* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PCDU Seminar Myriam Murillo 11 November 2015
Survey
Document related concepts
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
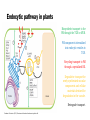
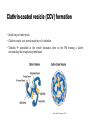
Endocytosis PCDU Seminar Myriam Murillo 11 November 2015 Content Endocytosis functions Endomembrane system Clathrin-mediated endocytosis Clathrin-independent endocytic pathway Endocytosis Functions • Engulfing external materials. • Regulating the abundance and distribution of plasma membrane (PM) proteins and lipids. • Occurs at the cell surface and involves the formation of membrane invaginations, followed by vesicle separation from the PM. • Removal or recycling of materials from the apoplasm or extracellular space. http://web.stanford.edu/group/virus/1999/jchow/endoem.jpg Endomembrane system • Synthesis, sorting, delivery and degradation of macromolecules within the cell. • Membrane-bound organelles that are connected either directly or through a series of transport vesicles. Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi complex and trans-Golgi network (TGN) Endosomes Lysosomes or vacuoles Endomembrane system MVB: Multivesicular Body CCV: Clathrin-coated Vesicle NCV: Non-coated Vesicle TGN: Trans-Golgi Netwrok Bassham & Contento. (2012). Structure and function of endosomes in plant cells. Endosomes • First point of fusion for endocytic vesicles, used to internalize extracellular materials. • Transport of materials. • Provide intermediate compartments where materials can be stored, sorted and then sent to a designated target. • Maintenance of the vacuole, cell growth and growth of specialized cells such as pollen tubes. • Platforms for signaling pathways. http://zmbe.uni-muenster.de/institutes/imv/schelhaas/schelres.htm Endocytic pathway in plants Biosynthetic transport to the PM through the TGN or MVB. PM components internalized into endocytic vesicles to TGN. Recycling transport to PM through a specialized RE. Degradative transport for newly synthesized vacuolar components and cellular materials destined for degradation in the vacuole. Retrograde transport. Bassham & Contento. (2012). Structure and function of endosomes in plant cells. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) Bednarek, Sebastian Y. (2013). Budding and braking news about clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Clathrin-coated vesicle (CCV) formation • Initial step of endocytosis. • Clathrin: major coat protein made up of a triskelion. • Triskelia assembled at the vesicle formation sites on the PM forming a lattice surrounding the invaginating membrane. Sigma Aldrich Company. (2015) CME mechanism 1. Binding of heterotetrameric adaptor protein 2 (AP-2) complex/clathrin to the PM. 2. Cargo recognition/recruitment. 3. Vesicle maturation. 4. Scission. 5. Dissociation. http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/107466/fpls-05-00408-HTML/image_m/fpls-05-00408-g004.jpg Adaptor protein 2 (AP-2) complex * Required for auxin transport, brassinosteroid signaling and cellulose metabolism. Bednarek, Sebastian Y. (2013). Budding and braking news about clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Cargo recognition motifs • Ubiquitination post-translational modification, which results in the covalent linkage of an ubiquitin molecule to a lysine residue on a target protein. At PM, cargo molecules can be ubiquitinated (sorting signal for internalization). Cargo molecules PM Endosomes Numerous cellular locations Proteins destined for degradation internal vesicles of LEs. Proteins destined for recycling limiting outer membrane. Scission by Dynamin and dynamin-related proteins (DRPs) • Required for clathrin-mediated trafficking. • GTPases tubulate membranes. • Assembles into helical structures at the neck of clathrin-coated buds and constricts and pinches off the bud neck membrane. • DRP1 and DRP2 roles in CCV formation during endocytosis. http://www.endocytosis.org/Endocytosis/CCVAssembly.html DRP1A and DRP2B • Associated with clathrin at the PM. • Expressed together. • Cytokinesis co-localized on the leading edge of the forming cell plate. • Both begin to accumulate at the vesicle formation sites of the plasma membrane after the clathrin assembly and detach from there at the same time as or immediately after the clathrin disassembly. • Their molecular properties are different. http://www.cmri.org.au/Research/Research-Units/Cell-Cycle/For-Researchers Regulation of CME • Plant developmental processes: polar growth of root hair cells, cell-to-cell communication, establishment of root cell polarity, and other auxin-dependent processes. Salicylic acid (SA) Strigolactone Auxin Clathrin-independent endocytic pathway • Requires the integrity of sterol-rich membrane microdomains within the PM. • Flotillin: membrane associated protein. Localized to the PM and endosomal structures. • Formation of membrane microdomains, membrane invaginations, and vesicle budding. • Functions in seedling development. • Arabidopsis required for optimal growth and forms large endocytic vesicles in root cells. http://www.nmr.uni-konstanz.de/research.html Flot1 and Flot2 • Co-assembled facilitate compartmentalization and functional specialization within the membrane. • Interface between signaling receptors interacting with and modulating the cytoskeleton. • Controlled by tyrosine residue phosphorylation (kinases). Benjamin J. Nichols. (2011). The roles of flotillin microdomains-endocytosis and beyond. Models of flotillin function in endocytosis No conclusive experimental evidence ! Benjamin J. Nichols. (2011). The roles of flotillin microdomains-endocytosis and beyond.