* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Semester Introduction to functional neurobiology
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
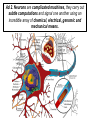
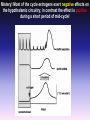
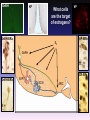
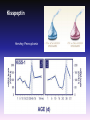
1. Seminar Basics of Neurobiology 2nd Semester: Introduction to Functional Neurobiology 1st Semester: Pázmány Péter Catholic University Faculty of Information Technology and Bionics Hungarian Academy of Sciences Institute of Experimental Medicine Department of Neurobiology Prof. Tamás Freund Dr. Imre Kalló Prof. Zsolt Liposits 1 Basics of Neurobiology – 1. Semester Introduction to functional neurobiology – 2. Semester Two major goals: (1) Use knowledge from neurobiology to revolutionise information technology (2) Employ the modern bio-, nano-, computer technology to simultaneously study a multitude of neurons Ad 1. Achievements of adaptation to changing environment, evolution and phylogenesis during billions of Years are “in front of our nose”. The “only” task is (1) to recognise them – studying the different forms of life (before we loose any species), and the normal and compensatory processes employed (2) to adopt them in our instruments and projects 300 mm slice ~706,5 cm2 400x625 mm surface ~ 2500 cm2 Narrowing the gap between technology and biology in physical terms is a success. 5.4 billion transistors in the SyNaptic chip 10-20 billion (109) neurons in the cortex 100-500 trillion (1012) synapses in the cortex In 2015 - 10 nm technology synaptic vesicles: 20-40 nm Multi-gate fin transistor Penryn processzor Poly Depletion Elimination: Metal Gate Gate Leakage Reduction: HiK• Tunnel transistor Why Can’t a Computer Be More Like a Brain? Speaker: Jeff Hawkins, the developer of the PalmPilot and Treo smartphone. Society for Neuroscience Annual Meetings in the US But there are a lot more to do in terms of function! Which one is a cat, and which one is a dog? 6 5 What features of these images can be used to determine, which one is a cat or a dog ? 4 1 3 2 7 12 10 8 9 11 14 13 15 16 Which fungus is eatable and which one is toxic? 4 2 3 1 8 7 6 12 10 9 11 The time spent on learning can not be saved! The human brain gains the informations also via learning, based on which it is able to identify subjects, animals, people within seconds. Our creativity is based on the aquired informations. Creativity is an attitude and an ability to bring aquired but originally isolated experiences together, which appear as new thinking schemes, new experiences, and imaginations or products, either in the art, science and technology or the everyday life. Pszichológiai Értelmező Szótár, 1981 Ad 2. Neurons are complicated machines, they carry out subtle computations and signal one another using an incredible array of chemical, electrical, genomic and mechanical means. ….and there are 100 billion (1011) neurons in the brain – the co-operative interaction among different subpopulations appears as a very high variety of human behaviors The challenge is there – investigate simultaneously a multitude of neurons The European Commission will award a total of two billion euros to two projects one of which focuses on basic research on the brain and brain diseases such as depression, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s and possibly develop new treatments. (Source: Reuters, Brussels, Monday, January 28, 2013) The Obama administration is planning a decade-long scientific effort to examine the workings of the human brain and build a comprehensive map of its activity, seeking to do for the brain what the Human Genome Project did for genetics. (Source: New York Times, New York, February 17, 2013) In Hungary National Brain Research Program (NAP) 12 billion Forints for 2014-2018. Instruments are needed to record and report ……and report about the chemical, electrical, genomic and mechanical changes of a multitude of neurons nanosensors supercomputers What do we aim during the seminars…. 1. To inform you about methods used in neuroscience 2. To provide a feed back about your progress in studying neurobiology 3. To give a handle to elaborate a topic and give a talk about it. 4. To gain experience about test-questions before the exams What we are going to do during the seminars…. 1. Filling out tests about topics presented during the lectures. Single tests – every week and multiple tests – midterm 2. Discussing methods used to collect data about the structure and function of the nervous tissue. 