* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on Mitosis
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
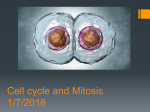
Notes on Mitosis Cell Division What are the benefits of reproducing asexually? It is fast. No partner is required - think of vast oceans, or of organisms that are not mobile. How would they be able to reproduce? Exact copies of parent. What are the stages in a cell cycle? 1. Interphase - this is when a cell grows and carries on it’s job. Late in this phase the chromosomes are duplicated (DNA replication) in preparation for cell division. This phase is the longest phase and it can also be broken down into 3 subphases; G1, S and G2. 2. Mitosis - which has 4 phases 3. Cytokinesis - the division of the cytoplasm and all organelles. 1 Of these stages where would the majority of a cell’s life be spent? The majority of a cell’s life is spent in INTERPHASE. This is where a cell grows and prepares for cell division. How many phases are there in mitosis? There are 4 phases. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. 2 What happens in Prophase? The longest phase of mitosis begins with duplicate chromosomes called sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are held together by a centromere. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintergrate. Centrioles form and move to opposite ends of the cell. Spindle fibers form. What happens in metaphase? The sister chromatids become attached to the spindle fibers. This allows the chromosomes to start aligning in the middle of the cell on what you might imagine to be the “equator”. I remember this phase for “M” middle. 3 What happens in Anaphase? The sister chromatids separate! Each half of the chromosome is pulled towards the opposite side of the cell. This ensures that each cell will have a complete copy of the chromosome. I remember this for “A” apart. 4 What happens in Telophase? The chromatids are now at opposite ends. Spindle fibers break down. The nucleolus reappears and a new nuclear envelope forms. A double membrane begins to form between the 2 new nuclei. I remember this for “T” tear apart. What is cytokinesis? This is the division of the cytoplasm and all the organelles. The end result is the formation of 2 separate cells. 5 What is the end result of mitosis? You get TWO IDENTICAL CELLS! 6