* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9th CBSE {SA - 1} Revision Pack Booklet-5
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
Revision Question Bank
Fundamental Unit of Life
1.
What are the main functions of each of the following cell components?
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Chromosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Ribosome
(e) Nucleus
(f) Mitochondria
Sol.
(a) Plasma membrane It acts as a semipermeable membrane and allows only
selective substances to pass through it.
(b) Chromosomes To carry hereditary characters from parents to offsprings, i.e., from
one generation to another.
(c) Lysosomes They act as 'digestive bags' which fight against any infection inside the
cell.
(d) Ribosomes They help in protein synthesis.
(e) Nucleus It controls all metabolic activities of the cell.
(f) Mitochondria It is the 'power house' of the cell, which stores and releases energy in
the form of ATP.
2.
Name the cell organelle, which is able to destroy a damaged cell.
Sol.
Lysosome is able to destroy a damaged cell,
3.
Give the term for the incipient nucleus of prokaryotes.
Sol.
Nucleoid is the Imn given for the incipient nucleus of prokaryoles.
4.
Give a scientific reason for the following:
(a) Inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded.
(b) Mitochondria are able to make some of their proteins.
Sol.
(a) The folds create a large surface area for ATP generating chemical reactions.
(b) Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes and hence can make their own
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
11
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
protein.
5.
A plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. What will happen? Will the cell burst? Why
or why not?
Sol.
When a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water enters into the cell and
cytoplasm will expand. However, the plant cell will not burst due to rigid cell wall.
6.
Name the cell organelles, which are called 'suicide bags' and 'power-house' of the cell.
Why are they so called? Give reason.
Sol.
Lysosomes are called 'suicide bags' of the cell as they can digest the entire damaged or
dead cell containing them.
Mitochondria are called 'power house' of the cell as they are sites for synthesis of energy
rich ATP (Adenosine Triphosphale) molecules by cellular respiration.
7.
Name the three major functional regions of cells. Briefly mention the component of each.
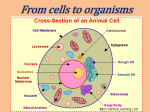
Draw a labeled diagram of a plant cell.
Sol.
All cells vary in their shape, size and activities and have three major functional regions,
viz., plasma membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
Plasma membrane or Cell membrane This is the outermost covering of the cell that
separates the contents of the cell from its external environment. Plasma membrane is a
living, thin, delicate, elastic, selectively permeable membrane made up of proteins and
lipids and is present in both plant and animal cells.
Functions of plasma membrane
(i) It is selectively permeable membrane.
(ii) It regulates the movement of ions in and out of the cell.
Nucleus Robert Brown in 1831 discovered the nucleus in the cell. Nucleus is the
largest cell structure. It is a spherical or oval prominent .structure, usually located in the
centre of the cell. Nucleus has the following important parts
(i) Nuclear membrane It is a double layered membrane, which separates nucleus from the
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
12
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm It is a homogeneous and granular dense fluid present inside the nucleus,
in which chromalin and nucleolus are suspended.
(iii) Chromatin material It consists of long, coiled network of thread-like structures. The
chroma tin material is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which is responsible for
storing and transmitting the hereditary information from one generation to the other.
(iv) Nucleolus It is more or less round structure found inside the nucleus.
Cytoplasm It is the Quid content of the cell, which is present between the plasma
membrane and the nuclear envelope. It contains various cell organelles which perform
different functions of the cell.
8.
What are lysosomes, peroxisomes and centrosomes? Write their functions.
Sol.
Lysosomes They are single-membraned small vesicular structures found in the
cytoplasm of all the eukaryolic cells except mammalian RBC's. They contain enzymes and
are formed by Golgi apparatus.
Functions They are involved in intracellular digestion of foreign food or microbes and
are also involved in aulolysis or self-digestion of cells after their death.
Peroxisomes They are found in photosynthetic cells of plants, liver and kidney cells of
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
13
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
the vertebrates bounded by a unil membrane and contain two types of oxidalive enzymes,
oxidasc and catalase.
Functions These are involved in removal of toxic substances by oxidative reactions. In
plant cells, these also help in photorespiration.
Centrosomes A centrosome is a light microscopic organelle formed of two darkly
coloured granules called centrioles surrounded by a transparent cytoplasmic area called
centrosphere. It lies near the nucleus.
Functions Centrosome helps in cell division in animal cells. They also help in the
formation of cilia and flagella of the cells.
