* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Vocabulary 5, test on Friday, 9/25/15
Survey
Document related concepts
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
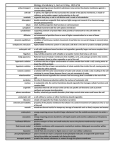
Biology Vocabulary 5, test on Friday, 9/25/15 active transport - energy-requiring process by which substances move across the plasma membrane against a concentration gradient cell wall - in plants, the rigid barrier that surrounds the outside of the plasma membrane, is made of cellulose, and provides support and protection to the cell centriole - organelle that plays a role in cell division and is made of microtubules chloroplast - double-membrane organelle that captures light energy and converts it to chemical energy through photosynthesis cilium - short, hairlike projection that functions in cell movement cytoplasm - semifluid material inside the cell's plasma membrane cytoskeleton - supporting network of protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell within the cytoplasm diffusion - net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration dynamic equilibrium - condition of continuous random movement of particles but no overall change in concentration of materials endoplasmic reticulum highly folded membrane system in eukaryotic cells that is the site for protein and lipid synthesis eukaryotic cell - a cell with membrane-bound nucleus and organelles; generally larger and more complex than a prokaryotic cell flagellum - long, tail-like projection with whiplike or propeller motion that helps a cell move Golgi apparatus - flattened stack of tubular membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into vesicles and transports them to other organelles or out of the cell hypertonic solution - a solution that has a higher concentration of solute outside than inside a cell, causing water to leave the cell by osmosis hypotonic solution - a solution that has a lower concentration of solute outside than inside the cell, causing water to flow into the cell by osmosis isotonic solution - a solution with the same concentration of water and solutes as inside a cell, resulting in the cell retaining its normal shape because there is no net movement of water mitochondrion membrane-bound organelle that converts fuel into energy that is available to the rest of the cell nucleolus - the site of ribosome production within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells nucleus - in eukaryotic cells, the central membrane-bound organelle that manages cellular functions and contains DNA organelle - specialized internal cell structure that carries out specific cell functions such as protein synthesis and energy transformation plasma membrane - flexible, selectively permeable boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell prokaryotic cell - a cell without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles ribosome - simple cell organelle that helps manufacture proteins selective permeability vacuole - property of the plasma membrane that allows it to control movement of substances into or out of the cell membrane-bound vesicle for temporary storage of materials such as food, enzymes and wastes endocytosis - energy-requiring process by which large substances from the outside environment can enter a cell exocytosis - energy-requiring process by which a cell expels wastes and secretes substances at the plasma membrane facilitated diffusion - passive transport of ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane by transport proteins fluid mosaic model - a plasma membrane with components constantly in motion, sliding past one another within the lipid bilayer lysosome - vesicle that uses enzymes to digest excess or worn-out cellular substances phospholipid bilayer - plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside transport protein - protein that moves substances or wastes through the plasma membrane