* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
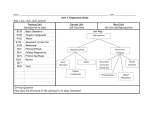
Cell Barriers and Transport 7-3 & more Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Plasma (Cell) Membrane Thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its environment Allows nutrients into the cell Allows waste to leave the cell Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Selective Permeability Some things can go through, while others cannot. The plasma membrane, with its embedded molecules, controls this. Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane is composed of the phospholipid bilayer. A phospholipid means: a hydrophilic phosphate group. two hydrophobic fatty acid chains Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipid bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in the membrane. Other Components Proteins Cholesterol Carbohydrates Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Proteins Transmit signals inside the cell Act as a support structure Provide pathways for larger substances to enter and leave the cell Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Cholesterol Prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 The Plasma Membrane Carbohydrates Attached to embedded proteins Identify chemical signals Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Passive Transport Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration without using energy Three Modes of Passive Transport Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Diffusion Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration Diffusion Initial Conditions Low High High Low Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Diffusion is controlled by Temperature Pressure Concentration Dynamic Equilibrium When diffusion of material into the cell equals diffusion of material out of the cell Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Diffusion in a Cell Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Facilitated Diffusion Movement of materials across the plasma membrane using proteins https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IX-kLh34KcQ Aquaporins – protein channels that allow water to flow across the cell membrane Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Two types of transport proteins: Channel Proteins Carrier Proteins Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Osmosis Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Three Types of Solutions • Isotonic • Hypotonic • hypertonic Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Isotonic Solution Water and dissolved substances diffuse into and out of the cell at the same rate. Plant Cell Blood Cell 11,397x Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Hypotonic Solution Solute concentration is higher inside the cell. Water diffuses into the cell. BLOWS UP the cell. Plant Cell Blood Cell 13,000x Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Hypertonic Solution Solute concentration is higher outside the cell. Water diffuses out of the cell. SHRINKS the cell. Plant Cell Blood Cell 13,000x 7.3 Cellular Transport: Passive Transport Plant cells in a hypertonic solution will plasmolyze. Plasmolysis: when the cell membrane peels off of the cell wall and the vacuole collapses when placed in a hypertonic environment http://ctle.hccs.edu/biologylabs/GB1/04Diffusion/04DiffusionIndex.html Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Active Transport Active Transport Movement of particles across the cell membrane using energy Three kinds: Molecular transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Active Molecular Transport Active Transport Using Carrier Proteins • Usually used to transport molecules against the concentration gradient Sodium-potassium pump http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapte r2/animation__how_the_sodium_potassium_pump_works.html Cellular Structure and Function 7.3 Cellular Transport: Active Endocytosis Process by which the cell surrounds and takes particles into the cell; two types: Phagocytosis Taking in large quantities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aWItglvTi Lc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z_mXDv ZQ6dU Pinocytosis Smaller quantities; more like taking little “sips”, or a “pinch”. 7.3 Cellular transport: Active Exocytosis • Secretion of material out of the plasma membrane – Waste vescicle fuses with cell membrane and releases particles – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U9pvm_4-bHg 7.3 Cellular Transport • What about plants? How do they “exocytose”? • They don’t. • Wastes and toxins get stored in their vacuoles. • What about food coming in? • They make their own, of course! • Is the cell wall selectively permeable? • No. Substances pass easily through rigid holes in the cell walls. 7.4 Cell Specialization • What types of organisms have specialized cells? • Multicellular ones • What are the levels of cellular organization? • Cells; similar cells work together to form… • Tissues; different tissues work together to form… • Organs; organs work together to form… • Organ systems, which work together to form… • An organism!