR markers • Current backlog of > 600,000 samples As of June, 2004 • Total profiles = 1,857,093 • Total forensic profiles = 85,477 • Total convicted offender = 1,771,616