* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2008 Unit 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
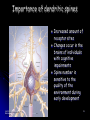
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
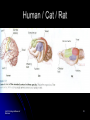
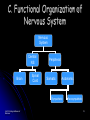
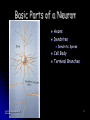
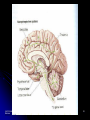
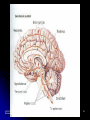
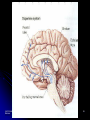
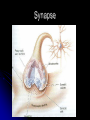
Victim of Nail-Gun Accident Survives a Delicate Operation LA Times May 6, 2004 Isidro Mejia – Dr. Rafael Quinonez Stumbled on scaffolding Fell on co-worker using a nail gun Several days of operations With X-rays and a camera scope Found the head of each nail and gently removed them Recovery Lost most his of Englishspeaking skills Full, if gradual, recovery predicted Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 1 III. Biological Bases of Behavior College Board - “Acorn Book” Course Description 8-10% Summary Outline A. Physiological Techniques B. Neuro-anatomy C. Functional Organization D. Neural Transmission E. Endocrine System F. Genetics Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 3 A. Physiological Techniques Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB) Lesioning also brain injury cases Electrical Recordings - EEG Brain Imaging Procedures CT Scan PET Scans MRI Scan Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 4 How can we teach about physiological techniques Brainstorming and Sharing Why is it important to cover this area? What’s important for the student to comprehend? Potential activities? Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 5 B. Neuroanatomy Brain Structure and Function Brainstorming and Sharing Why is it important to cover this area? What’s important for the student to comprehend? Potential activities? Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 6 Activities Neuroanatomy Brain Structure and Function Making Brain our of Play-do Making neuron models Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 7 Study Chart to Aid Learning About Brain Structure Martin Anderson Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 8 Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 9 Human / Cat / Rat Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 10 Right Brain v. Left Brain Opposite side body control Functional differences Split brain research Split visual field Split sensory fields Language differences Role of corpus callosum Misuses of concept Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 11 C. Functional Organization of Nervous System Nervous System Central NS Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Somatic Autonomic Sympathetic Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Parasympathetic 12 Brainstorming and Sharing Why is it important to cover this area? What’s important for the student to comprehend? Potential activities? Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 13 Central Nervous System Activity Simple Cognitive Mapping Students tend to pass over this diagram This activity is a quick and easy way to understand and review the chart Students make a blank diagram Students make post it notes of terms that go onto the diagram Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 14 D. Neural Transmission Neuronal Structure Glia – The Support System Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Action Potential All-or-none Response Refractory Period Electrical Transmission (Positive and Negative Ions) 15 Activities Chain Reaction Time Conduction of a Neuronal Impulse Wertheimer/ Boring (APA Activities Handbook 1 – Activity 84) Using class to measure simple and choice reaction times Right hand / Opposite hand Kasschau (APA Activities Handbook 1 – Activity 84) Several rows / message goes forward and to left or right How Fast are Your Nerves? Catching a falling meter stick under varied conditions Preferred hand v. opposite hand Sight / Sound / Touch Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 16 Basic Parts of a Neuron Axons Dendrites Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Dendritic Spines Cell Body Terminal Branches 17 Importance of dendritic spines Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Increased amount of receptor sites Changes occur in the brains of individuals with cognitive impairments Spine number is sensitive to the quality of the environment during early development 18 Classification of Neurons Based on Number of Neurites (Axons and Dendrites_ Unipolar Bipolar Multipolar Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Based on Dendrites (Shape of the dendritic tree) Stellate cells (starshaped) Pyramidal cells 19 Classification of Neurons Based on Connections Sensory Neurons Axons form synapses with muscles Interneurons Only connect with other neurons Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Based on Axon Length Golgi Type I Neurons Motor Neurons Dendrites on surface areas such as eye and skin Projection neurons Extend Golgi Type II Neurons Local circuit neurons 20 Classification Based on Neurontransmitter Amino acid and amine transmitters Generally each stored in and released by separate sets of neurons Choloneric Neurons Release acytelcholine (Ach) at their synapses Includes all motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 21 Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 22 Norepinephrine system Locus coeruleus in the pons (one on each side) Innervates almost every area of the brain One neuron can make more than 250,000 synapses (it can have one axon branch in the cerebral cortex and another in the cerebellar cortex) Involved in attention, arousal, sleep-wake cycles, learning, memory, anxiety, pain, mood, and brain metabolism. Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 23 Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 24 Seratonin system Mostly clustered in the nine raphe nuclei Lie to either side of the midline of the brain stem Each nucleus projects to different parts of the brain Those in the medulla innervate the spinal cord Modulate pain-related sensory signals Those in the pons and midbrain innervate most of the brain (as the Locus coeruleus neurons do) Part of the ascending reticular activation system Implicated in mood and emotional behavior Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 25 Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 26 Dopamine system Substantia nigra Produce and distribute dopamine Ventral tegmental area Facilitate the initiation of voluntary movements Degeneration of these cells produces Parkinson’s Disease Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Produce and distribute dopamine Innervates a part of the frontal cortex and parts of the limbic system Involved in a “reward system that assigns values to certain adaptive behaviors Implicated in psychiatric disorders 27 Glia support neuronal functions. Most glia are astrocytes which fill the spaces between neurons Glia envelop synaptic junctions restricting the flow of neurotransmitters Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 28 Myelinating Glia Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Insulate axons Help speed transmission Interrupted by nodes of Ranvier 29 Neurotransmitters (See handout – Major Neurotransmitter Chart Amines Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine Serotonin Amino Acids Peptides Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior GABA Glutamates CCK Endorphins (Enkephalins) Substance P 30 Synapse Synaptic Sites E. Endocrine System Endocrine (glands) Adrenal Glands Exocrine (ducts) Hormones Thyroid Gland Insulin, glucagon Testes, Ovaries Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior ACTH - adrenocorticotropic hormone Pancreas Thyroxine Pituitary Gland Epinephrine, norepinephrine Testosterone, estrogen 33 F. Genetics Dominant Traits Recessive Traits Genotypes Phenotypes Possible gene combinations Observable result Chromosomes and Chromosomal Abnormalities (23/23) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 34 How Different are We? PHENOTYPE QUESTIONNAIRE Non -blue eyes Straight hair Free earlobes Bent little finger PTC taster Widow’s Peak Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior Blue eyes Non-straight hair Attached earlobes Straight little finger Non-PTC taster Straight hair line 35 Phenotype Chart Free earlobes Straight Hair Attached earlobes Non-Blue Eyes Free earlobes Non-straight Hair Attached earlobes Free earlobes Straight Hair Attached earlobes Blue eyes Free earlobes Non-straight Hair Attached earlobes Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior 36