* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell City
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
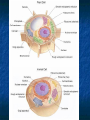
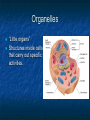
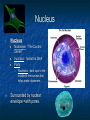
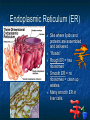
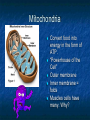
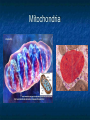
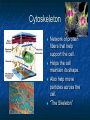
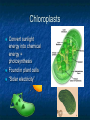
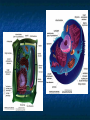
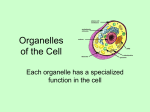
A TOUR OF THE CELL TEM of Animal Cell TEM of Plant Cell Organelles “Little organs” Structures inside cells that carry out specific activities. Nucleus 1. Nucleus Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA Parts: Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes Surrounded by nuclear envelope =with pores. Nuclear Membrane Pores Centriole Found in cytoplasm. Always two of them. Participate in cell division. Made of protein fibers. Cytoplasm Portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Ribosomes 2. Ribosomes Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Made of RNA Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Site where lipids and proteins are assembled and delivered “Roads” Rough ER = has ribosomes Smooth ER = no ribosomes = clean up wastes. Many smooth ER in liver cells. Golgi Apparatus Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the ER. “Shipping station” Structure = Pancake stacks. Vesicle Function in transporting substances out of the cell = “transport sack” Are released from the Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Small organelles filled with enzymes. Digest and break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. “Clean-up crew” Lysosome Animation http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student _view0/chapter5/animations.html# Mitochondria Convert food into energy in the form of ATP. “Powerhouse of the Cell” Outer membrane Inner membrane = folds Muscles cells have many. Why? Mitochondria Cytoskeleton Network of protein fibers that help support the cell. Helps the cell maintain its shape. Also help move particles across the cell. “The Skeleton” Cell Membrane Cell membrane = controls what enters and leaves the cell = selectively permeable “The Gates” Provides protection and support. Phospholipid bilayer Structures Found in Plants Only Chloroplasts Convert sunlight energy into chemical energy = photosynthesis Found in plant cells “Solar electricity” Vacuoles Saclike structures Store materials (water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates) “Storage room” Plants contain one large vacuole filled with liquid. Cell Wall Provides support and protection for the cell. Found outside the cell membrane. Comparing Plants and Animal Cells: Venn Diagram Plant Animal Let’s Practice! http://www.wisconline.com/objects/index_tj.asp?o bjid=AP11403 The Virtual Cell http://aimediaserver.com/studiodai ly/videoplayer/?src=harvard/harva rd.swf&width=640&height=520 Review Questions Why do cells that make a lot of protein have more Rough ER than cells that don’t? Why is it important that the cell’s digestive enzymes are enclosed inside the lysosome? Compare a cell to a factory, a city, or a school. Use analogies for each organelle.