* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
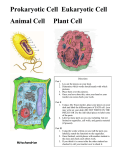
Cell Structure Organelles Cell Structure Notes: Getting started • Using your textbook on pages 73-81 label the structures on your handout. • Then as we go through the notes, cut and paste the appropriate organelle with your notes. Recall the Characteristics of Life • All Living things share the following: – – – – – – Cells Organization Energy use Homeostasis Growth/Development Reproduction 2 Levels of Organization • Molecular and Cellular • Macromolecules are organized into structures called organelles. Organelles working together make up a cell. • One cell has all it needs to carry out all life processes. – The organelles carry out all of the functions of life. How is a single, tiny little cell able to do so much? • Each organelle in the cell performs a specific function. • Remember, all cells have (prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells) – A cell membrane – DNA (genetic information) – cytoplasm • BIG IDEA: Only eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp04/0402001.html Title Page • Think of a drawing for your title page. Will you use an animal cell drawing with labels…what kind of drawing do you want to have for your catalog. (1 point) • Label the drawing (1 point) • Think of a name for your catalog of organelles (What analogy will you use for this catalog) (1 point) • Put your name, date and period on this page (1 point) • Finish for homework tonight, and study for your Lab 6 quiz tomorrow. Cell Membrane • The cell membrane is the boundary between the inside of the cell and the external environment. • Cells must acquire nutrients and get rid of wastes. • The membrane controls traffic of substances into/out of the cell. • Analogy: security guard 4 macromolecules make up organelles • Proteins, lipids (fats), carbohydrates, and nucleic acids • The cell membrane is mostly made of lipids (phospholipids) with some proteins as well. • All cells have cell membranes, but only some cells (plant/fungi/bacteria) have cell walls. cell walls. • plant/fungi/bacteria only The wall is rigid and helps support and protect the cell. The cell wall is mainly made of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate Phospholipid bilayer The cytoplasm contains the organelles of a cell • The cytoplasm is the region of the cell between the membrane and the nucleus. It consists of a gelatin-like fluid which “bathes” the organelles. – It is a solution with dissolved salts, minerals, etc. • Region where most of the cell’s activities are carried out. Organelles provide compartments for specialized activities to occur • Mitochondria (or mitochondrion) – Transfers energy from organic compounds (food) to ATP (a molecule that provides energy for the cell to do “work”). – Analogy: Power Plant- converts energy to a usable form. – Think of ATP as a cell’s “energy bank” – Structure: surrounded by 2 membranes; a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. The folds allow for a lot of space for chemical reactions to occur. Mitochondrion Ribosomes • DNA contains the instructions that control growth and development of an organism. However, it is only like the blueprints for a new house. A contractor is needed to build the house according to the plans in the blueprint. • Growth and development depends on the production of proteins. – Ribosomes make (synthesize) proteins • Analogy: Construction workers. Ribosomes Go back over your notes • Write out a question for each organelle • Use a different color to underline each organelle along with it’s structure and function More on Ribosomes • Structure: made up of proteins and RNA. – They are not membrane-bound so they are found in both prokayotic and eukaryotic cells. • Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum; others float freely in the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic Reticulum • It’s an “intracellular highway”; molecules move from one part of the cell to another through the ER. • Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; plays a role in protein synthesis. • Smooth ER: synthesizes lipids, breaks down toxic substances. • Structure: membranous tubules and sacs • Analogy: factory; conveyor belts, machines, etc. Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus • Works closely with the ER. It processes, packages, and helps release substances made by the cell (ex: proteins). – A protein made by a ribosome on the ER will be transported to the golgi where it is processed and given a “shipping label” before being secreted (released) from the cell. • Analogy: shipping department, Post Office • Structure: flattened membranous sacslike pancakes. Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes • Contain enzymes (a special type of protein) that digest (break down) molecules, old organelles, viruses, and bacteria. • Analogy: garbage/waste disposal. • Structure: spherical, single membrane – Note: rare in plant cells Lysosomes Cytoskeleton • Provides support for the cell, may allow for movement of the cell or within the cell. • Analogy: frame of a car/house. • Made of microfilaments and microtubules; strands of protein. • Not surrounded by membrane. Cytoskeleton Nucleus • Besides the cytoplasm the nucleus is the other major region of a cell. • Stores hereditary (genetic) informationDNA. It also synthesizes RNA. • Analogy: county office that stores the original building blueprints. “Brain”, stores info and sends out messages. • Structure: surrounded by a double membrane = nuclear envelope. Membrane has pores that allow molecules to pass through. Nucleus •Inside the nucleus is an area called the nucleolus which is where ribosomes are made. Go back over your notes • Write out a question for each organelle • Use a different color to underline each organelle along with it’s structure and function Choose an organelle page to work on. Everyone at your table will do a different organelle • Describe the organelle’s structure and function (2 points) • Draw a picture (1 point) • Decide a price (1 point) • Next show your group what you did Plant cells and Animal cells have some key differences • A cell wall • Vacuole: stores salts, minerals, nutrients, water, etc., and plays an important structural role for the plant • Surrounded by a membrane • Analogy: Warehouse Vacuole Plastids • Plastids: contain pigments, may store food (starch) – Chloroplasts: transfer energy from the sun to make organic compounds (food) – Structure: surrounded by doublemembrane, contain chlorophyll. – Analogy: solar panels Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Wall Nucleus Cell Membrane Nuclear membrane Nucleus