* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Transport
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
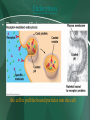
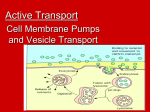
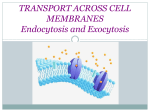
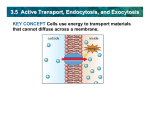
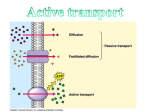
5.2 Active Transport Page 100 Standards • CLE 3210.1.5 - Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell. • SPI 3210.1.8 - Compare active and passive transport. • RLE 2010.2.1 - Recognize the importance of homeostasis as a survival mechanism. Active Transport • Active Transport: Requires the use of energy. • Why does it use energy? Energy is required to move something from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. • Example: The paramecium moving water out of it’s cell. Cell Membrane Pumps • Transport Proteins: Some transport proteins can move material from low concentration to high concentration. They are called “pumps.” • Example: Sodium Potassium Pump. Sodium Potassium Pump - Page 104 Vesicles: Active transport for large molecules • Endocytosis: the process by which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell • Exocytosis: he process by which a substance is released from the cell through a vesicle that transports the substance to the cell surface and then fuses with the membrane to let the substance out Endocytosis • Three Types of Endocytosis: – Pinocytosis The movement of fluids and small molecules into the cell in vesicles. – Phagocytosis The movement of large particles or whole cells into the cell in vesicles. – Receptor-mediated endocytosis (not in your book) When particles bind to receptor proteins it causes the cell to pull the bound particles into the cell. Exocytosis • Exocytosis: the process by which a substance is released from the cell through a vesicle that transports the substance to the cell surface and then fuses with the membrane to let the substance out • What gets exported this way? Any molecules packaged by the Golgi Apparatus and waste products. • In paramecium Review • Active Transport – Three main types: – “Protein Pumps” move things from low to high concentration. – Endocytosis – moving things into cell • Pinocytosis • Phagocytosis – Exocytosis – moving things out of the cell