* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function VOCABULARY active transport p
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
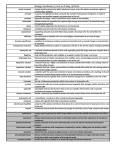
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, WORKBOOK - Biology Topic 3: Cell Structure and Function VOCABULARY active transport – energy-requiring process by which substances move across the plasma membrane against a concentration gradient cell – basic unit structure and organization of all living organisms cell theory – states that (1) organisms are made of one or more cells; (2) cells are the basic unit of life; and (3) all cells come only from other cells, passing copies of their genetic material on their daughter cells cell wall – in plants, the rigid barrier that surrounds the outside of the plasma membrane, is made of cellulose, and provides support and protection to the cell centriole – organelle that plays a role in cell division and is made of microtubules chloroplast – double-membrane organelle that captures light energy and converts it to chemical energy through photosynthesis chlorophyll – green pigment cilium – short, hairlike projection that functions in cells movement cytoplasm – semifluid material inside the cell’s plasma membrane cytoskeleton – supporting network of protein fibres that provide a framework for the cell within thy cytoplasm diffusion – net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration dynamic equilibrium – condition of continues , random movement of particles but no overall change in concentration of materials endocytosis – energy-requiring process by which large substances from the outside environment can enter a cell endoplasmic reticulum – highly folded membrane system in eukaryotic cells that is the site for ribosome attachment eukaryotic cell – unicellular organism with membrane-bound nucleus and organelles; generally larger and more complex than a prokaryotic cell exocytosis – energy-requiring process by which a cell expels wastes and secretes substances at the plasma membrane facilitated diffusion – passive transport of ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane by transport proteins flagellum – long, tail-like projection with a whiplike motion that helps a cell move through a watery environment fluid mosaic model – a plasma membrane with components constantly in motion, sliding past one another within the lipid bilayer Golgi apparatus – flattened stack of tubular membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins into vesicles and transports them to other organelles or out of the cell hypertonic solution – a solution having a higher concentration of solute than inside a cell, which shrinks or shrivels when water leaves the cell by osmosis hypotonic solution – solution that has a lower concentration of solute; more water outside of the cell than inside the cell isotonic solution – a solution with the same concentration of water and solutes as inside a cell, resulting in the cell retaining its normal shape because there is no net movement of water INVESTICE DO ROZVOJE VZDĚLÁVÁNÍ Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, WORKBOOK - Biology lysosome – vesicle that uses enzymes to digest excess or worn-out cellular substances mitochondrion – membrane-bound organelle that converts fuel into energy available to the rest of the cell nucleolus – the site of ribosome production within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells nucleus – in eukaryotic cells, the central membrane-bound organelle that manages cellular functions and contains DNA organelle – specialized internal cell structure that carries out specific cell functions such as protein synthesis and energy transformation osmosis – diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane phospholipid bilayer – plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside plasma membrane – flexible, selectively permeable boundary that helps control what enters and leaves the cell prokaryotic cell – microscopic, unicellular organism without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles ribosome – simple cell organelle that helps manufacture proteins selective permeability – properly of the plasma membrane that allows it to control movement of substances into or out of the cell stroma – a gel-like matrix in chloroplasts tonoplast – a membrane bounding vacuole transport protein – protein that moves substances or wastes through the plasma membrane vacuole – membrane-bound vesicle for temporary storage of materials such as food, enzymes, and wastes virus – nonliving strand of genetic material that cannot replicate on its own, has a nucleic acid core, a protein coat, and can invade cells and alter cellular function INVESTICE DO ROZVOJE VZDĚLÁVÁNÍ