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
14
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
Chapter Test {Fundamental Unit of Life}
M: Marks: 30
1.
M: Time: 40 Min.
Name the two nucleic acid present in the cell.
[1]
Sol.
DNA — Deoxyribonucleic Acid
RNA —Ribonucleic Acid
2.
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
[1]
Sol.
Proteins in RER and lipids in SER.
3.
What will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a hypotonic solution?
[1]
Sol.
It will swell due to entry of water by the process of osmosis.
4.
Write two differences between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
[3]
Sol.
Difference between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell are
S. No. Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cell
(i) Nuclear region is
Nuclear region is
not well defined well defined and
due to absence of surrounded by
nuclear membrane,
nuclear membrane.
(ii) Membrane bound Membrane bound
cell organelles are cell organelles are
absent. present.
5.
What will happen to a plant cell, if it is kept in sugar solution?
[2]
Sol.
(a) Sclerenchyma, mainly sclereids (stone cells).
(b) Lignin is deposited in the walls of sclerenchyma cell/tissue.
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
15
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
6.
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
Name the three major functional regions of the cells. Briefly mention the component of
each and explain the function of each.
(a) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured
components?
[3]
Sol.
7.
Write the main function of each of the following cell components.
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Chromosomes
(d) Ribosomes
(e) Lysosomes
(f) Golgi apparatus
[3]
Sol.
(a) It regulates entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents
movements of some other materials.
(b) Also known as power house of the cell. Cellular respiration takes place in this
organelle resulting in release of energy.
(c) Chromosomes contain genes. Genes are segments of DNA and are bearers of heredity
characters. These are responsible for inheritance.
(d) Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis in a cell.
(e) These are also known as suicide bag of the cell. They contain digestive
enzymes.
They kill bacteria and remove worn out cell organelles.
(f)Golgi apparatus or Golgi body are the secretory organelle of the cell. They are also
involved in formation of lysosomes.
8.
What is cell theory and who proposed this theory? What modification Virchow made in
this theory?
[3]
Sol.
Cell theory was presented by two biologists, Schleiden and Schwann. According to this
(i) cell is the basic unit of structure.
(ii) cell is the basic unit of function.
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
16
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
Rudolf Virchow further modified the cell theory by stating that all cells arise from
pre-existing cells.
9.
Why plant cell contain large size vacoule, as compared to animal cell?
[2]
Sol.
In plant cell, vacuole plays very important role as they store toxic metabolic byproduct
or end product and provide turgidity and rigidity to plant cell.
So, they are
comparatively larger in size than animal cell
10. What is the difference between the plasma membrane and cell wall? Give
[3]
the functions of each one.
Sol.
The differences between plasma membrane and cell wall are given below
S.No.
(i)
Plasma Membrane
It is made up of
lipids and proteins.
Cell Wall
It is made up of
mostly cellulose.
(ii)
It is living.
It is dead.
(iii)
Present in both plant
Found exclusively in
and animal cells. plant cells.
Cell membrane or plasma membrane regulates entry and exit out of molecules in and
out of the cell. Cell wall provides structural strength to the plants.
11. (a) What are chromosomes? Write their chemical composition,
[3]
(b) What is the relationship between chromatin material and chromosomes.
Sol.
(a) Chromosomes are rod-shaped structure present in nucleus. They contain
information for inheritance of features from parents to
next generation in the form of DNA. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and protein.
(b) When the cell is not dividing, DNA is present as part of chromatin material, which is
visible as entangled mass of thread-like structures. When the cell is about to divide, the
chromatin material gets organised into chromosomes and perform cell division.
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
17
Pioneer Education {The Best Way To Success}
IIT – JEE /AIPMT/NTSE/Olympiads Classes
12. Name the plastid involved in conversion of a green tomato to red.
[1]
Sol.
The conversion of chloroplast to chromoplast takes place when green tomato turns red.
13. Name a cell organelle found only in plant cell. Name its types and functions.
[3]
Sol.
Plastids are found only in plant cell.
They are of three types
(i) Leucoplasts
(ii) Chromoplasts
(iii) Chloroplasts
14. Which produces more severe burns : boiling water or steam at 100°C ?
[2]
Sol.
Steam at 100°C produces more severe burns because it contains greater amount of heat
than the boiling water at 100°C by an amount equal to latent heat of vaporisation.
www.pioneermathematics.com S.C.O. - 326, Sector 40–D, CHD. Phone: 9815527721, 4617721
18