3. Demonstrations of selected topics. Work during the seminars – 30% of the total performance can be managed 1. Tests written every week from topics of the preceeding lectures - 10 points. 2. Prezentations given at set dates from selected topics of the preceeding lectures - 5 points. 3. Midterm test – 15 points Calculation of the points – Performance is measured in percentage (achieved point/maximum achievable points x100) and converted to 10 points Slide presentation One has to prepare a short (5 slide-) presentation and a single page word document from selected topics of the lectures. The date of presentation is arranged in advance. The word document and the presentation has to be sent to me before the seminar [email protected] The presentation has to be given during the seminar Sources to be used– Slideshows of lectures and seminars, materials provided at the Neurobiology folder, internet, books. Evaluation of the performance Tests every week: Presentation once during the semester: Mid-term test: 0-10 0-5 0-15 The 3 best performing students will receive 10 additional points! To register for the exam, students’performance ought to reach 50% during the semester! Final exam: 0-70 -------------------0-100 COLLECTION OF INFORMATION FROM THE INTERNET PUBMED is a bibliographic database of NLM (National Library of Medicine) . http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi Papers E-books Search Keywords Authors Journals Downloads – full text is only from Journals with free access e.g. http://www.pnas.org/ pdf , html, PubReader, ePUB Service payed by the goverment SCIENCE DIRECT is a fulltext and database service of Elsevier . WEB OF SCIENCE is a bibliographic database and citation index of ISI (Institute for Scientific Information). Citation Impact factor After registration one can access them from the following websites: http://www.eduport.hu/ http://www.eisz.hu/hu Further sources Neuroscience societies Society for Neuroscience (SFN) http://www.sfn.org/ International Brain Research Organization (IBRO) http://www.ibro.org/ Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) http://www.fens.org/ Universities, research institutes and groups e.g. http://www.nih.gov/science/ Companies and distributors e.g. http://www.probes.com/ Foundations e.g. http://www.wellcome.ac.uk/ A few questions in neuroscience: I. Puberty Rapid changes of mood. Burst of anger. Endless laughing, etc. Why? Answer: changes occur in the brain Girls Boys Hypothalamus LHRH LH FSH Testosterone DHT Estradiol Mistery! Most of the cycle estrogens exert negative effects on the hypothalamic circuitry; in contrast the effect is pozitive during a short period of mid-cycle! GnRH KP What cells are the target of estrogens? GnRH-ERa VP VP-ERb E2 GnRH D A CR-ERa GnRH-ERb B AVPV SCN ARC E Kisspeptin Hershey, Pennsylvania The kisspeptin system shows sex differences A few questions in neuroscience: II. Estrogen effects Estrogen receptors – regulation of certain genes Effect of dioxin Dioxin sources New approaches in neuroscience: Optogenetics Lin D, Boyle MP, Dollar P, Lee H, Lein ES, Perona P, Anderson DJ.: FUNCTIONAL IDENTIFICATION OF AN AGGRESSION LOCUS IN THE MOUSE HYPOTHALAMUS. Nature. 2011 Feb 10;470(7333):221-6. Division of Biology 216-76, California Institute of Technology,1201 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91125, USA. Howard Hughes Medical Institute, California Institute of Technology,1201 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91125, USA. Allen Institute for Brain Science, Seattle, Washington, 98103, USA. Computation and Neural Systems 136-93, California Institute of Technology, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91125, USA. The plot of the action thriller „Universal soldier” covers most of the results of this paper US. Special Forces revealed, how to seize control over selected soldiers. Authors of this paper identified the brain region involved in aggression. US. Special Forces treat the soldiers with drugs and the soldiers execute commands emotionless. Authors of this paper modify a selected part of the brain, stimulate it through optic fibers and the mice attack any moving objects including females, which induce normally mating behavior. US. Special Forces recognise, that some soldiers escape from the control. Authors prevent mice from attacking intruders by modifying a selected part of the brain. Resident-intruder test C57BL/6♀ Stimulus R BALB/c♂ Stimulus BALB/c♀ Stimulus R R